Autism
5-13-2021 links: reference:
- (Fitzgerald, 2007) Genius Genes: How Asperger’s syndrome Changed the World. A book. A case study of 21 famous, creative intellectual figures, arguing they exhibited autistic mindsets.
- Synaptic, transcriptional and chromatin genes disrupted in autism
- Aluminium in brain tissue in autism
- file:///home/Documents/Reading/Bio/Neuro/NEUROSCIENCE/NEUROPATHOLOGY/The Neurochemical Basis of Autism. From Molecules to Minicolumns. Gene J. Blatt 2009.pdf
- https://opentheory.net/2023/05/autism-as-a-disorder-of-dimensionality/
Autism #
- Lower circulating endocannabinoid levels in children with autism spectrum disorder
- Effectiveness of the gluten-free, casein-free diet for children diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder: based on parental report
- Much less prevalent in females. It might have something to do with mercury/selenium.
- Correlates with Hair Loss. Low glutamine can point to this. Much more likely to have a shorter lifespan.
-
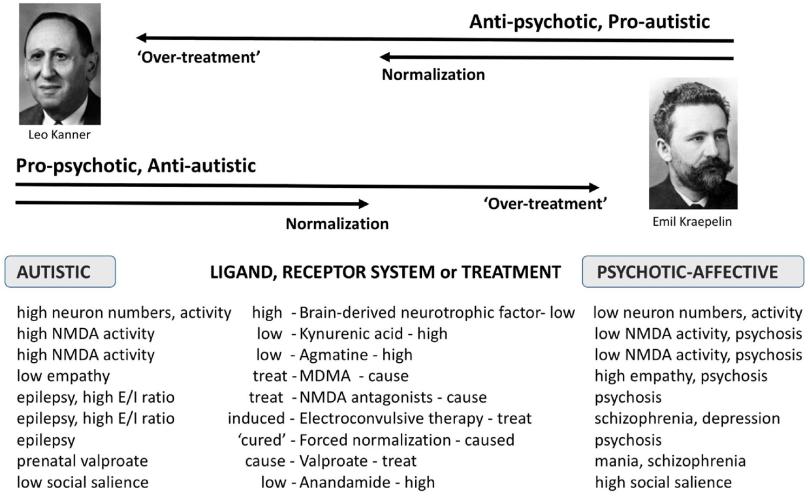
Comparative psychopharmacology of autism and psychotic-affective disorders suggests new targets for treatment
-
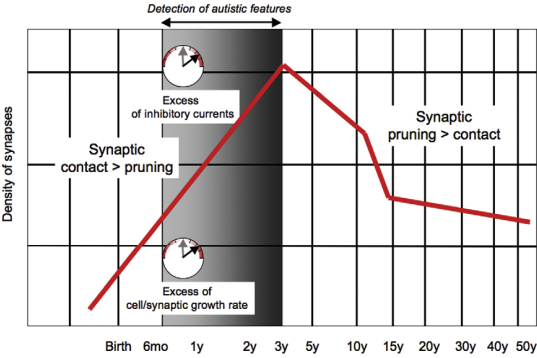
Pruning/Neurogenesis #
-
Loss of mTOR-Dependent Macroautophagy Causes Autistic-like Synaptic Pruning Deficits (Tang et al. 2014) that’s kind of a misleading title
- Indeed, ASD shows spine pruning defects and impaired mTOR-autophagy and mTOR overactivation causes spine pruning defects. Nothing new here.
- Synaptic mTOR integrates signaling from various ASD synaptic and regulatory proteins, including SHANK3, FMRP, and mGluR1/mGluR5
- Neuronal autophagy enabled spine elimination wth no effects on spine formation.
- Rapamycin corrected spine pruning in TSC1-CKO mice to control levels with no effect on basal dendritic branching.
-
A synaptic trek to autism
- … whereas the Neurexin–Neurologin–SHANK pathway is associated with synaptogenesis and imbalance between excitatory and inhibitory currents.
- The PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway may be modulated by SERT mutations.
-
 similar:
similar:
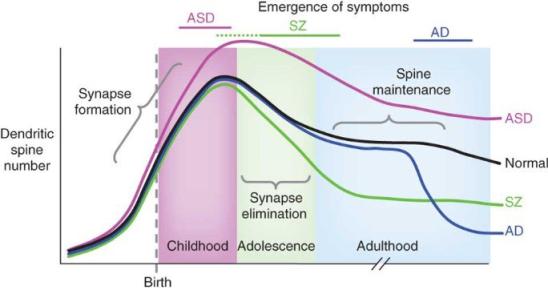
- of note also of course, is excess inhibitory currents!
- Reduced Gamma in autism/FMRP-knockout.
-
Cellular and synaptic network defects in autism
- Dysfunction in PDZs Postsynaptic Density scaffolding proteins, etc. have implications in ASD, especially SHANK3.
-
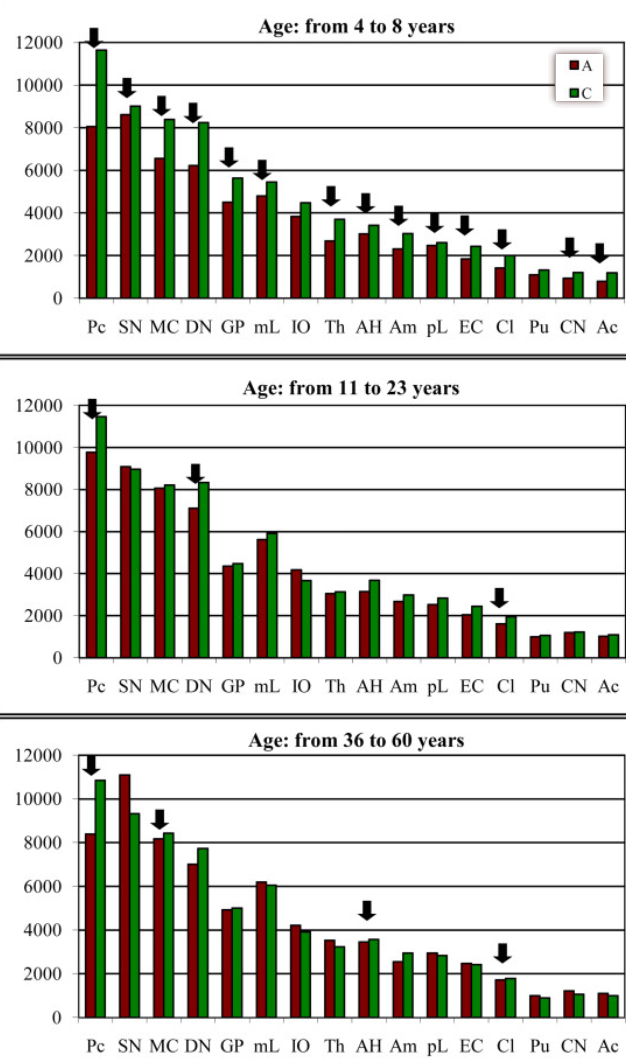
Brain-region–specific alterations of the trajectories of neuronal volume growth throughout the lifespan in autism mean neuronal volume:
-
Excitatory/inhibitory imbalance in autism spectrum disorders: Implications for interventions and therapeutics
- Increased E-I ratio in prefrontal cortex =characteristic behavioral/social impairments of ASD. News to me actually. Rett syndrome has decreased E-I ratio and has autistic-like features.
- Local hyperconnectivity and long-range hypoconnectivity and disconnection between neural circuits in ASD:
-
Why the frontal cortex in autism might be talking only to itself: local over-connectivity but long-distance disconnection (Courchesne 2005)
- Neuroinflammatory reactions involving glial activation, migration defects and excess cerebral neurogenesis and/or defective apoptosis might generate frontal neural pathology early in development. It is hypothesized that these abnormal processes cause malformation and thus malfunction of frontal minicolumn microcircuitry.
- The authors documented the first direct evidence of immune-mediated mechanisms in the neuropathology of autism: Neuroglial activation and neuroinflammation in the brain of patients with autism (Vargas et al. 2005)
- Disorganized and inadequately selective. Toddlers have enlarged brain volumes [R](Early brain overgrowth in autism associated with an increase in cortical surface area before age 2 years), but this is not maintained; followed by slow/arrested growth: R
- Frontal and temporal sulci are abnormally shifted superiorly and posteriorly in autistic children: Cortical sulcal maps in autism
- Increased frontal cortical folding in autism: a preliminary MRI study frontal cortex gyrification.
- Identified the presence of activated glia and neuroinflammatory response in frontal and cerebellar cortices
- Reduced correlation of frontal cortex and parietal cortex activity, indicating impaired connection: R
-
Functional connectivity in an fMRI working memory task in high-functioning autism (Koshino 2004) n=28 (14 control)
- Reduced activation of right DLPFC. Increased/decreased activation of the right/left inferior parietal lobe respectively. Greater temporal lobe activation.
- Indeed, Executive Network dysfunction is seen R
- Since verbal and nonverbal working memory is associated with left and right PFC, it’s possible they processed the task using visual codes instead of verbal.
- Reduced activation of right DLPFC. Increased/decreased activation of the right/left inferior parietal lobe respectively. Greater temporal lobe activation.
- Neuroinflammatory reactions involving glial activation, migration defects and excess cerebral neurogenesis and/or defective apoptosis might generate frontal neural pathology early in development. It is hypothesized that these abnormal processes cause malformation and thus malfunction of frontal minicolumn microcircuitry.
- Brain functional networks in syndromic and non-syndromic autism: a graph theoretical study of EEG connectivity (Peters 2013) pretty good; just corroborating the idea above.
-
Autism as a disorder of neural information processing: directions for research and targets for therapy (Belmonte et al. 2004)
- Low signal-to-noise in developing neural assemblies?
- The numbers of Purkinje cells, and to a lesser extent granule cells, in cerebellar cortex are abnormally low [16] —presum- ably leading to disinhibition of the cerebellar deep nuclei and consequent overexcitation of thalamus and cerebral cortex.
- Neurons in hippocampus, amygdala, and other limbic regions are abnormally densely packed [16], [17] (unlike the Golgi analysis below)
- Minicolumnar pathology in autism (Casanova 2003) smaller cortical minicolumns, and an increase in cell dispersion within minicolumns—characteristics that could increase the total number of them and thus the degree of connectivity between them. This could contribute to decreased signal-noise ratio.
-
An Artificial Neural Network Analogue of Learning in Autism (Cohen 1994) pretty good basic computational !Neuroscience.
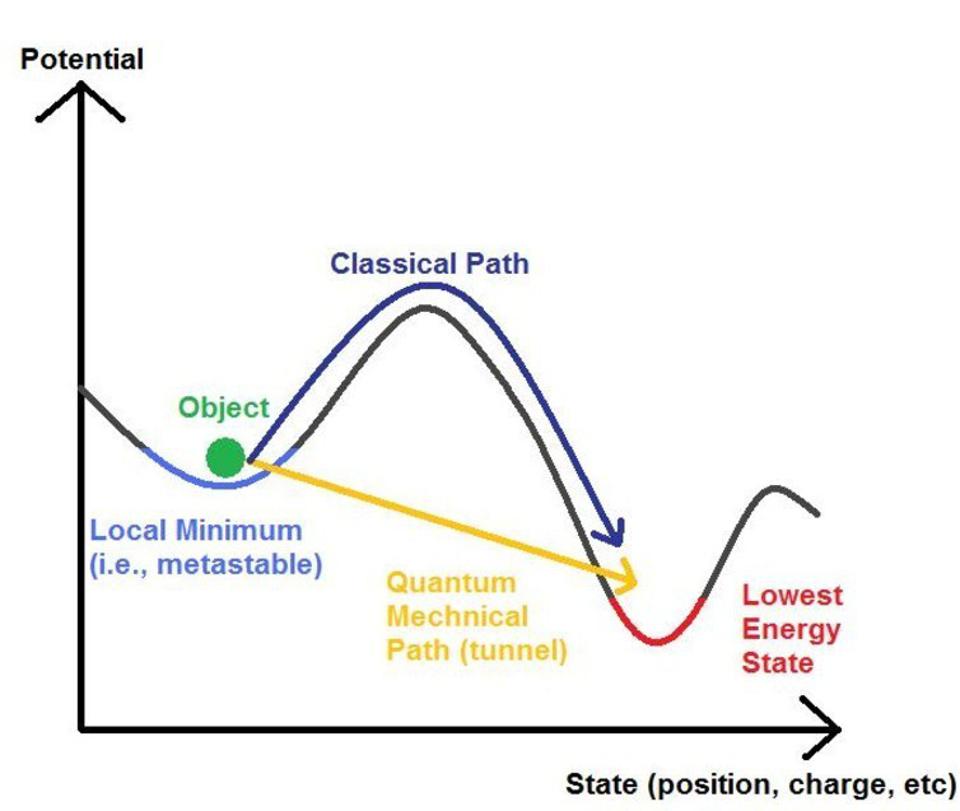
- Weights are modified in many systems according to a gradient descent rule which forces the network to find a configuration of weights in which the objective is to lead to a global minimum error solution in what is known as “weight space - this is the optimal state of a network. But local minima are undesirable, but thus noise facilitates pushing the network over such energy barriers. This is fascinating and surely is key for the Free Energy Principle:
-
- Children with autism are superior to controls in recognizing upside-down faces.
- Savantism seen in people with e.g. eidetic memory could be excessive neurons in areas associated with learning, acquiring numerous unique details which end up interfering with discrimination->generalization.
- However, some ASD children may lack neurons/connections in associative areas such as the amygdala and hippocampus, impairing discrimination->generalization (Raymond et al 1989)
- Hippocampus in autism: a Golgi analysis (Raymond 1995) showed smaller and fewer dendritic branching of CA4 and CA1 neurons.
- Yet, in the case of excessive hippocampal interconnectivity, you would see the spatial overfitting (like a room being completely different when one thing changes) another example of impaired ‘generalization’.
- Abnormally high activity in stimulus-driven areas () and decreased activity in areas associated with higher-order processing ().
- In the absence of a normally functional mechanism to bias sensory processing towards attended stimuli, all stimuli receive much the same degree of sensory evaluation, and the irrelevant stimuli must then be actively discarded in a manner that creates a processing bottleneck
-
Why the frontal cortex in autism might be talking only to itself: local over-connectivity but long-distance disconnection (Courchesne 2005)
FMRP #
- Aβ is a potent antimicrobial agent and this imbalance in APP processing in autism, leading to lower Aβ production could well explain the high prevalence of prenatal and infantile infection in relation to autism.
- Problems in myelination can also be related to infection via the integrated stress response pathway.
-
Finding novel distinctions between the sAPPα-mediated anabolic biochemical pathways in Autism Spectrum Disorder and Fragile X Syndrome plasma and brain tissue
- LNGFR is a sAPPα receptor. It upregulates mature Oligodendrocytes, which produce ADAM17.
- Increased sAPPα signaling = increased microglial activation? sAPPβ as well, without offering neuroprotection.
-
Microglial activation by Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein and modulation by apolipoprotein E
- Amyloid β activation of microglia is mediated through AGE receptors (RAGE): RAGE and amyloid-β peptide neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease
-
Microglial activation by Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein and modulation by apolipoprotein E
Prenatal #
- Things in the environment, or substances produced in reactions to environmental stress, that might cause autism, include prenatal and neonatal exposure to: Radiation, including isotopes from the power industry, bomb testing, Chernobyl, and Fukushima; Exposure to air pollution, including nitrogen oxides, ozone, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and particles (Jung, et al., 2013) Aluminum (Mold, et al., 2018), lead, mercury, manganese, arsenic, cadmium, chromium, nickel (Windham, et al., 2006) Acetaminophen, infections, endotoxin, endogenous and exogenous estrogens, hypothyroidism, Progesterone deficiency, Agmatine deficiency, serotonin excess, endogenous Nitric Oxide (Sweeten, et al., 2004) And Vitamin D deficiency. All of these have established associations with risk of autism. - Ray Peat - Autism and Causality (May 2018)
-
Serotonin, pregnancy and increased autism prevalence: is there a link?
- This study makes the case that prenatal hyperserotonemia actually leads to downregulation of 5HT terminal production, which leads to specific neuroanatomical defects. Not the impression I got reading the body of the study.
Neuroanatomy #
- Cerebral cortex and Hippocampus-Amygdala showed trends towards being disproportionately smaller.
R
- I’ve heard the converse with regards to the amygdala though. Maybe in aspergers
-
Evidence of neurodegeneration in autism spectrum disorder (Kern et al., 2013)
- (1) neuronal cell loss, (2) activated microglia and astrocytes, (3) proinflammatory cytokines, (4) oxidative stress, and (5) elevated 8-oxo-guanosine levels.
Neurotransmitters #
-
Genetic variation in the oxytocin receptor (OXTR) gene is associated with Asperger Syndrome
- Decreased plasma Oxytocin.
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid Vasopressin and Symptom Severity in Children with Autism
- Normal CSF Oxytocin levels but low Vasopressin.
- Cholinergic Abnormalities in Autism Is There a Rationale for Selective Nicotinic Agonist Interventions
Serotonin #
- Elevated Serotonin Levels in Autism: Association with the Major Histocompatibility Complex
-
Serotonin and serotonin transporter levels in autistic children
- SERT and Serotonin levels significantly increased:
- Serotonin levels were 80.63± 21.83 ng/ml in mild, 100.39±23.07 ng/ml moderate, and 188.7±31.72 ng/ml severe autistic patients.
- Serotonin transporter levels were 10.13±4.51 ng/ml in mild, 13.15±4.71 ng/ml moderate, and 16.32±6.7 ng/ml in severe autistic patients.
- SERT and Serotonin levels significantly increased:
- Hyperserotonemia in autism: activity of 5HT-associated platelet proteins
-
Brain Serotonin and Dopamine Transporter Bindings in Adults With High-Functioning Autism
- SERT binding was significantly lower throughout the brain.
- DAT binding was significantly inversely correlated with SERT binding in the Orbitofrontal Cortex.
Dopamine #
-
Elevated Homovanillic Acid (in the cerebrospinal fluid) R
-
LGD targets in affected females significantly overlap the targets in males of lower intelligence quotient (IQ), but neither overlaps significantly with targets in males of higher IQ. R
-
The prevalence of the A1 allele of the D2 receptor is significantly increased in autism, whereas the D1 receptor gene may be a risk gene… R
Glutamate/GABA #
- Could be GABAeric inhibition on pyramidal neurons. Excessive extracellular glutamate can imply NMDA dysfunction. Pax says many intellectual disabilities are implicated by excessive GABA and as a consequence, cholinergic deafferentation.
-
GABAergic/glutamatergic imbalance relative to excessive neuroinflammation in autism spectrum disorders
- Autistic patients exhibited Glutamate Excitotoxicity based on a much higher glutamate concentration in the autistic patients than in the control subjects. Unexpectedly higher GABA and lower glutamate:GABA levels.
- TNF-α and IL-6 were significantly lower, whereas Interferon-γ and IFI16 were remarkably higher in the autistic patients than in the control subjects.
-
Relationship between absolute and relative ratios of glutamate, glutamine and GABA and severity of autism spectrum disorder
- Children exhibited a significant elevation of GABA, glutamate:Glutamine ratio, significantly lower levels of glutamine, and a lower glutamate:GABA ratio.
- No significant correlation was found between glutamate levels and the severity of autism… Glutamine appeared as the best predictive prognostic markers.
- “The study also indicates that an increased plasma level of GABA can be potentially used as an early diagnostic biomarker for ASD.”
-
NMDA receptor dysfunction in autism spectrum disorders
- Knockout of pro-NMDA genes like Neuroligin, SHANK2, GLUD1 are more consistent with a phenotype of ASD-like behavior.
- Mice with reduced NMDA receptor expression: more consistent with autism than schizophrenia?
Genetics/Synapse #
- A Subset of Autism-Associated Genes Regulate the Structural Stability of Neurons
-
Synapse dysfunction in autism: a molecular medicine approach to drug discovery in neurodevelopmental disorders a brief list:
- Cell adhesion and scaffolding
- NLGN-3, NLGN4X
- NRXN1
- SHANK3
- CNTN3
- CNTNAP2
- CDH9
- PCDH10
- L1CAM
- NRCAM
- Signal transduction, transcription/translation
- FMR1
- TSC1
- PTEN
- mTOR
- NF1
- MECP2
- A2BP1
- ZNF533
- BFAR
- CREBBP
- MRTF
- TBX6
- UBN1
- Receptors and enzymes
- TAS2R1
- GRIN2A
- SSTR5
- UBE3A
- ABAT
- Transport and trafficking
- NHE9
- NHE6
- DIA1
- NOSTRIN
- EMP2
- Unknown
- AUTS1
- AUT
- Cell adhesion and scaffolding