Dopamine
links: Neurotransmitter Catecholamine reference:
- What does dopamine mean? (2018) - good read? >400 citings 4-11-2021
Dopamine
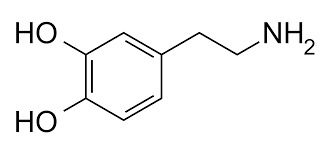 #
#
- Has 5 receptors (all metabotropic): D1 to D5; D2 being the Autoreceptor. D1 consists of 2 subtypes: D1 & D5; D2 consisting of D2, D3, & D4.
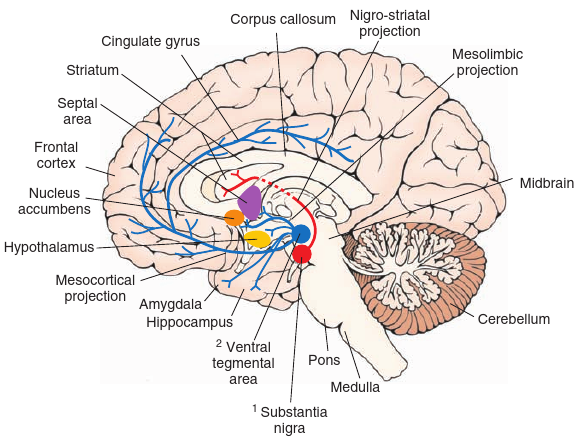
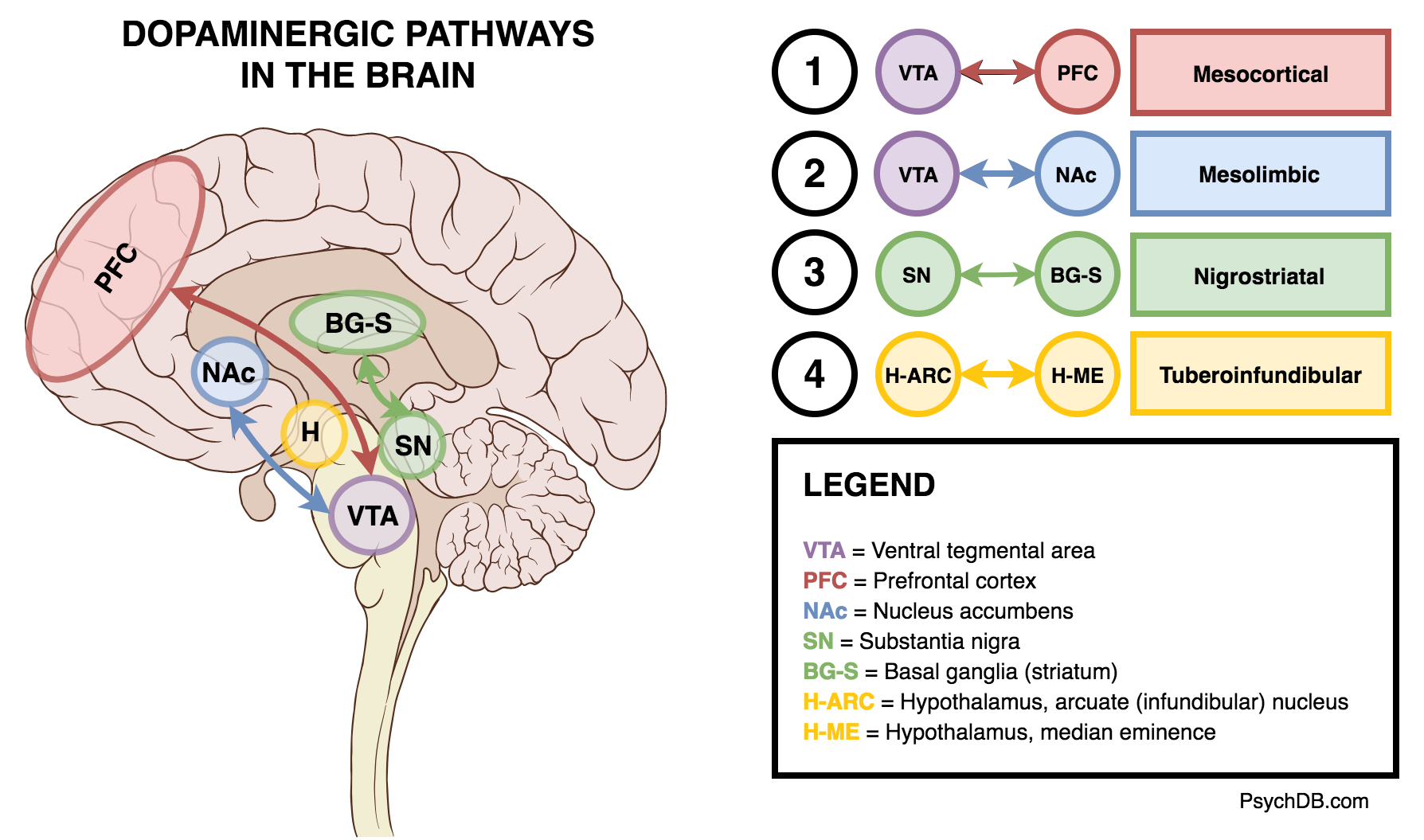
- There are four major dopamine pathways: Mesolimbic Pathway, Mesocortical Pathway, Nigrostriatal Pathway, and Tuberoinfundibular Pathway
- So apparently, the Substantia Nigra mediates wanting, and the VTA mediates liking.
-
Phasic versus tonic dopamine release and the modulation of dopamine system responsivity: A hypothesis for the etiology of schizophrenia
- Tonic DA regulates extracellular levels, whereby D2-type receptors are bound to homeostatically increase the DA threshold. In Schizophrenia, this tonic release is lowered, leading to abnormally large responses.
- Dopaminergic control of corticostriatal long-term synaptic depression in medium spiny neurons is mediated by cholinergic interneurons
Metabolism #
- Dopamine $\ce{->[COMT]}$ 3-Methoxytyramine $\ce{->[MAO]}$ Homovanillic Acid
- Dopamine $\ce{->[MAO]}$ DOPAC $\ce{->[COMT]}$ Homovanillic Acid
Iron #
-
The role of metal ions in dopaminergic neuron degeneration in Parkinsonism and Parkinson’s disease this topic is epic. Dopamine neurotoxicity relies on fenton reactions.
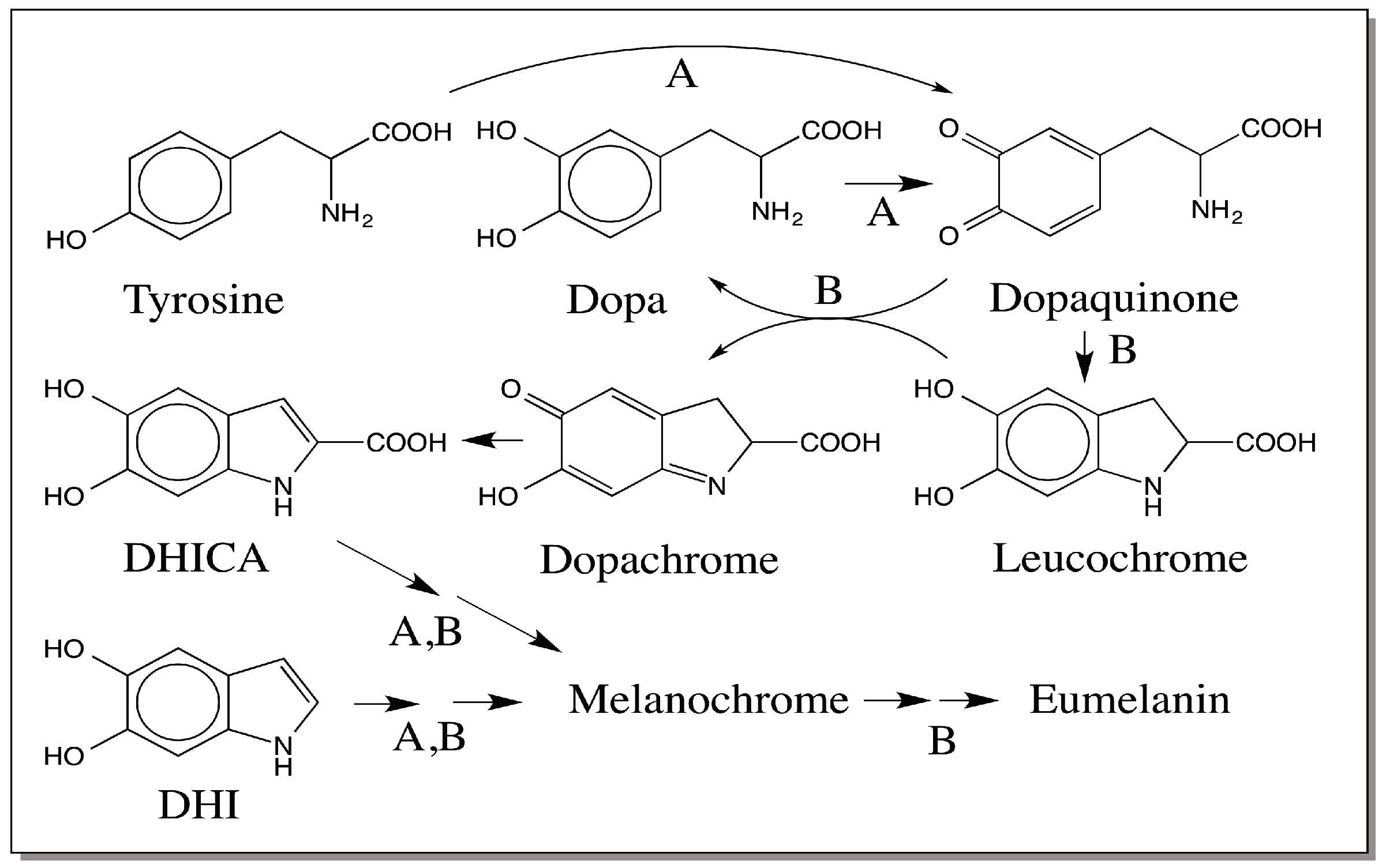
- Manganese 3+ is a strong oxidizing agent, which oxidizes Dopamine to aminochrome (dopaminochrome), the precursor of Neuromelanin, a polymer of 5,6-dihydroxyindole.
R
- Neuromelanin blocks the hydroxyl production via Fenton Reaction, and inhibits iron-mediated oxidation of Ascorbic acid, and the complexing prevents dopamine oxidation itself.
- Copper is able to complex with dopamine inducing caspase-independent cell death with formation of autophagic vacuoles.
- Iron is able to complex with dopamine as well in the extracellular space.
-
 copper has the same cascade, besides the Fenton reaction: formation of the hydroxyl radical via ferrous iron and Hydrogen Peroxide: $\ce{Fe^{2+} + H2O2 -> Fe^{3+} + ^{.}OH + OH^-}$ (and similar things), and like using $\ce{Cu^{+}}$.
copper has the same cascade, besides the Fenton reaction: formation of the hydroxyl radical via ferrous iron and Hydrogen Peroxide: $\ce{Fe^{2+} + H2O2 -> Fe^{3+} + ^{.}OH + OH^-}$ (and similar things), and like using $\ce{Cu^{+}}$. - There is also $\ce{Fe^{3+} + H2O2 -> Fe^{2+} + HOO^{.} + H^+}$, forming the hydroperoxyl radical.
- Not shown here is oxidopamine/6-OHDA, which converts to and from dopamine–quinone and into aminochrome:
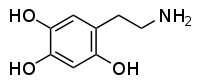
- Its rate increases with more acidic pH. Which is counterintuitive if pH and redox potential are to have an inverse relationship.
- Ferritin Heavy Chain overexpression in dopamine neurons is neuroprotective.
- Lisuride protects against iron-induced lesions.
- Noradrenaline competes with dopamine for(/with?) Fe3+, forming a complex that is not neurotoxic.
-
- VMAT2 sequesters iron in an acidic environment, where oxidation is not possible:
- Manganese 3+ is a strong oxidizing agent, which oxidizes Dopamine to aminochrome (dopaminochrome), the precursor of Neuromelanin, a polymer of 5,6-dihydroxyindole.
R
-
-
Iron and dopamine: a toxic couple (lol)
- Neurodegeneration in the affected regions may result from the potent redox couple formed by iron and dopamine itself
-
Dopamine and DOPA cause release of iron from ferritin and lipid peroxidation of liposomes
- Funny: high DA/DOPA concentrations inibited the iron-lipid peroxidation. There must be a curve
Behavior #
- DA does not signal reward per se but rather mediates a learning signal that allows the system to predict better when rewards are likely to occur and thereby contribute to the optimization of reward-seeking behaviors R
- See Histamine and its behavioral effects. Has some important interactions with Histamine. High histamine usually means low dopamine, but high dopamine doesn’t necessarily mean low histamine. Sometimes they can increase eachother, but in healthy conditions, they become more inversely correlated.
- Lowers the perceived cost of doing tasks. Higher-effort tasks for higher rewards.
Addiction #
‘High dopamine’ is anti-addiction. A lack of dopamine or an excess of serotonin causes adhedonia. Specifically, excess serotonin with low dopamine contributes to impulsivity. R
- Low dopamine makes one crave something, but once you get it, the boost in dopamine is rather minor. This promotes drug use, binging on sweets, and stuff like that. It obviously also promotes ADHD/ADD and reduces learning/cognition. It’s the unexpected rewards that cause a surge in dopamine. R