MAO-B
links: MAO reference: 10-4-2021
MAO-B #
-
“While people lacking the gene for MAO-A display mental retardation and behavioral abnormalities, people lacking the gene for MAO-B display no abnormalities except elevated Phenethylamine levels in urine, raising the question of whether MAO-B is actually a necessary enzyme.”
-
Located in outer mitochonrial membrane.
-
Catalyzes oxidative deamination and catabolism/degredation of amines (including amphetamines),
but mainly Dopamine.- The resulting metabolites are significantly neurotoxic, as they are ROS.
-
When inhibited, dopamine is metabolized using enzymes like diamine oxidase, which result in non-neurotoxic metabolites.
-
Increases with aging, starting in your 50’s. (So that’s why JC said Selegiline isn’t that great until then)
-
Degrades benzylamine and Phenethylamine.
-
Mice unable to produce MAO are resistant to Parkinson’s.
-
Inhibitors tend to be sedating.
GABA #
So the inhibition of GABA synthesis in the basal ganglia still, of course, disinhinibts regions like the SN.
-
Glial GABA, synthesized by monoamine oxidase B, mediates tonic inhibition
- MAO-B 60% KO or Selegiline treatment eliminated tonic GABA currents from granule neurons and MSNs.
- Reduced Ca2+-dependent (and basal) astrocytic GABA release. A GAT inhibitor did not change this.
- GABA content was changed, but not GABA-A receptor expressionm, since currents from agonist application were not changed,
- Somehow, 10mg/kg (HED 116) completely inhibited MAO-B activity but did not affect MAO-A activity. Wtf?
-
Integration of quanta in cerebellar granule cells during sensory processing
- the input layer of the cerebellum balances exquisite sensitivity with a high signal-to-noise ratio. Granule cell bursts are optimally suited to trigger glutamate receptor activation and plasticity at parallel fibre synapses, providing a link between input representation and memory storage in the cerebellum.
- GAD is rarely expressed in glia - only in distinct neuronal populations.
- GABA synthesis via putrescine pathway, which is MAO-B dependent.
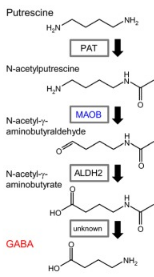
- GABA-T aka ABAT (4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase) catalyzes GABA into succinic semialdehyde and glutamate by transferring an amino group to GABA. Cerebellar glial cells lack this enzyme, unlike purkinje cells.
- There are minimal tonic GABA-A currents in the hippocampus: The amount of astrocytic GABA positively correlates with the degree of tonic inhibition in hippocampal CA1 and cerebellum
- MAO-B 60% KO or Selegiline treatment eliminated tonic GABA currents from granule neurons and MSNs.
-
- found no change of dopamine concentration in striatum acutely treated with selegiline and a small increase of dopamine on chronic treatment.
-
Cat’s claw is a popular inhibitor.