mTOR
links: Serine-Threonine Protein Kinase reference: 11-3-2021
mTOR #
-
AKA FK506-binding protein 12-rapamycin-associated protein 1 (FRAP1).
-
I guess mTORC1 is more for classic anabolism, while mTORC2 is more involved in ‘survival’ type things, including immunity, which is why lower doses of rapamycin are quite safe and saying “immunosuppressant” could be misleading.
-
As you’d assume, it is activated during abundance of Amino Acids (and inactivated with their deprivation), perhaps especially by Leucine (so maybe other BCAAs?).
- Specifically, leucine inhibits Sestrin-2, an mTOR inhibitor.
-
Plays a key role in Muscle hypertrophy
-
Where is mTOR and what is it doing there?
- … basically, it’s everywhere (but not mitochondria). Various cell types and techniques from dozens of studies. Though I’d say if you have to pick one spot it would be on the outer lysosomal membrane.
Signaling #
- Pax: Activation is high in Autism. This hyperactivity leads to reduced brain autophagy, synaptic pruning, and cell cycle abnormalities. This is due to greatly increased extracellular GABA and Ca2+ levels and reduced activation of glutamate-expressing cells, leading to its accumulation, promoting excitotoxicity through postsynaptic NMDARs.
- What is autophagy you my ask? Formation of autphagosomes, which capture and transport components to lysosomes.
- (did he mean eNMDAR?)
- This is of course an interesting meditation on the Connectome
-
mTOR signaling in growth control and disease (2013)
- Long-term exposure to rapamycin inhibits mTORC2 in some cell types by sequestering newly synthesized mTOR molecules and suppressing its assembly.
- Rapamycin’s MOA is by forming a complex with FKBP12, which is much more selective for mTORC1 especially at the lower typical doses.
- AKT activates mTORC1 directly by means of inhibiting pras40. AMPK phosphorylates Raptor, allosterically inhibiting mTORC1.
- DNA damage induces expression of TSC2 and PTEN, and activates AMPK dependent on Sestrin1/2.
- Some targets of mTORC1 and mTORC2:
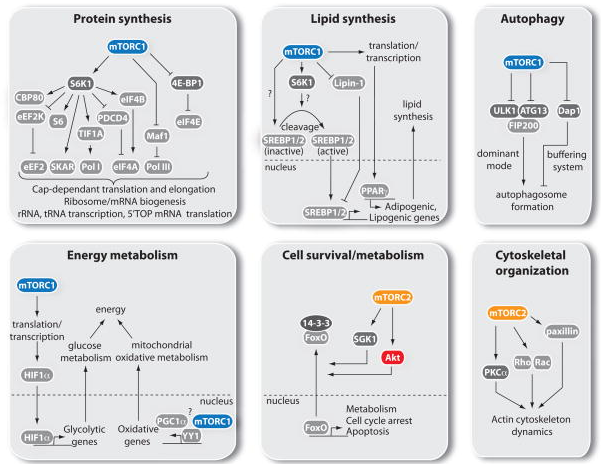
- Upon mTOR inhibition, Autophagosomes form. They engulf cytoplasmic proteins and fuse with lysosomes.
- A common event in Cancer is the loss of p53, which promotes mTORC1 activation.
- RTK->PI3k->PDK->AKT Thr308 upregulation, a negative feedback loop, may be disinhibited/activated following mTOR inhibition. Naturally.
- Figure 4 demonstrates that reduced insulin signaling leads to obesity and type 2 Diabetes. In adipose tissue, it reduces GLUT4 and overactivates PPAR-γ