NMDAR
links: NMDA, Neuroreceptors, eNMDAR reference:
NMDA Receptor #
- Blocking NMDA receptors inhibits release of dopamine bursts during stress (which leads to a drop after the stress has passed.)
- Both its hypo- and hyperfunction is implicated in Alzheimer’s and other neurological disorders. Positive allosteric modulation of NMDA receptors: mechanisms, physiological impact and therapeutic potential
- NMDA activation increases extracellular choline, associated with a reduction of Membrane Phosphatidylcholine preceding cell death. R
- About 20 per Postsynaptic Density. This is fairly consistent across synapses and time unlike AMPAR.
- Can form heteromers with Dopamine receptors.
-
Differential Roles of NR2A and NR2B-Containing NMDA Receptors in Cortical Long-Term Potentiation and Long-Term Depression (Massey 2004)
- LTD can be readily induced in adult cortex by the activation of NMDA receptors (NMDARs), after inhibition of glutamate uptake. Interestingly there is no need to activate synaptic NMDARs to induce this LTD, suggesting that LTD is triggered primarily by eNMDAR. We also find that de novo LTD requires the activation of NR2B-containing NMDAR, whereas LTP requires activation of NR2A-containing NMDARs. Surprisingly another form of LTD, depotentiation, requires activation of NR2A-containing NMDARs.
-
Triheteromeric NR1/NR2A/NR2B receptors constitute the major N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor population in adult hippocampal synapses (Rauner 2011)
- NR1/NR2A/NR2B.
- The contribution of NR1/NR2B receptors to evoked NMDA EPSCs is negligible in adult CA3-to-CA1 synapses.
- Histamine site:
Subunit-specific potentiation of recombinant N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors by histamine (Williams 1994)
- Potentiated NR2B-containing but not NR2A/NR2C.
- glun2a activation downregulates glun2b and glun2b activation downregulates ampa
- Tripartite signalling by NMDA receptors
Structure #
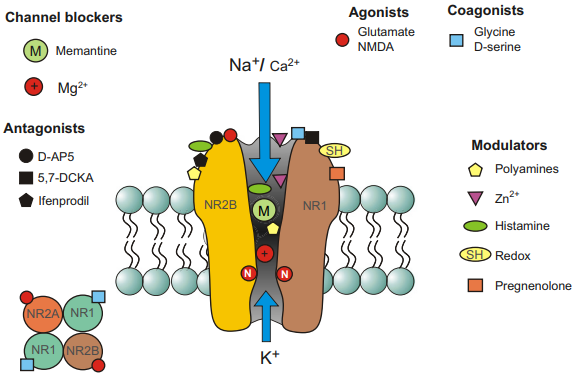
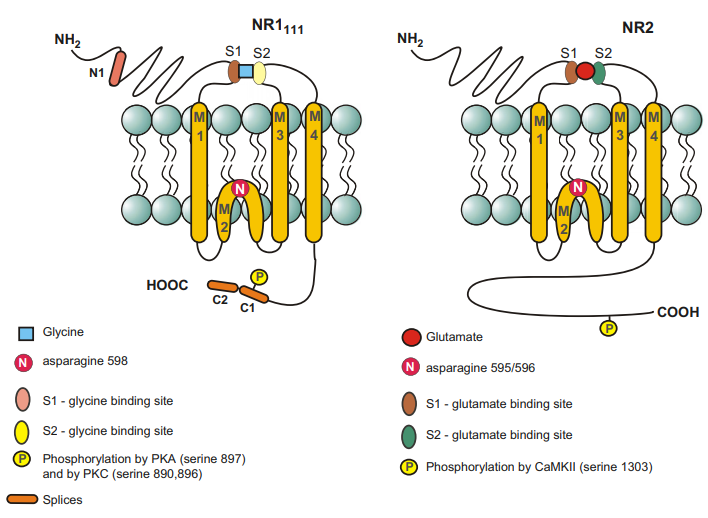
- Heterotetramers of 2 NR1x for coagonists, and 2 NR2x/3x for agonists.
- Could be wrong though… I think it opens only after glutamate binds to all four.
- 7 subunits: NR1A, NR2A, NR2B, NR2C, NR2D, NR3A-B (mainly motor neurons, etc).
- Directly bind to PSD-95 at the PSD.
Mechanism #
-
Often described as a ‘coincidence decetor’, as its conductance requires both ligand binding (BOTH agonist and coagonist) and a removal of the $\ce{Mg^2+}$ blockade.
- And what causes depolarization? Usually by proxy of AMPAR Na+ influx. This doesn’t induce a conformational change like voltage-gated Ion Channels, but just causes Mg2+ dissociation.
- Probably has something to do with $V_{Ca^{2+}} = +123 \\ mV$ and $V_{Mg^{2+}} = +9.26 \\ mV$ but at first glance now it makes even less sense.
- All I know is the NMDARs have ‘remarkably high permability’ to Ca2+.
- I think Na+ actually makes up the majority of depolarization though?
- All I know is the NMDARs have ‘remarkably high permability’ to Ca2+.
- Probably has something to do with $V_{Ca^{2+}} = +123 \\ mV$ and $V_{Mg^{2+}} = +9.26 \\ mV$ but at first glance now it makes even less sense.
- FYI it’s not like the Mg is an actual blockage, but an affinity for their influx. I think perhaps they’re not electronegative enough to fully penetrate or something though.
- And what causes depolarization? Usually by proxy of AMPAR Na+ influx. This doesn’t induce a conformational change like voltage-gated Ion Channels, but just causes Mg2+ dissociation.
-
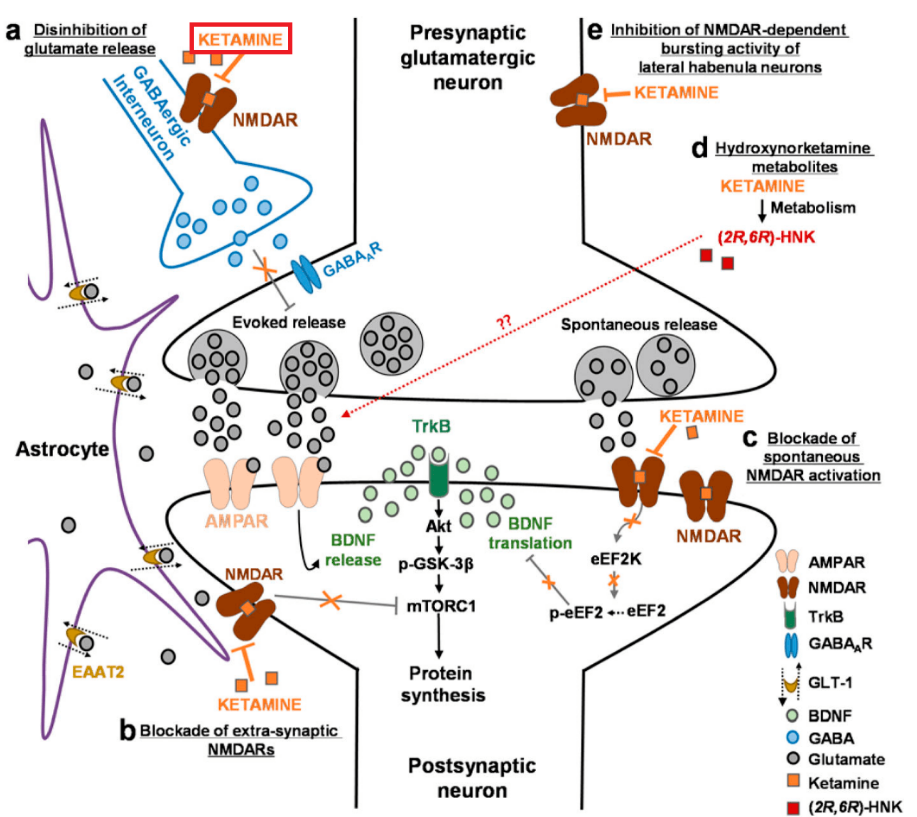
- Looks like we’ve got both PKC and AKT at work. I see AMPAR is capable of creating BDNF out of thin air.
-
Certain calcium-dependent proteases and phospholipases produce free radicals and are toxic to the cell.
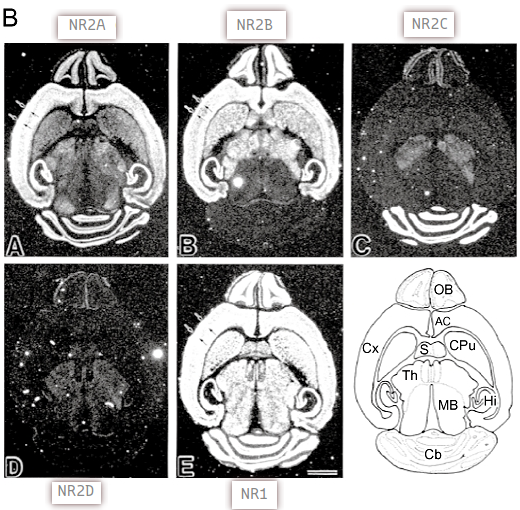
Location #
Cognition #
-
Cognition, NMDA receptors, and gamma oscillations: implications for schizophrenia (big ass PhD thesis)
- PCP and Ketamine induce psychosis/cognitive impairments alsmost indistringuishable from those seen in schizophrenia patients…
Antagonism #
- Excessive antagonism can lead to dissociation (Ketamine and stuff). All dissosiative drugs either directly antagonize it or are κ-Opioid Receptor agonists.
-
Persisting cognitive deficits induced by low-dose, subchronic treatment with MK-801 in adolescent rats
- Induces cognitive deficits that resemble schizophrenia.
-
A pharmacological model for psychosis based on N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor hypofunction: molecular, cellular, functional and behavioral abnormalities
- Reduced parvalbumin-positive GABAergic interneurons.