Prolactin
links: Hormones Neuropeptide reference: Prolactin: Structure, Function, and Regulation of Secretion (Freeman et al., 2000) (practicaly a textbook) 4-11-2021
Prolactin #
AKA luteotropic hormone (LTH). Neuropeptide secreted from the Pituitary Gland.
-
Ideal is 4-7ng/dL in men, 10-12 for women. Stimulatory when its level increases within the normal range, and inhibitory when over the normal range. Very delicate, it seems.
-
Excessive amounts can lead to asexual tendencies.
-
High amounts seen in tumors/Cancer
-
I don’t think it’s even necessary for survival. RPF
-
More reliable than cortisol as a biomarker of prolonged stress.
-
Promotes storage to adipose tissue by increasing certain enzymes (GLUT4, PPARγ, etc. which promote storage of glucose and fat)
-
Prolactin decreases beard growth, libido, desire, temp, and increases Acne, Muscle loss, and Hair Loss. It mimics androgen-induced skin symptoms.
-
Activates Sebum
-
Inhibits Lipolysis and blood flow and increases Lipogenesis, and fat storage
-
Promotes Water retention by increasing Aldosterone, Vasopressin, oxytocin, and Adrenocortocotropic Hormone.
-
Diagnosis and management of hyperprolactinemia (2003)
- Can result from Hypothyroidism.
-
Prolactin modulation of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate secretion
- Increase/decrease in plasma PRL is correlated with corresponding DHEA-S concentrations.
-
Prolactin has a direct effect on adrenal androgen secretion
- PRL potentiates ACTH’s effect on DHEA(-S) - they say prolonged elevation is necessary for prolactin to have an effect on the secretion of adrenal androgens; prolactin alone has no effect.
-
Associated with elevated Parathyroid Hormone and vice versa.
-
Increases Androgen Receptor density, including in the prostate, consistent with an enhanced secretory activity.
-
Increases 5-AR activity, as does DHEA.
-
Progesterone and 5α-DHP lower prolactin
-
Increases Estrogen Receptors. R
-
Lowers Progesterone production.
-
Stimulates Parathyroid Hormone release and vice versa.
-
Long-term hyperprolactinemia reduces the ability of tuberoinfundibular neurons to synthesize Dopamine. Tuberoinfundibular Pathway. R
-
D2 is needed for suppression of prolactin, not D1.
-
Lowers Insulin and Leptin sensitivity via reducing Adiponectin levels.
Hypoprolactinemia #
-
HYPOPROLACTINEMIA AS RELATED To SEMINAL QUALITY AND SERUM TESTOSTERONE
- <6 ng/mL is hyporpolactinemia, and >26 is hyper.
- Increases testicular responsiveness to Luteinizing Hormone. Increases oxygen uptake by spermatozoa: enhancing sperm motility.
- Hyperprolactinemia, and hypoprolactinemia alike for at least some of these, is associated with male infertility, hypogonadism, impotence, oligozoospermia, and azoospermia.
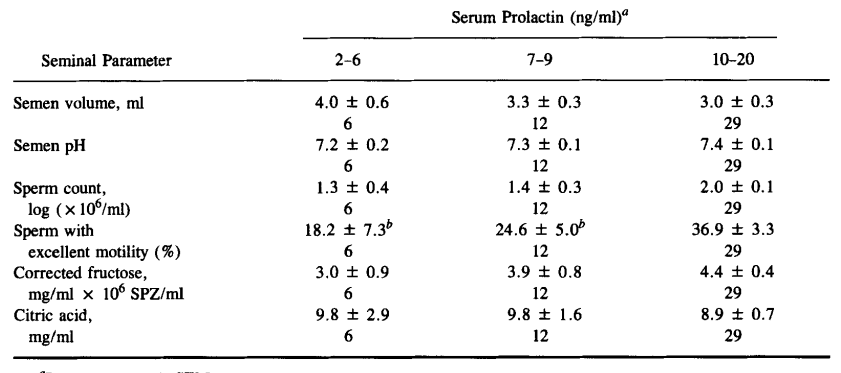
- The reason why Pineapples and similar fruits supposedly make your cummies tastier is because of its acidic pH. Can’t help but think the Citric Acid content also plays a role.
- 67% of the hypo group had low serum Testosterone, while only 33% in the hyper group.
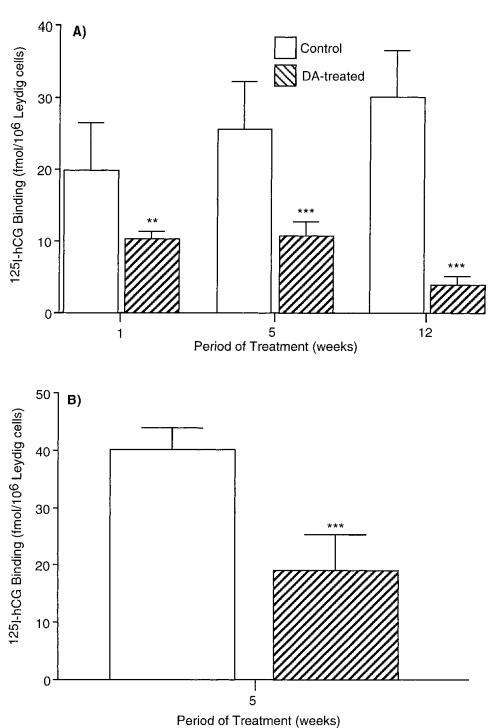
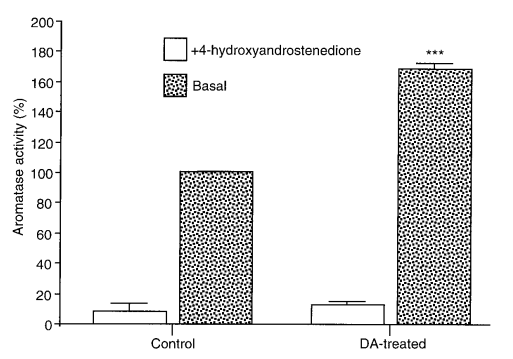
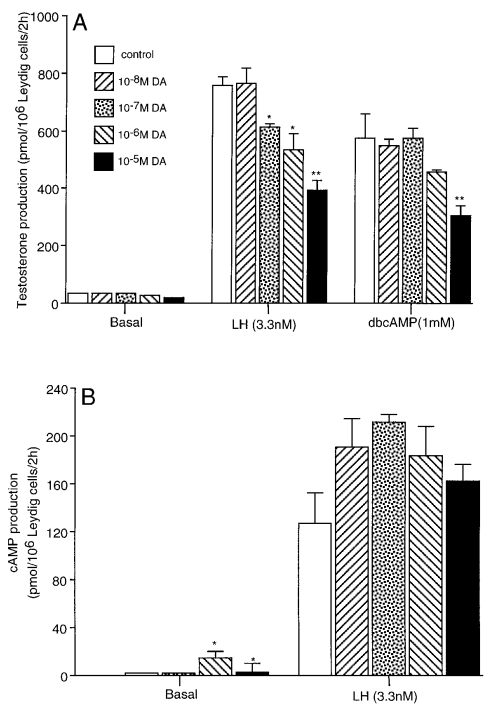
Effect of a Dopamine Agonist on Luteinizing Hormone Receptors, Cyclic AMP Production and Steroidogenesis in Rat Leydig Cells (Dirami and Cooke, 1997) #
- Mesulergine 2mg/kg/day for rats (HED = 22.6 @ 70kg) in food @ 1,5,12 wk.
The results are pretty brutal. But this might be a very high dose. Metergoline for instance is like 4-8mg.
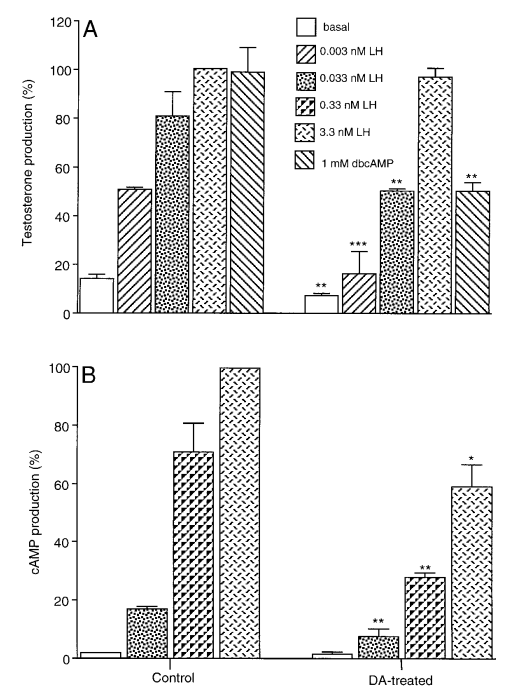
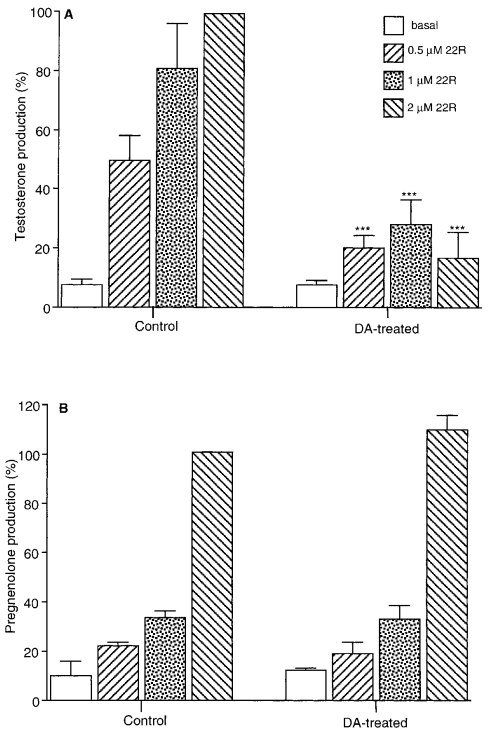
Effects of chronic bromocriptine-induced hypoprolactinemia on plasma testosterone responses to human chorionic gonadotropin stimulation in normal men (Oseko et al., 1991) #
- Bromocriptine 5mg oral daily for 8 weeks in five men age 20-35.
- I don’t really know what hCG ‘stimulation’ is…