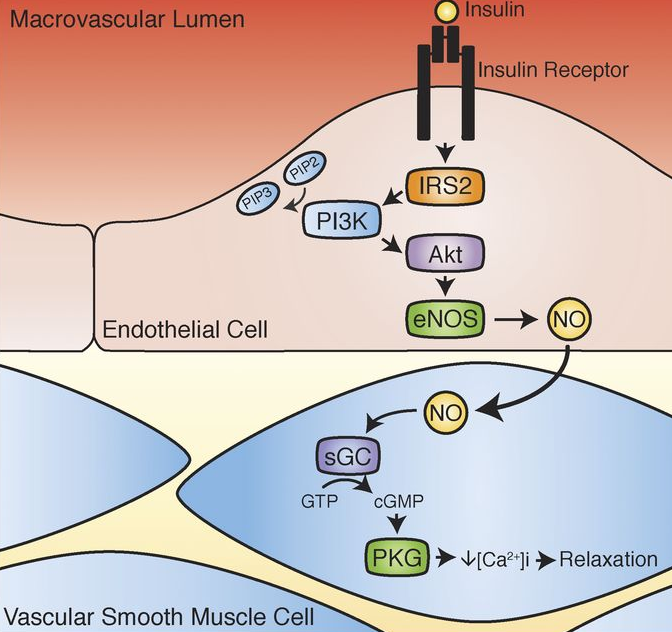
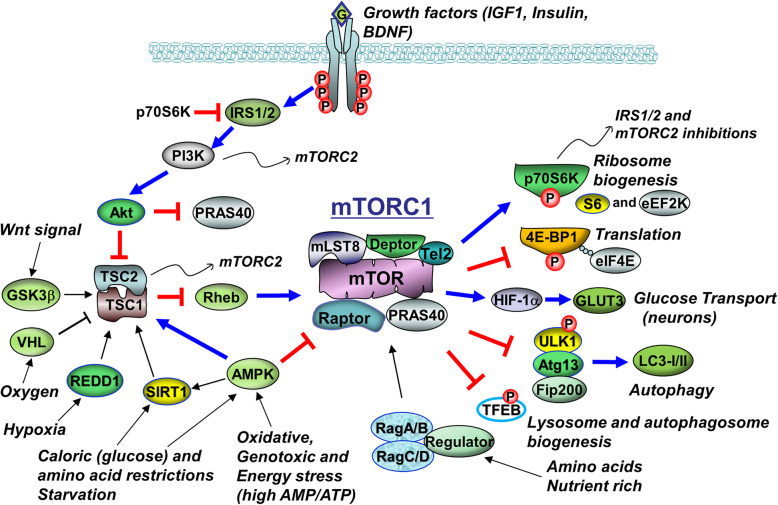
Insulin
links: reference: @Age-related hyperinsulinemia leads to insulin resistance in neurons and cell-cycle-induced senescence (Chow et al. 2019) 4-22-2021
Insulin #
Peptide Hormone produced by Beta Cells.
- Can aggregate into hexamers. Insulin aspartate doesn’t do this.
-
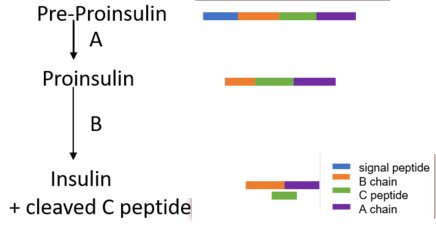
- C-peptide administration does have some actions:
- Reversed TBI-induced movement disabilities.
- Sold kinda commercially as vargapeptide.
- Physiological effects and therapeutic potential of proinsulin C-peptide
- Effects of proinsulin C-peptide on oxygen transport, uptake and utilization in insulinopenic diabetic subjects–a review
-
C-peptide, Na+,K(+)-ATPase, and diabetes
- Arguments have been developed showing that the diabetes-induced decrease in Na+,K(+)-ATPase activity compromises microvascular blood flow by two mechanisms: by affecting microvascular regulation and by decreasing red blood cell deformability, which leads to an increase in blood viscosity. C-peptide infusion restores red blood cell deformability and microvascular blood flow concomitantly with Na+,K(+)-ATPase activity.
- Proinsulin C-peptide elicits disaggregation of insulin resulting in enhanced physiological insulin effects
- C-peptide administration does have some actions:
Signaling #
- Insulin causes a spike in brain uptake of tyrosine and tryptophan, which can increase dopamine synthesis.
- Can lower SHBG
- Insulin resistance can lead to increased levels of MAO-A and MAO-B R
- Increases surface expression of GABA-A R
- Downregulates Histamine, Noradrenaline, Dopamine and increases Serotonin (questionable??)
R
-
Insulin modulates emotional behavior through a serotonin-dependent mechanism
- Stimulates 5-HT1A. This is necessary for anxiolysis from intranasal insulin.
-
Insulin modulates emotional behavior through a serotonin-dependent mechanism
- Reduces tNF, IL, TGF, and promotes glutamate uptake.
-
Insulin Resistance and Hyperinsulinemia
- With continuously elevated levels of Gonadotropin-releasing Hormone, the precocious puberty is inhibited. Removal of the hormone is followed rapidly by a recrudescence of the pubescent process
-
Insulin Signaling And Insulin Resistance
- interference with angiotensin signaling improves insulin sensitivity and it provides a general overview of insulin action and factors that control insulin sensitivity
Brain #
- Insulin signaling inhibits the 5-HT2C receptor in choroid plexus via MAP kinase
-
Broadening the Defintion of Brain Insulin Resistance in Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease
- Alzheimer’s brains displayed region-specific reductions in insulin concentrations together with elevations in Insulin Receptor densities Rng
- The brain even has localized insulin production.
- Insulin promotes glycogen storage and cell proliferation in primary human astrocytes
- Role of Insulin in Neurotrauma and Neurodegeneration: A Review
-
Hyperinsulinemia Induces Insulin Resistance in Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons
- Chronic treatment (this means prolonged! Cells were in insulin soup for 24 h.) resulted in increased basal AKT phosphorylation. More importantly, acute insulin stimulation after chronic insulin treatment resulted in blunted phosphorylation of Akt, S6K, and GSK-3β.
- Interestingly, when the cells were treated with PI3K pathway inhibitor, but not MAPK pathway inhibitor, chronic insulin treatment did not block acute insulin treatment-induced Akt phosphorylation
- Hyperinsulinemia increases Drp1, used for Mitochondrial Fission
-
Insulin promotes rapid delivery of N-methyl-D- aspartate receptors to the cell surface by exocytosis (2001) (Xenopus oocytes)
- Increases open time probability and NR1 surface expression.
- Insulin modulates hippocampal activity-dependent synaptic plasticity in a N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor and phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase-dependent manner (CA1)
- Insulin reduces neuronal excitability by turning on GABA(A) channels that generate tonic current (CA1)
-
Insulin enhances striatal dopamine release by activating cholinergic interneurons and thereby signals reward #
-
Brain insulin receptors and spatial memory. Correlated changes in gene expression, tyrosine phosphorylation, and signaling molecules in the hippocampus of water maze trained rats
- Insulin receptor mRNA is raised during memory tasks. How’s that for LTP?
Intranasal #
- Insulin increases excitation and reward through activation of Nachar receptors on somatostatin interneurons which promote synchronicity in the brain and disinhibition of dopamine expressing cells.
- Intranasal insulin protects against substantia nigra dopaminergic neuronal loss and alleviates motor deficits induced by 6-OHDA in rats
- Intranasal insulin administration may be highly effective in improving cognitive function in mice with cognitive dysfunction by reversing brain insulin resistance
- Intranasal insulin improves memory in humans: superiority of insulin aspart
- Intranasal Insulin Improves Age-Related Cognitive Deficits and Reverses Electrophysiological Correlates of Brain Aging Intranasal does not alter bodily insulin receptors. It just delivers it to the brain.
- Intranasal insulin administration appears safe, does not affect systemic glucose control, and may provide acute improvements of cognitive function in patients with type 2 DM R
- Awake intranasal insulin delivery modifies protein complexes and alters memory, anxiety, and olfactory behaviors
-
Effect of intranasally administered insulin on cerebral blood flow and perfusion; a randomized experiment in young and older adults
- Young group was mean age 22 and not diabetic or anything.
-
Central insulin administration improves whole-body insulin sensitivity via hypothalamus and parasympathetic outputs in men (2014)
- Nondiabetic participants. 10 of which ~21.8 BMI: + 41 $\pm$ 8% increase in peripheral insulin sensitivity. 5 33.2 BMI obese patients saw… -0.7 $\pm$ 18% change.
- This change was associated with hypothalamic activity.
- Began with 6.25 mU/kg insulin bolus followed by 0.25mU/kg/min iv. Then, 160 U insulin intranasal.
-
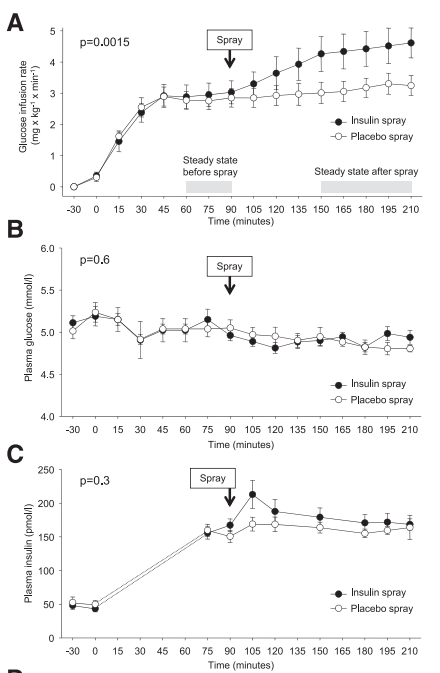
- Nondiabetic participants. 10 of which ~21.8 BMI: + 41 $\pm$ 8% increase in peripheral insulin sensitivity. 5 33.2 BMI obese patients saw… -0.7 $\pm$ 18% change.
-
Dose-Dependent Effects of Intranasal Insulin on Resting-State Brain Activity
-
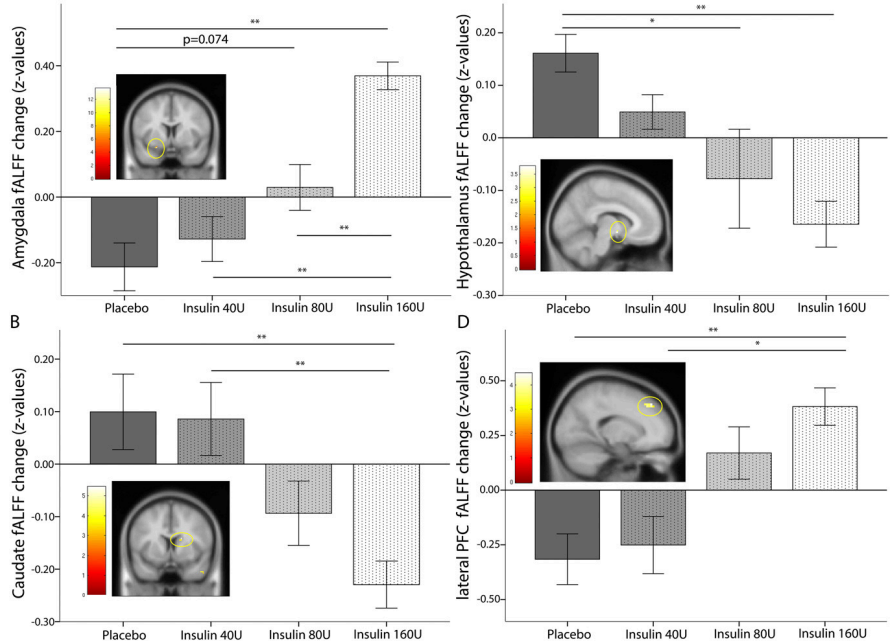
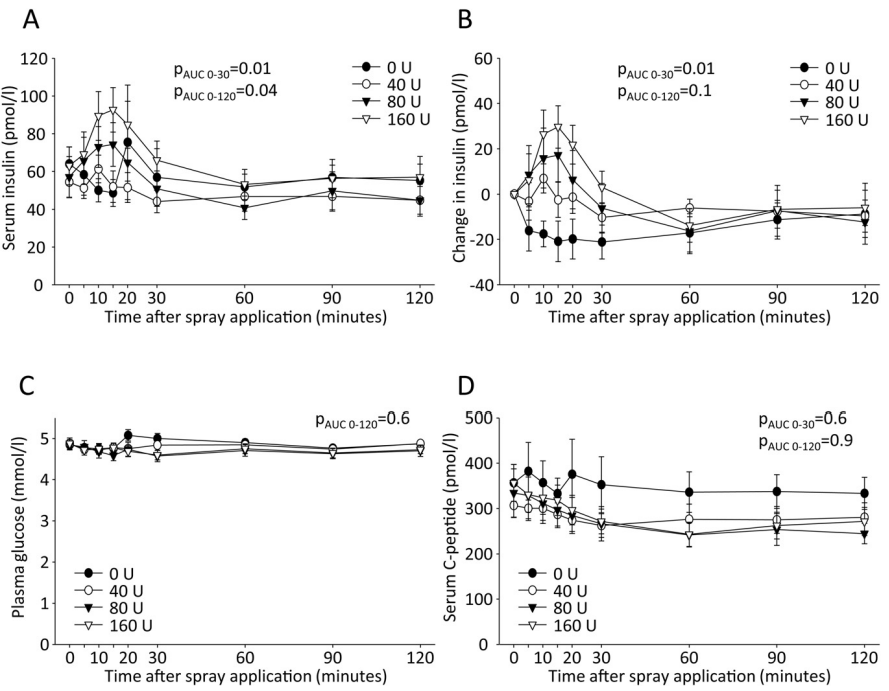
- Nine healthy young men. 0, 40, 80, or 160. After application of 160 IU as a nasal spray, ~0.1 enter the bloodstream, as shown in previous studies.
- No differences for LH, FSH, Test, ACTH, cortisol, TSH.
-
-
Intranasal Insulin Administration Dose-Dependently Modulates Verbal Memory and Plasma β-Amyloid in Memory-Impaired Older Adults
- Plasma insulin and glucose levels were unaffected by treatment.
- 20 IU was the most efficacious dose.
- Promotes breakdown of Amyloid β
- CSF Amyloid β levels are reliably lower in Alzheimer’s! Evaluation of CSF-tau and CSF-Abeta42 as diagnostic markers for Alzheimer disease in clinical practice Mixed results for plasma, though. In this study, it was usually increased.
- Intranasal insulin improves memory in humans reduced plasma Cortisol. This may facilitate Aβ clearance via Insulin Degrading Enzyme.
- It is reasonable to speculate that in the long term, chronic intranasal administration may produce similar adverse effects centrally. Long-duration trials that include a late-stage test of acute brain insulin resistance could address this concern. Even such trials may not go far enough: the extent to which dose timing and frequency impact central insulin resistance is also a mystery. This despite the fact that, for instance, insulin sensitivity of peripheral tissues exhibits a clear circadian pattern in healthy humans (Boden et al., 1996). Additionally, the impact of dose frequency is poorly understood. With these thoughts in mind, future trials investigating both timing and frequency may help to develop an optimal dosing “schedule” that effectively balances efficacy and safety. R
-
Nasal insulin changes peripheral insulin sensitivity simultaneously with altered activity in homeostatic and reward-related human brain regions #
-
Effects of intranasal insulin on hepatic fat accumulation and energy metabolism in humans
- Overweight, elderly T2D group and lean healthy participants (control). Hepatic insulin sensitivity as not changed. In control, hepatocellular lipids decreased by 35% and hepatic ATP concentration increased by 18% after 3h.
-
Intranasal Insulin Therapy for Alzheimer Disease and Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment
- Benefits persisted 2 months after for the 20 IU group.
- Insulin given intranasally induces hypoglycaemia in normal and diabetic subjects (1982) Hard to read graphs…
- 40IU QID: Intranasal insulin did not demonstrate statistically significant improvements on overall mood, aspects of emotional processing, neurocognitive function, or self-reported quality of life patient reported outcomes. R
Dose #
(For some reason, closed vials must be refrigerated, but open can last for ~28 days) U100= 100IU per 1mL.
- 20-30-40IU 4x/day (before meals) - 160 IU as a single dose or 120 IU/day are common in studies.
Humulin R/novolin R are effectively the same - inulin NPH. Pax: I use a luer slip syringe which allows me to pull the needle off and I stick the blunt end deep into my nose till i nearly touch the back of my nasal cavity and then squirt it out while sniffing. Insulin passes into the brain by certain cells in the brainstem that are reliant on serotonin.