Estrogen
4-11-2021 links: Hormones Steroid reference:
- @Regulation of Arcuate Nucleus Synaptology by Estrogen (Leedom et al. 1994)
- @Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate and estrone sulfate reduce GABA-recurrent inhibition in the hippocampus via muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (Steffensten et al. 2006)
Estrogen #
-
oestrus () = mad impulse; frenzy
-
Can make the bladder more irritable, giving a diuretic effect. This can be attenuated with antihistamines like aspirin, vitamin D, or thyroid, which will reactive the anti-diuretic hormone.
-
Increases Free radicals production and NADPH Oxidase R
-
Increases the free fatty acids in blood circulation, shifting metabolism to fat oxidation, contributing to diabetes.
-
Lowers body Temperature via heat loss and decreasing heat production. It increases blood flow to the skin in response to the environment.
-
Reduces Thyroid function via: R
- Inhibits the proteolytic enzymes that allow the thyroid to release its hormones
- Inhibiting T4->T3 Conversion
- Blocking the metabolism
- Increases the amount of thyroid hormone binding globulin (TBG).
-
Impact of estrogens in males and androgens in females #
-
Activates mast cells to release serotonin and histamine.
-
Estrogen decreases LDL particle size, androgens increase it
-
Increases the formation of aminolevulinic acid, a precursor of porphyrin, and increases the risk of excess porphyrin increasing light sensitivity. Both aminolevulinic acid and excess porphyrins are toxic to mitochondria, apart from their photosensitizing actions.
-
Excess can lead to migraines RPF
-
Inhibits COMT. As a result, women have ~30% higher baseline dopamine than men.
-
Inhibits 17α-Hydroxylase R
-
Directly stimulates the Adrenal Cortex.
-
Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Tied to Endogenous Estrogen Exposure in Women - from Reproductive period and preclinical cerebrospinal fluid markers for Alzheimer disease: a 25-year study
Brain #
-
Neuron-Derived Estrogen Regulates Synaptic Plasticity and Memory
- Lots of interesting references
- Aromatase knockout (FBN-ARO-KO) mice (70-80% decrease in A and E2) exhibited significant deficits in forebrain spine and synaptic density, as well as hippocampal-dependent spatial reference memory, recognition memory, and contextual fear memory.
- In vitro studies revealed that amplitude of LTP was significantly decreased.
Estrogen and brain aging in men and women: Depression, energy, stress (Peat 1999) #
- Progesterone’s antiestrogen action can prevent masculinization by estrogen and testosterone.
- “This substance, which came into medical use as “the female hormone” for the treatment of “female problems,” especially for improving fertility, and then for preventing fertility as the oral contraceptive, is now being aimed primarily at the post-reproductive population, for problems that are essentially unrelated to femininity.”
- Activates the excitotoxic Glutamate pathway
- Adenosine helps maintain brain Glycogen stores
- Two days of estradiol treatment increased the density of NMDAR agonist, but not of competitive nor noncompetitive NMDA antagonist binding sites exclusively in the CA1 region of the hippocampus
- Our results show that Glutamate uptake inhibition leads to marked neuronal damage in energy-deficient rats but not in intact animal. R
Metabolism/Biosynthesis #
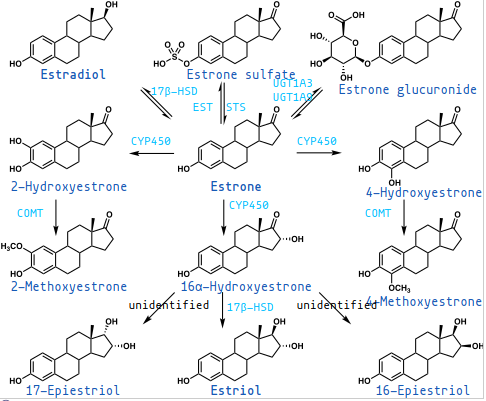
-
The 4-hydroxy metabolites are thought to be harmful and cancerous; the 2-hydroxy metabolites are the safe ones.
- 2-hydroxy metabolites inhibit dopamine synthesis, increase prolactin and promote oxidative stress.
- (There are 4- and 2- metabolites for all 3 estrogens.)
-
https://men-elite.com/2020/01/08/how-to-interpret-your-testosterone-blood-test-results-in-order-to-focus-on-whats-most-important/ It all mostly begins with Estrone:
-
17β-HSD is to convert it to and from Estradiol.
- COMT metabolizes them further into 2- or 4-methoxyestrone.
- I suppose 4-methoxy is safe; therefore COMT and methylation from B-vitamins is protective in this circumstane.
- COMT metabolizes them further into 2- or 4-methoxyestrone.