Erythropoietin
2022-05-02: reference:
Erythropoietin #
(Be not afraid. Most of these notes are on efficacy for cognitive enhancement and not much mechanisms. I can wave through all of this without getting too caught up.)
General #
- Induction of erythropoiesis is dependent on increasing Frataxin.
- Upregulates FGF21. Erythropoietin Receptor knockout mice are obesogenic and insulin resistant.
- Activates STAT3->UCP1
- Antagonizes inflammatory cytokines; improves IL-10.
- Acivates AKT and negatively controls nuclear translocation and post-translational processing of the FOXO family. Employs SIRT1.
-
Erythropoietin use and abuse: When physiology and pharmacology collide (on doping)
- Hematocrit = volume % of red blood cells in blood, compared with hemoglobin, white blood cell, and platelet, I htink.
- Elevation of the red cell mass by recombinant human erythropoietin is associated with a reduction in plasma volume and in some patients, hypertension is induced. Elevation of the red cell mass is also associated with a reduction in cerebral blood flow.
- When the normal hematocrit level (40.7–50.3%) is exceeded, the risk for thrombotic events increases since blood viscosity varies exponentially with the hematocrit
- Paradoxically, its effects are the opposite of those of endurance training, namely a change in red cell mass without an increase in the total blood volume.
- Pericytes: new EPO-producing cells in the brain
- Hormone released by the Kidneys, small amounts in the liver, aand the uterus, aaand the heart in response to Hypoxia to stimulate Erythrocyte production (erythropoiesis). It takes place in red bone marrow.
- Astrocytes and neurons as well.
-
Neurons and astrocytes express EPO mRNA: oxygen-sensing mechanisms that involve the redox-state of the brain
- Addition of H2O2 decreases the hypoxia-induced Epo mRNA levels.
- Erythropoietin receptor is expressed in rat hippocampal and cerebral cortical neurons, and erythropoietin prevents in vitro glutamate-induced neuronal death
-
A novel site of erythropoietin production. Oxygen-dependent production in cultured rat astrocytes (1994)
- Oxygen-dependent regulation of epo production operates at mRNA level. Epo acts on neurons in a paracrine fashion.
-
Neurons and astrocytes express EPO mRNA: oxygen-sensing mechanisms that involve the redox-state of the brain
- Astrocytes and neurons as well.
- Wikipedia: Risks of therapy include death, myocardial infarction, stroke, venous thromboembolism, and tumor recurrence. Risk increases when EPO treatment raises Hemoglobin levels over 11 g/dL to 12 g/dL: this is to be avoided.
- WTF? Reference range is 13-17.7 on that hormone panel I got.
- Much greater subjective rating of physical performance and endurance. R
Brain/Cognition #
There’s demonstrated proof that engaging in cognitive work increases the long term potentiation or the “connections between neurons” through a variety of mechanisms and models that test this are called “environmental enrichment” within the literature. Increasing the load or demand that we place on our neurons when we learn strengthens the connections between neurons as well as neuronal morphology through induction of functional hypoxia.
- Introducing neuroepo:
- Nasal administration of the neuroprotective candidate NeuroEPO to healthy volunteers: a randomized, parallel, open-label safety study n=25 and 20% them got headaches and 20% saw increase in liver enzymes. They call that ‘well tolerated’.
- The Effect of Neuroepo on Cognition in Parkinson’s Disease Patients Is Mediated by Electroencephalogram Source Activity
-
Erythropoietin: a candidate compound for neuroprotection in schizophrenia showed 5,000 IU/kg in mice injected ip.:
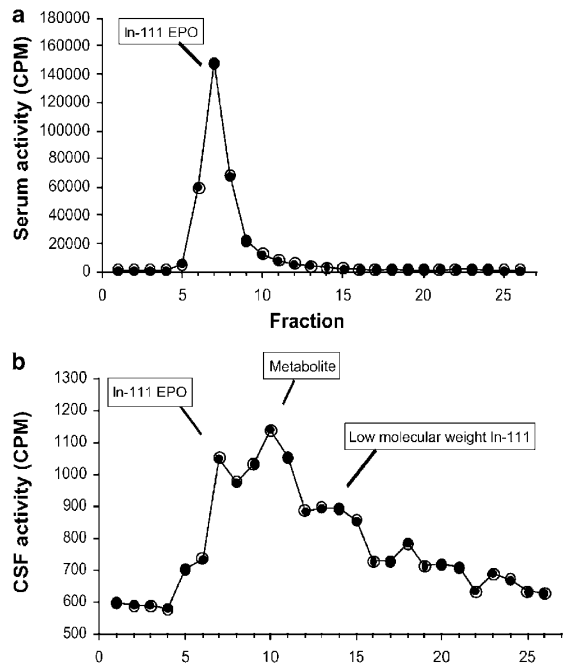
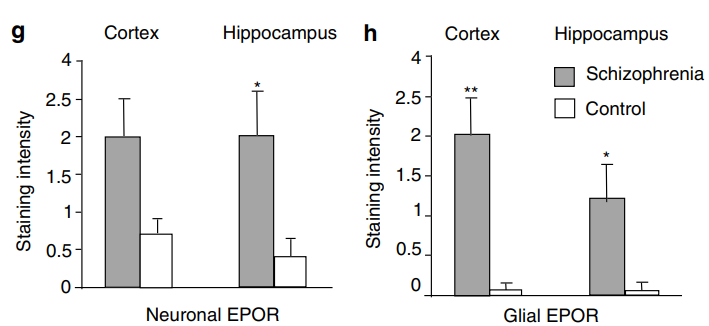 holy fuck
holy fuck -
Emerging biological roles for erythropoietin in the nervous system
-
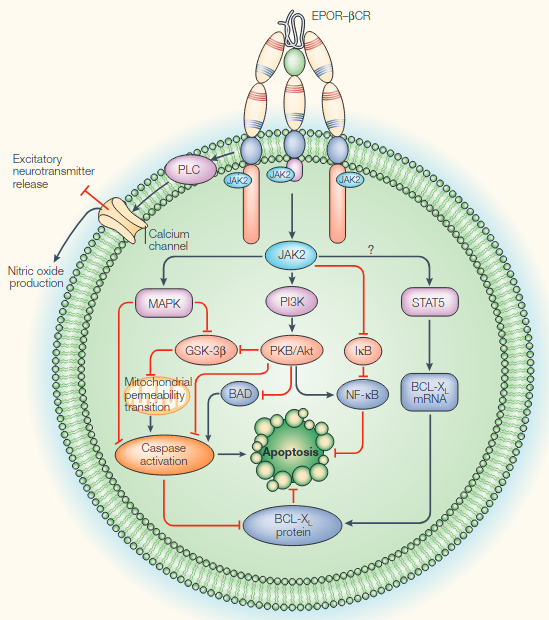
- JAK2-STAT is found on the C-terminus of Erythropoietin Receptor (and βCR)
-
-
Erythropoietin Enhances Hippocampal Response during Memory Retrieval in Humans
- In healthy humans, 40,000 IU rhEPO IV increased the hippocampal response during memory retrieval 1 week later!
-
Erythropoietin enhances hippocampal long-term potentiation and memory (in young healthy mice)
- This selective improvement was maintained for an EPO treatment-free period of another 3 weeks
- It exerts hematopoieis-independt effets on the NS. Maybe this was obvious but I assumed it was all by proxy of something to do with hematology at least.
- Derivatves like CEPO (carbamoylated EPO) exert similar neuroprotective properites, but not erythropoietic effects. Epobis counts too I’m sure.
- Made some interesting electrical changes in CA1 slices, especially quite a huge drop in short-term depression fEPSP slope.
- Decreased amplitude and frequency of spontaneous EPSC in CA1 and increased SIPSC frequency - 50%?
- Did not reveal differences in epression of synaptic proteins or postsynaptic receptor proteins and their subunits.
- Evoked excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC) amplitudes in EPO-treated neurons were reduced to about 60% of control in these autapic neurons… why did they choose them..? No diference in NMDA/AMPA ratio.
- Synaptic boutons per neuron increased, but reduces the amount of primed vesicles? EPO is likely to reduce the number of active synapses without altering total synapse number
- Hematocrit seems irrelevant. In our study, the hematocrit was already back to control levels when we still observed a significant effect on
-
Expression of constitutively active erythropoietin receptor in pyramidal neurons of cortex and hippocampus boosts higher cognitive functions in mice
- Constitutively active = no need for agonist.
- Effects of recombinant human erythropoietin on cognition and neural activity in remitted patients with mood disorders and first-degree relatives of patients with psychiatric disorders: a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- Differential effects of erythropoietin on neural and cognitive measures of executive function 3 and 7 days post-administration
-
Erythropoietin improves operant conditioning and stability of cognitive performance in mice
- It is not produced solely by the kidneys, but is also produced in astrocytes. In line with renal production, hypoxia enhances it here, too.
- Insulin-like growth factors and insulin stimulate erythropoietin production in primary cultured astrocytes: they did not directly stimulate it, rather they increased mRNA level.
- They did the 5CSRTT (Five Choice Serial Reaction Time Task). It was consistenyl superior in like every measure.
- It is not produced solely by the kidneys, but is also produced in astrocytes. In line with renal production, hypoxia enhances it here, too.
-
Acute and chronic elevation of erythropoietin in the brain improves exercise performance in mice without inducing erythropoiesis
- The increase in maximal exercise performance is independent of changes in total hemoglobin mass, whole blood volume, and cardiovascular parameters. Also greater self-esteem and mood/euphoria.
- Tg21 transgenicity overexpresses rhEPO independent of oxygen.
-
Effects of erythropoietin administration on cerebral metabolism and exercise capacity in men
- 3 days of high-dose NO effect in healthy subjects on exercise capacity or cognition.
-
Effects of erythropoietin administration on cerebral metabolism and exercise capacity in men
-
Recombinant erythropoietin improves cognitive function in chronic haemodialysis patients
- Adjusting for control, their WAIS IQ increased by about 6 points.
- Prolonged astrocyte-derived erythropoietin expression attenuates neuronal damage under hypothermic conditions
-
Regulation of muscle and metabolic physiology by hypothalamic erythropoietin independently of its peripheral action
- While blood EPO raises with aging and obesity, hypothalamic EPO decreased.
- Aged mice were chronically treated with EPO in the hypothalamic ventricle, showing an increase in lean mass, while body weight and fat mass decreased as a result of a moderate reduction of food intake. Both muscle and metabolic functions were improved.
-
Intranasal erythropoietin therapy in nervous system disorders
-
- Erythropoietin restrains the inhibitory potential of interneurons in the mouse hippocampus
Neurogenesis #
-
Introducing the brain erythropoietin circle to explain adaptive brain hardware upgrade and improved performance
- rhEPO (recombinant human) treatment of young rodents or EPO receptor (EPOR) overexpression in Pyramidal Neurons caused remarkable and enduring cognitive improvement, together with enhanced LTP. The ‘brain hardware upgrade’, underlying these observations, includes an EPO induced ~20% increase in Pyramidal Neurons and Oligodendrocytes in CA hippocampi in the absence of elevated DNA synthesis.
- Reduces Microglia numbers and dampens their activity as prerequisites for undisturbed EPO-driven differentiation of pre-existing local neuronal precursors.
- It’s extremely potent and thus very sparse and hard to measure its relative expression.
- Erythropoietin protects primary hippocampal neurons increasing the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor
-
Revisiting adult neurogenesis and the role of erythropoietin for neuronal and oligodendroglial differentiation in the hippocampus (2016)
- Similar group to the study below.
- BrdU labels mitotic brain cells I guess.
- At week 4 we found a reduction in BrdU+ cells in DG/SVZ, likely as a consequence of temporary depletion of progenitors or negative feedback on neurogenesis.
- Increased apoptosis, potentially because of abnormal crowding of maturing neurons.
- Healthy young mice (starting at 4 weeks old or 11 weeks old) 3-week EPO administration i.p. (5000IU/kg = HED ~27k) every other day.
- Increased number of pyramidal neurons and oligodendrocytes in the hippocampus of ~20%. Under ’enduring cognitive challenge’, they were preserved. This is concomitant with an increased hippocampal volume. in the 11->14 week mice.
- They of course both increased, in similar amounts, because new axons need to be myelinated.
- OPC = olgodendrocyte precursor cells. Can differentiate into them without dividing.
- *this EPO effect involves stimulation of precursor differentiation rather than proliferation or anti-apoptosis
- Decreased number and diameter of ’neurospheres’, culture of clustered NSCs. Inhibitory of their proliferation.
- Pax6 and doublecortin-positive cells (i.e. immature) were reduced after 3 days compared to control. This may imply that the increase in neurons was due to accelerated differentiation of neural progenitors.
- They used leucine incorporation as a marker of protein synthesis sans proliferation. And it actually increased ~20%.
-
Functional hypoxia drives neuroplasticity and neurogenesis via brain erythropoietin (2020)
- High-ose EPO amplifies auto-/paracine EPO/EPOR signaling prompting emergence of new CA1 neurons and enhanced dendritic spine densities.
-
Matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) and MMP9 secreted by erythropoietin-activated endothelial cells promote neural progenitor cell migration
- EPO activates endothelial cells, which promote endogenous neuroblast migration by secreting MMPs that degrade extracellular matrix (ECM) components.
-
Regeneration in the nervous system with erythropoietin
- Relies on WISP1 signaling to foster stem cell survival and to block FOXO activity. Relies on mTOR for induction of plasticity/differentiation/etc.
- In contrast to its mTOR activation I suppose, in some conditions it increases AMPK and auotphagy activity.
- EPO increases WNT signaling expression.
- +Wnt3 expression:
Survival, neuron-like differentiation and functionality of mesenchymal stem cells in neurotoxic environment: the critical role of erythropoietin
- NGF levels remained the same, contrary to hypothesis. LIF (type of IL-6) was upregulated in hypoxia and normoxia.
- +Wnt3 expression:
Survival, neuron-like differentiation and functionality of mesenchymal stem cells in neurotoxic environment: the critical role of erythropoietin
- Expression is increased by cytokines like TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6. Stimulated by Selenium depletion, xenon, and microglial inhibitors.
-
Insulin-like growth factors and insulin stimulate erythropoietin production in primary cultured astrocytes
- Stimulatory effect of IGF-1/2 on EPO was not affected by oxygen concentration, obviously unlike its normal induction from hypoxia.
-
Insulin-like growth factors and insulin stimulate erythropoietin production in primary cultured astrocytes
Supplementation #
A recognized PED.
- It’s 30 KDa, so it really isn’t going to cross the BBB much - but it does to some degree. How much?