α7 nAChR
2022-03-04: reference:
α7 nAChR #
- Exists as a homomer: has the highest Ca2+ permeability of all the subunits. They generally have a really low opening probability, and low affinity for acetylcholine.
- Even more Ca2+ permeability than NMDAR!
- α7 subunits are also found within heteromers i.e. α7β2.
- Fast desensitization. Partial agonists and PAMs slow this down.
-
Activation and Desensitization of Nicotinic α7-type Acetylcholine Receptors by Benzylidene Anabaseines and Nicotine sirsadalot: I believe this is the case with all nicotinic receptors But mainly α7 and α4β2 since those are the most excitatory.
- Like yeah, nicotinic receptors upregulate when they’re bound, maybe because agonists trap them in a desensitized state.
-
Activation and Desensitization of Nicotinic α7-type Acetylcholine Receptors by Benzylidene Anabaseines and Nicotine sirsadalot: I believe this is the case with all nicotinic receptors But mainly α7 and α4β2 since those are the most excitatory.
- Implicated in Angiogenesis
-
Depression-like phenotype by deletion of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: Role of BDNF-TrkB in nucleus accumbens
- α7 deletion = increased BDNF-TrkB signaling in the nucleus accumbens but not PFC/Hippocampus; administration of TrkB antagonist showed rapid antidepressant effect by normalizing increased synaptogenesis in the NAc.
- Essential role of BDNF in the mesolimbic dopamine pathway in social defeat stress
- Regional differences in brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels and dendritic spine density confer resilience to inescapable stress
-
Alterations in brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and its precursor proBDNF in the brain regions of a learned helplessness rat model and the antidepressant effects of a TrkB agonist and antagonist - Depression
- LH rats showed a reduction of BDNF in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), CA3, and dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus, whereas LH rats showed an increase in BDNF in the nucleus accumbens (NAc). Furthermore, levels of proBDNF, a BDNF precursor, were higher in the mPFC, but lower in the NAc, of LH rats:
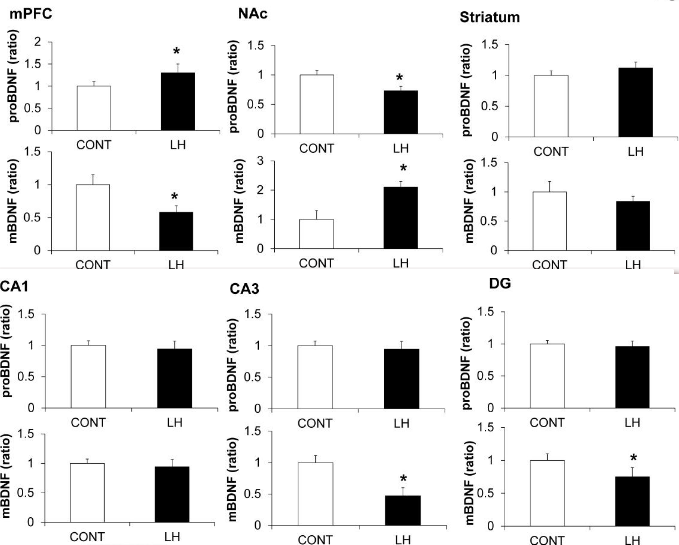
- LH rats showed a reduction of BDNF in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), CA3, and dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus, whereas LH rats showed an increase in BDNF in the nucleus accumbens (NAc). Furthermore, levels of proBDNF, a BDNF precursor, were higher in the mPFC, but lower in the NAc, of LH rats:
- α7 deletion = increased BDNF-TrkB signaling in the nucleus accumbens but not PFC/Hippocampus; administration of TrkB antagonist showed rapid antidepressant effect by normalizing increased synaptogenesis in the NAc.
-
The interaction between alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and nuclear peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α represents a new antinociceptive signaling pathway in mice
- α7 activation increases Palmitoylethanolamide and Oleoylethanolamine levels.
- Increases PPAR-α levels in the brain, and PEA and OEA, in a Ca2+-dependent manner.
- Activation of alpha7 acetylcholine receptors reduces neuropathic pain by decreasing dynorphin A release from microglia
- Layer-Specific Modulation of the Prefrontal Cortex by Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors (Poothuis et al 2013)
-
Nicotinic α7 receptors enhance NMDA cognitive circuits in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (Yang, Arnsten, et al. 2013)
- Postsynaptic colocalization with NMDAR in the dlPFC: We additionally show that α7-nAChR stimulation is needed for NMDA actions, suggesting that it is key for the engagement of dlPFC circuits.
- They note that this is an intesesting way of thinking about how certain mental states are shaped during Sleep (such as deep sleep when there is none).
- Along with just parietal association cortex → dlPFC (also, isn’t this the Executive Network?!): persistent firing also may involve reciprocal excitation with longer-range cortical–cortical circuits, for example, with the parietal association cortex Matching patterns of activity in primate prefrontal area 8a and parietal area 7ip neurons during a spatial working memory task (Chafee & Goldman-Rakic 1998)
- The spatial tuning of dlPFC delay cells is refined by GABAergic lateral inhibition from local basket and chandelier cells
- Postsynaptic colocalization with NMDAR in the dlPFC: We additionally show that α7-nAChR stimulation is needed for NMDA actions, suggesting that it is key for the engagement of dlPFC circuits.
-
BDNF up-regulates alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor levels on subpopulations of hippocampal interneurons
- This effect is abolishied with NMDA antagonism. (Interesting when you consider the case of Memantine)
- Neuronal Nicotinic Receptors as New Targets for Amphetamine-Induced Oxidative Damage and Neurotoxicity α7 agonism strongly potentiates neurotoxicity from Amphetamines. The thing is, α7 full agonists in and of themselves are typically neurotoxic.
D-Serine #
- Increasing D-serine release might be the main way it actually facilitates LTP beyond just Ca2+ influx - because the former is astrocytic; the question is what type of neurons α7 localizes on in the hippocampus?
- [Activation of α7 acetylcholine receptors augments stimulation‐induced hippocampal theta oscillation]
- Hippocampal astrocytes sense wakefulness-dependent activity of septal cholinergic fibers through α7 to drive D-Serine release. R (that’s literally like the whole paper)
- Septal Cholinergic Neuromodulation Tunes the Astrocyte-Dependent Gating of Hippocampal NMDA Receptors to Wakefulness
- Nicotinic ACh receptors in the hippocampal circuit; functional expression and role in synaptic plasticity
Cognition #
- Critical for (working) memory, learning, attention.
- Highly expressed in the Hippocampus.
-
Allosteric Agonism of α7
- We will use the term ‘allosteric modulator’ to describe any ligand that alters the functional properties of nAChRs by interacting with a site that is distinctfrom the orthosteric site. The most effective PAMs bind within the transmembrane domain. (What other options do they have my guy?)
-
Acetylcholine α7 Nicotinic and Dopamine D2 Receptors Are Targeted to Many of the Same Postsynaptic Dendrites and Astrocytes in the Rodent Prefrontal Cortex
- The stimulation of D2Rs in astrocytes increases their intracellular levels of Ca2+. WTF?
- Nicotinic α7 receptor activation selectively potentiates the function of NMDA receptors in glutamatergic terminals of the nucleus accumbens
-
Effect of R3487/MEM3454, a novel nicotinic α7 receptor partial agonist and 5-HT3 antagonist on sustained attention in rats
- α7 is reduced in Schizophrenia, possibly why they smoke that Nicotine so much.
- It was recently demonstrated that ABBF, a nicotinic α7 receptor full agonist with 5-HT3 receptor antagonist properties, also improved working and recognition memory in rodents, effects specifically mediated by α7
-
Selective a7 nicotinic receptor activation by AZD0328 enhances cortical dopamine release and improves learning and attentional processes (2009)
- Increased object exploration and improved memory.
- EVP-6124, a novel and selective a7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist, improves memory performance by potentiating the acetylcholine response of a7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (2012)
Inflammation #
- Also regulates anti-inflammatory actions of the Vagus Nerve. GTS-21, a partial agonist, is even more potent than nicotine in this regard.
-
Molecular Mechanisms Regulating LPS-Induced Inflammation in the Brain
- LPS decreases α7 density in the brain (RNA+protein) and AChE RNA - sensitized brain mitochondria to apoptogenic effect of Ca2+ and so on.
-
Reflex control of immunity (Kevin J Tracey 2015)
- Essentially it inhibits the peripheral release of Cytokines; or release from the cytoplasm, in response to TLR4/NLR agonism.
- α7 agonism doesn’t cause immunosuppression or anything; just reverts immune responses to healthier levels.
- This guy is involved in some other papers published in Nature and so on about the vagus nerve and neuroimmunity. Not sure if the earlier ones are worth reading because they all seem about the same; like there’s a dozen of these things. Really fascinating stuff, and possibly a good entry into learning about T Cells and stuff or something:
- The inflammatory reflex (2002)
-
The vagus nerve and the inflammatory reflex–linking immunity and metabolism (2012)
-
-
Mechanisms and Therapeutic Relevance of Neuro-immune Communication (2017)
-

- Noxious stimulus → TRPV1 and other channels → gene upregulation and releases of peptides like CGRP, Substance P, VIP, Galanin, and Somatostatin.
- Mitochondrial α7! Inhibits mtDNA release, inhibiting inflammasome activation.
- AC6 inhibits NF-κB activation.
-
- Molecular and Functional Neuroscience in Immunity (2018)
- This guy is involved in some other papers published in Nature and so on about the vagus nerve and neuroimmunity. Not sure if the earlier ones are worth reading because they all seem about the same; like there’s a dozen of these things. Really fascinating stuff, and possibly a good entry into learning about T Cells and stuff or something:
- Microglia have α7 receptors:
Cholinergic modulation of microglial activation by α7 nicotinic receptors
- Stimulation of toll-like receptor 4 downregulates the expression of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors via histone deacetylase in rodent microglia
-
Anti-inflammatory role of microglial alpha7 nAChRs and its role in neuroprotection -
- Activates JAK2-STAT3 -> NF-κB translocation inhibiton.
- JAK2 -> PI3K -> AKT -> inhibition of GSK-3β -> inhibition of NRF2 nuclear translocation (thus disinhibition) -> HO-1 expression -> neuroprotection.
- NRF2 has many functions; why would they imply neuroproptection from it is bottlenecked by HO-1? Like wut?
- nAChRs, which are the prototype of the cys-loop family of ligand-gated ion channels that also include GABAA, GABAC, glycine, 5HT3 receptors and 5-HT-gated chloride channels
- So that sounds like the reason why Tropisetron binds to 5-HT3.

