Choline
4-12-2021 links: reference:
Choline #
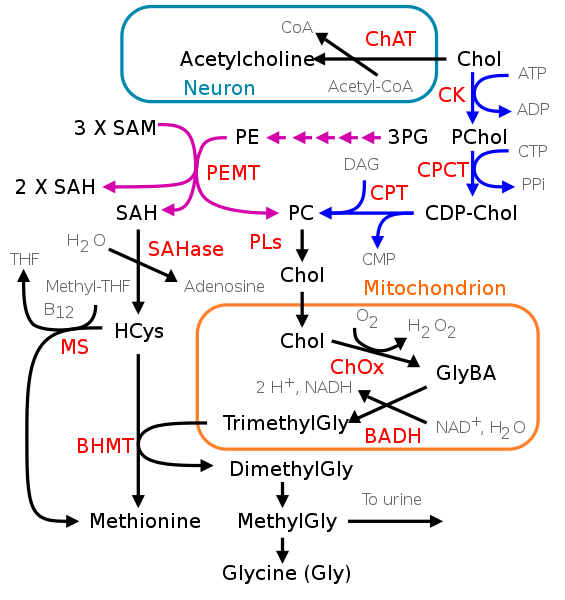
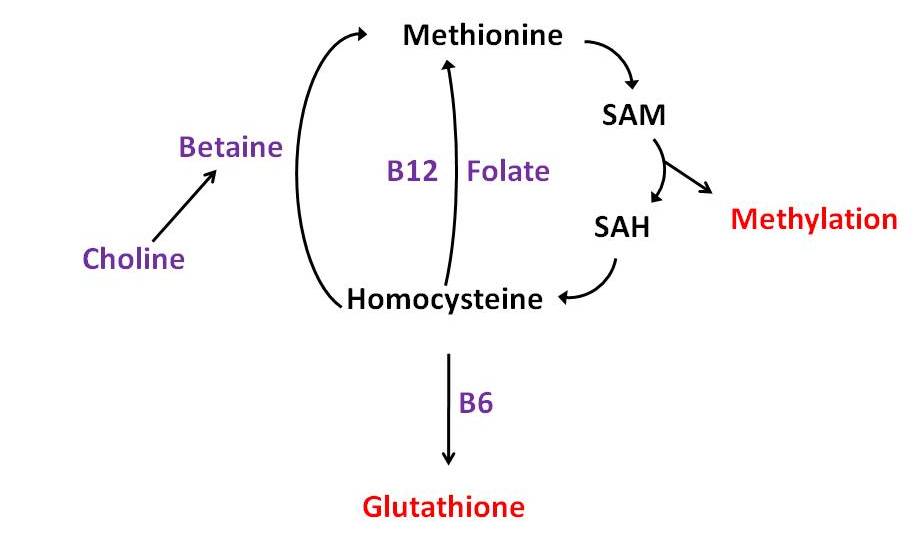
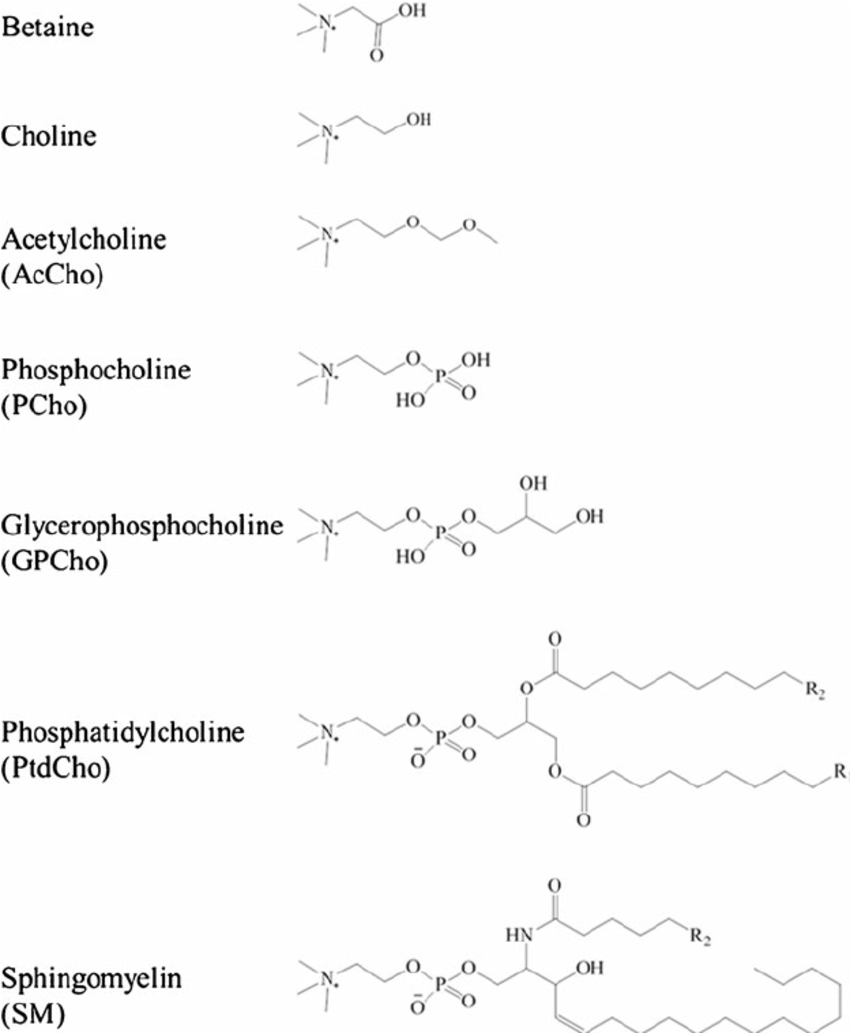
(Phospho)Lipids #
-
The biosynthesis of choline and its relation to phospholipid metabolism
- Rats synthesized it from Serine and Methionine.
- “On the basis of these results it is concluded that Phosphatidylserine is decarboxylated to phosphatidylaminoethanol and that the latter compound is methylated to form Lecithin. In this reaction all the methyl groups of choline are incorporated by transmethylation from SAM-e.”
-
- Choline and Trimethylglycine caused Glycerol accumulation and reduced Sarcosine, Taurine, acetate, and β-hydroxybutyrate levels.
-
Amazoniac - Incomprehensive/ble Notes On Choline
- “Choline has much to do with the oxidation of fats. It prevents the conversion of amino acids and of sugars to fats under the influence of cholesterol… when the rest of the oxidation mechanism is normal. The restoration of a vigorous oxidation catalysis removes the offending substance, no matter what its origin may be, and thus establishes the basis for recovery.”
- Lipid accumulation within hepatocytes begins within hours after rats are started on a choline-deficient diet, peaks within the first 6 months, and then diminishes as liver becomes fibrotic. Choline deficiency also sensitizes to hepatic and breast carcinogens.
- Choline deficiency results in liver dysfunction owing to massive accumulation of triacylglycerol within the hepatocyte. Undermethylation of DNA, observed during choline deficiency (despite adequate dietary methionine), may be responsible for carcinogenesis. When rats eat a choline-deficient diet, increased Lipid Peroxidation occurs within liver.
- A lipotropic effect of manganese on the rat liver was reported. Manganese as well as choline prevented deposition of excess fat in the livers of manganese-deficient rats than in the livers of rats receiving adequate manganese. When level of choline in the diet was low, the lipotropic action of manganese was greater, indicating a manganese-choline interaction. Rats placed on a choline-deficient diet for 25 days exhibited lower hepatic manganese levels (and vice versa) than those of controls.
- Has some kind of direct interactoin with Vitamin A content in the liver.
Physiology #
Made primarily in the liver via phosphatidylethanolamine methylation.
-
https://chrismasterjohnphd.com/blog/2010/12/04/meeting-choline-requirement-eggs-organs/
-
The Sweet Truth About Liver and Egg Yolks — Choline Matters More to Fatty Liver Than Sugar, Alcohol, or Fat
- Lab rats are choline deficient. It is capable of completely protecting lab rats against NAFLD induced by sugar+fat+alcohol.
- So, pregnant rats fed 3x their normal amount had their progeny see a lifelong 30% increase in visuospatial and auditory memory.
-
Effect of different dietary fats on choline requirement of rats (1957)
- Saturated fats require more choline than PUFAs to prevent liver steatosis.
- This is rather remarkable, because much lower concentrations of sucrose started spontaneously producing fatty liver disease in lab rats in the late 1970s and early 1980s once the American Institute of Nutrition set standards for purified rodent diets that relied exclusively on isolated vitamins and minerals rather than whole-food supplements like cod liver oil, yeast, and wheat germ.
- Lab rats are choline deficient. It is capable of completely protecting lab rats against NAFLD induced by sugar+fat+alcohol.
-
The Sweet Truth About Liver and Egg Yolks — Choline Matters More to Fatty Liver Than Sugar, Alcohol, or Fat
-
Choline Redistribution during Adaptation to Choline Deprivation
- Deprivation is achieved by feeding PEMT-/- mice a choline-deficient diet. Lethal due to liver failure. Apparently lacking MDR2 (multiple drug-resistant protein 2) allows hepatic choline recycling!
- The mice lacking PEMT still initiated choline redistribution.
- Normal levels of choline-containing metabolites were maintained in the brains of choline-deficient Mdr2–/–/Pemt–/– mice for 90 days despite continued choline consumption via oxidation. Choline oxidase activity had not been previously detected in the brain. Plasma levels of choline were also maintained for 90 days, whereas plasma phosphatidylcholine levels decreased by >60%.
- Deprivation is achieved by feeding PEMT-/- mice a choline-deficient diet. Lethal due to liver failure. Apparently lacking MDR2 (multiple drug-resistant protein 2) allows hepatic choline recycling!
Supplementation #
It’s complicated.
- PC increases choline stores and is ~13%.
- Alpha-GPC is more for enhancing its release in the brain and is 40% by weight.
- ‘Lecithin’ is 10-20% PC, thus like 1-2% choline.
- Phosphatidylcholine = 15%?.
- Citicoline is ~18.5% by weight.
- Betaine is worth something like 25% its does in choline?
- CMJ recommends to have it be <=50% of choline intake if you choose to supplement with it.
- I think supplementation-induced depression is possibly from excessive methylation via conversion into Trimethylglycine and onwards to DMG -> sarcosine. Longecity. Another explanation is maybe overencoding of negative experience due to excessive brain ACh R
- Water-soluble choline bompounds (PChol/GPC) can enter the portal circulation of the liver intact. Lipid-soluble (PC/SPM (sphingomyelin) are either hyrdrolysed by phospholipases or enter the lymph incorporated into chylomicrons. R
-
Differential metabolism of choline supplements in adult volunteers
- 740mg chloride; 1336mg bitartate, (549mg) 1358 Alpha-GPC (~543), or 4018mg egg-PC (PC=13%=522mg). One must wonder what is the difference is between phosphatidylcholine and ‘Egg-PC’?
-
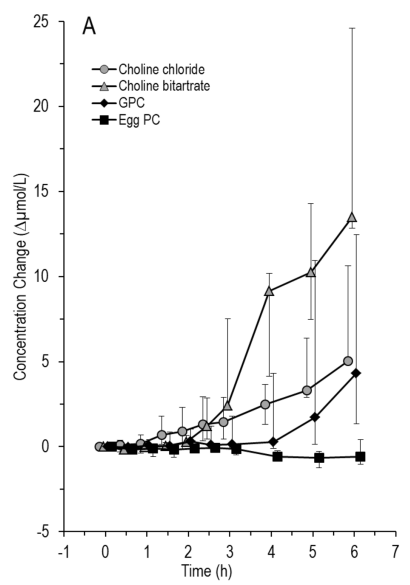
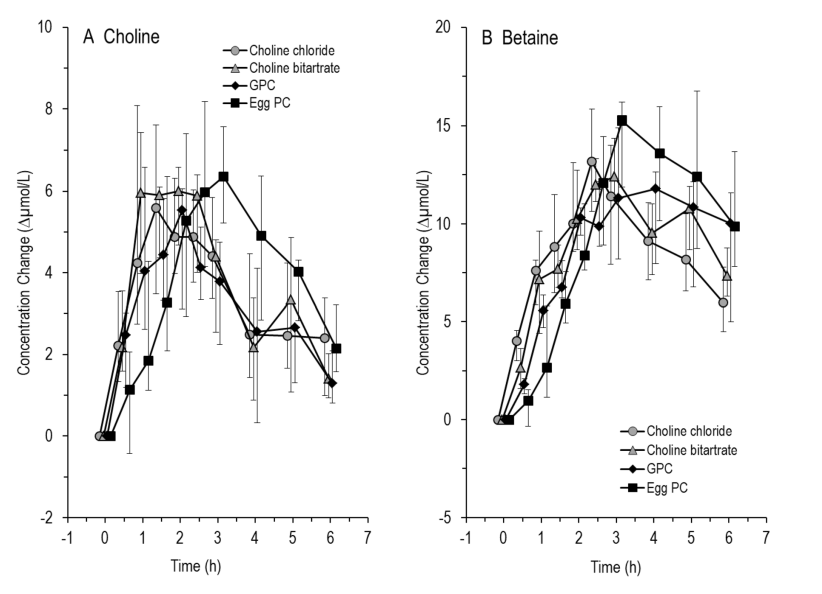
- I’d like to see brain, not just serum levels. Not sure
-
- 740mg chloride; 1336mg bitartate, (549mg) 1358 Alpha-GPC (~543), or 4018mg egg-PC (PC=13%=522mg). One must wonder what is the difference is between phosphatidylcholine and ‘Egg-PC’?
Requirements #
- I think promoting Acetylcholinesterase would be a good way of raising pysiological choline without depression in the brain.
Masterjohn #
-
CMJ - Meeting the Choline Requirement — Eggs, Organs, and the Wheat Paradox
- Bear in mind only methionine can actually be used to make choline, while B6/8/12 and TMG merely spare it.
- PEMT ctually creates homocysteine in the process of creating choline! So, if your PEMT is running smoothly, you can make your own choline, but you still need more betaine and B vitamins to neutralize the homocysteine that’s generated in the process. If your PEMT engine is working like this, however… well, then, you’ve got another problem: If PEMT isn’t using up your methionine to make choline, the methionine is just going to go further on down that pathway shown above and make more homocysteine anyway! Thus, although having a PEMT gene that Uncle Buck would surely envy might lower our choline requirement, consuming lots of methionine won’t help us at all. In fact, extra methionine just gives us more homocysteine and thereby increases our need for choline, betaine, folate, B12, and B6.
- Chris Masterjohn calculator says I need 1124 mg Choline daily. WTF!
- The calculator uses SNPs in the folate transporter (SLC19a1, rs1051266, G80A), the enzyme that helps make the precursor to methylfolate (MTHFD1, rs2236225, G1958A), and the enzyme that helps make methylfolate itself (MTHFR, rs1801131, A1298C and rs1801133, C677T) to develop a “methylfolate score.” This is used to calculate how much choline you should aim for.
- It then uses a polymorphism in the enzyme that helps make phosphatidylcholine, a specific form of choline that protects against fatty liver disease, promotes gall bladder health, and facilitates healthy digestion of dietary fats and absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (PEMT, rs7946, 5465G>A). This is used to tell you the likelihood that missing your choline requirement will hurt these functions in your body.
- So: $\ce{\text{THF}->[\text{SLC19A1}]\text{5,10-MTHF}->[MTHFR]\text{5-MTHF}}$
| RS# | Gene | Result | Call | Variant Allele | Variation | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1051266 | SLC19A1 | +/- | TC | T | - | |
| rs2236225 | MTHFD1 | -/- | GG | A | G1958A | |
| rs1801131 | MTHFR | -/- | TT | G | A1298C | |
| rs1801133 | MTHFR | +/+ | AA | A | C677T | -75% |
| rs7946 | PEMT | +/+ | TT | T | 5465G>A |
- SLC19A1 (folate transporter 1) activity = -25%.
- MTHFD1 score: -0%.
- MTHFR score: -75% decrease (in Methylfolate production) = double choline requirement.
- rs1801133 = idek I must be retarded since SNPedia C->T. Maybe that’s equivalent to A;A? And 1131 = A;A->C;C meanwhile I’m T;T->G;G like lolwut? Are the bases reversed?
- CMJ says it’s highly likely this decrease in activity is due to decreasing Riboflavin binding (such that the daily intake approaches 3mg).
- Optimizing magnesium helps retain riboflavin or use it efficiently or something.
- CMJ says it’s highly likely this decrease in activity is due to decreasing Riboflavin binding (such that the daily intake approaches 3mg).
- rs1801133 = idek I must be retarded since SNPedia C->T. Maybe that’s equivalent to A;A? And 1131 = A;A->C;C meanwhile I’m T;T->G;G like lolwut? Are the bases reversed?
- PEMT’s rs7946: Associated with NAFLD, lowering PC production and slowing fat export from the liver. Not related to requirements per se but does exacerbate deficiency.
- “If you’ve got a defective PEMT gene like i have, you can’t convert the choline into the phospkhatidylcholine that you need to reverse fatty liver. Just as a test, try taking a capsule of phosphatidylcholine. Five minutes after ive taken it my stomach shrinks from bloated to completely flat.” RPF
- There are other SNPs just like it though.: https://www.snpedia.com/index.php/PEMT In total, this amounts to 81% decrease in methylfolate.
So like, if I get 400mg/day from diet andor + citicoline, I’ll add a few hundred mg of betaine and a few hundred mg of PC to get to at least 1g.