Acetylcholine
links: Neurotransmitter reference: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MJECqcYJhmo (epic channel)
- https://web.archive.org/web/20140627061754/http://blog.naturalstacks.com/assembling-acetylcholine-puzzle-part-1/
- The role of acetylcholine in negative encoding bias: Too much of a good thing? 4-16-2021
Acetylcholine #
We know more about this than any other neurotransmitter, and was the first to be discovered.
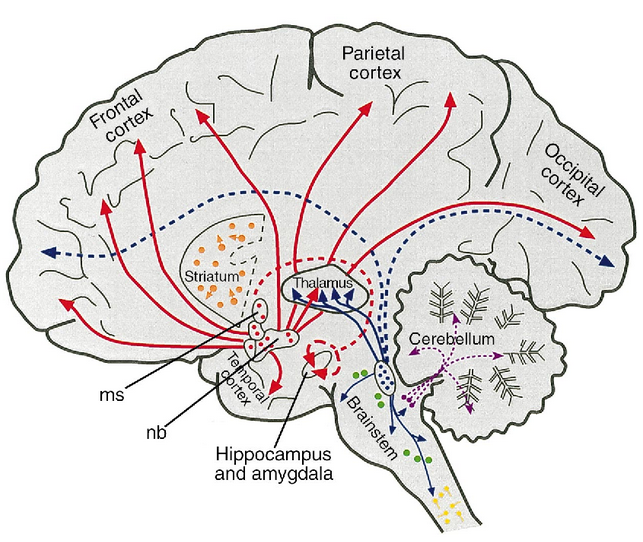
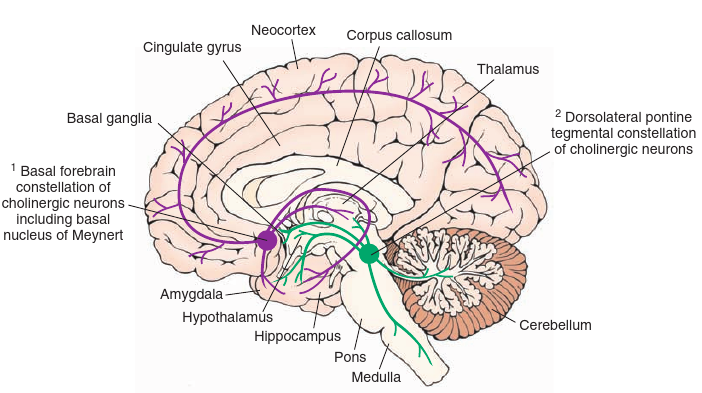
- All PNS motor neurons release it besides post-ganglionic sympathetic, aside from sweat glands: all somatic motor neurons, all parasympathetic neurons (pre- and post-anglionic) and all pre-ganglionic sympathetic neurons (besides sweat glands).
- Not to do with the basal ganglia. PreGanglionic: Originates in brainstem/spainal cord; postganglionic lies outside the CNS.
Transmission #
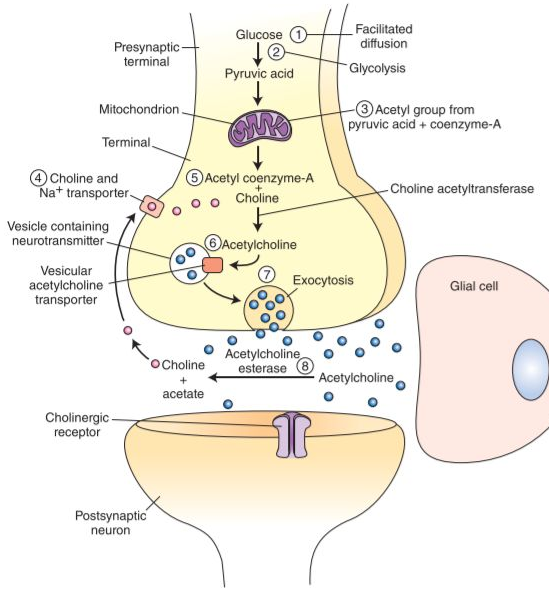
- In the terminal membrane, choline transporters (ChT) bring Ch from extracellular space into the cytoplasm.
- Then ACh is synthesized from Acetyl-CoA + Choline via choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) (of which there is plenty). It is brought back into the cytoplasm by the same enzyme.
- It is degraded by acetylcholine esterase in the snaptic cleft, breaking it down to choline and acetate.
-
Acetylcholine in mind: a neurotransmitter correlate of consciousness?
-
Interactions #
- Excess can cause hyperfocused rumination, while too little can contribute to ADHD.
-
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5vNhePt8tWc
- Immune-derived ACh is necessary for T cells to migrate to infected cells.
- Alzheimer’s, parkinson’s, and patients have low acetylcholine levels. Delirium can be caused by dopamine excess relative to ACh.
- Excess ACh compared to other neurotransmitters can lead to anxiety, hypervigilance, fear learning, increasing CB1 receptors.
- Second to Glutamate as the most abundant excitatory NT.
- Increases body temperature, pressure, flushing, and increases release of Stomach Acid.
- In clinical situations:
- AChE inhibitors (Acetylcholine esterase (AchE) breaks down ACh) and mAChR (Muscarinic; even induced depression) agonists worsened depression. Implying ACh is elevated in depression.
- AchE also reduced mania and depression and AchR agonists reduced mania and worsened Depression in bipolar.
- Antimuscarinics are antidepressant.
- Proliferation and apoptosis of cancer cells are mediated by overexpression of AChRs in different kinds of tumors
- Enhances aggression when in excess
- Insulin opposes acetylcholine.
- Serotonin inhibits ACh release from striatal cholinergic neurons by acting on a presynaptic receptor localized on cholinergic terminals.
- SSRIs reduce ACh activity in certain areas of the brain
- GABA is reduced as ACh increases.
- Endocannabinoids work with Acetylcholine Receptor in emotional learning/memory.
- Cortisol is stimulated by ACh.
- ACh may increase T4 and T3 may inhibit ACh.
- Antagonizes Testosterone
- DHEA increases release, but reduces AChR activity.
- Progesterone reduces Acetylcholine Receptor permeability.
- Estrogen increases ACh levels.
- Dopamine is increased when Acetylcholine Receptors are activated.
https://men-elite.com/2020/06/26/the-high-acetylcholine-syndrome/ - ==Inhibits tonic Dopamine, but promotes phasic bursts.== Meaning overall levels will be low, but there will be larger bursts when it is released. - "nAChR α3, α6 and β3 subunits are enriched in midbrain nuclei associated with behavioral reinforcement. Blocking mAChR have anti-addictive properties." - ACh improves attention, and therefore learning and memory, but in the absence of cholinergic neuronal loss, stimulation of ACh signaling can impair memory. - Increased levels of ACh in the brain during depressive episodes and increased symptoms of anxiety, depression, and reactivity to stress when ACh breakdown is impaired. Overly high levels of cholinergic signaling promote encoding of stressful events, leading to the negative encoding bias that is a core symptom of Depression. R - ACh slows pulse. - Increases aldosterone and vasopressin, therefore increasing blood pressure. - Reduces thirst by inhibiting parasympathetic activity. - Increases cortisol and prolactin release. - Can cause illusory sensations
Increasing #
-
https://men-elite.com/2020/06/26/the-high-acetylcholine-syndrome/
- High CO2/ATP increase the release of ACh.
- Vitamins A and K decreased synthesis in low and increasing concentrations.
- Vitamin D decreases ACh synthesis in high doses.
- Vitamin D’s active form increases ACh synthesis.
- B1 slightly increases ACh synthesis in low concentrations, and decreases it in higher ones.
- B1 deficiency results in reduced activity of ChAT.
- Trimethylglycine, Folate and B12 spare choline through the methylation cycle.
- Vitamin E increases synthesis