A2A
2022-01-25 links: Adenosine Receptor reference:
- Modulation of adenosine A2A receptor function by interacting proteins. New targets for Huntington’s disease (2012) - a 133-page dissertation.
Adenosine A2A #
- Gs-protein coupled. As opposed to Adenosine A1, it is found in sleep-promoting neurons. It antagonizes the Histaminergic system.
- Agonize with D-Limonene
-
An adenosine A2a agonist increases sleep and induces Fos in ventrolateral preoptic neurons
- A2A antagonist blocks the sleep induced by PGD2 (which activates sleep-promoting neurons in ventrolateral preoptic area)
- Adenosine A2A receptors enhance GABA transport into nerve terminals by restraining PKC inhibition of GAT-1
- Differential effects of presynaptic versus postsynaptic adenosine A2A receptor blockade on Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) self-administration in squirrel monkeys
-
Accumbal adenosine A2A receptor inactivation biases for large and costly rewards in the effort- but not delay-based decision making
- “Go big or go home” mindset?
- Nucleus Accumbens is important for cost-benefit decision making.
-
Striatopallidal adenosine A2A receptor modulation of goal-directed behavior: Homeostatic control with cognitive flexibility
- Striatum projects MSNs to the globus pallidus.
- Striatopallidal A2AR exert an overall “break” control of a variety of cognitive processes. - antagonism enhances goal-directed behavior and cognitive flexibility.
-
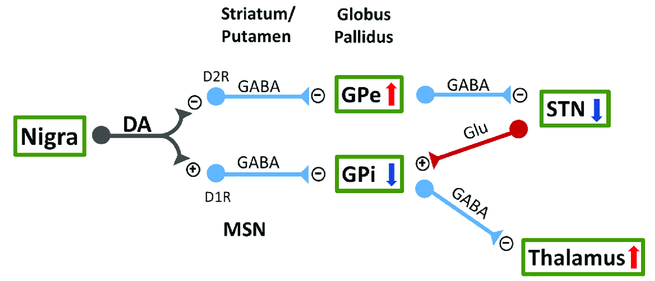
- A2AR indirectly increases GABA via dopamine/D2 activation or via increasing Glutamate release
Effect of adenosine A2A receptor stimulation on GABA release from the striatum of young and aged rats in vivo
- In contrast, A2AR antagonists inhibit Glutamate release: Modulation of glutamate release and excitotoxicity by adenosine A2A receptors.
- Adenosine A2A Receptor Antagonists Affects NMDA Glutamate Receptor Function. Potential to Address Neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s Disease
-
Adenosine A2A receptors in neuronal outgrowth a target for nerve regeneration?
- Neurite outgrowth depends on the receptor repertoire present at each moment: A2A activation promotes TrkB-induced dendritic branching, and PI3k/MAPK/PLC-induced axonal elongation!
-
An Adenosine A2A Receptor Antagonist Improves Multiple Symptoms of Repeated Quinpirole-Induced Psychosis
- Quinpirole: D2 and D3 agonist. Induces OCD-like behaviors. May have CB1 effects as well.
- Increases during aging, it seems:
-
Age-related shift in LTD is dependent on neuronal adenosine A2A receptors interplay with mGluR5 and NMDA receptors
-
Targeted neurogenesis pathway-based gene analysis identifies ADORA2A associated with hippocampal volume in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease
- rs9608282 (no data for me): larger hippocampal volume (synaptic loss???). Upstream in the coding sequence, merely implying it could alter A2AR expression.
- There is compelling evidence from animal models of a cortical and hippocampal upsurge of A2AR in glutamatergic synapses upon aging and AD (then proceeds to give 7 references)
- A2A -> PKA/cAMP/CREB -> glutamate release & Ca2+ influx -> and then… hippocampus-dependent cognitive deficits?
-
The caffeine-binding adenosine A2A receptor induces age-like HPA-axis dysfunction by targeting glucocorticoid receptor function
- A2AR overexpression -> loss of plasmatic corticosterone circvadian oscillation, and reduction of Glucocorticoid receptor levels in the hippocampus.
-
The caffeine-binding adenosine A2A receptor induces age-like HPA-axis dysfunction by targeting glucocorticoid receptor function
-
Targeted neurogenesis pathway-based gene analysis identifies ADORA2A associated with hippocampal volume in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease
-
Age-related shift in LTD is dependent on neuronal adenosine A2A receptors interplay with mGluR5 and NMDA receptors
-
Adenosine A2A Receptors Control Glutamatergic Synaptic Plasticity in Fast Spiking Interneurons of the Prefrontal Cortex
- A2AR are enriched at mPFC (layer V) synapses.
- At the network level, extracellularly induced LTP of population spikes was reduced by A2AR blockade. The interneuron-specificity of A2AR in controlling glutamatergic synapse LTP may ensure that during periods of high synaptic activity, a proper excitation/inhibition balance is maintained within the mPFC.
-
Impact of in vivo chronic blockade of adenosine A2A receptors on the BDNF-mediated facilitation of LTP
- Most of BDNF synaptic actions, namely on LTP, require activation of A2A.
- … how? For one thing, is TrkB even expressed outside the basal ganglia? Or, why would synaptic effects of BDNF rely on adenosinergic efferents?
- results showed that chronic blockade of A2AR in male Wistar rats inhibits the facilitatory action of BDNF upon LTP on hippocampal CA1 area and decreases both mRNA and protein levels of the TrkB-FL receptor in hippocampus
- Most of BDNF synaptic actions, namely on LTP, require activation of A2A.
Inflammation #
- Downregulates M1 Macrophage phenotype.
- Cutting edge: Physiologic attenuation of proinflammatory transcription by the Gs protein-coupled A2A adenosine receptor in vivo
- A2A-deficient mice: enhanced NF-κB activity
-
A2A adenosine receptor stimulation ameliorated diabetic-induced osteoporosis in rats
- Agonist increased: serum insulin level, glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activity, bone expression of osteoprotegerin (Opg) and β-catenin (Ctnnb1), and cortical and trabecular bone thickness,
- Agonist decreased: serum fasting glucose, malondialdehyde (MDA), TNF-α bone expression of RANKL, runt-related transcription factor-2 (Runx2), and sclerostin (Sost)
Heteromers #
- G protein-coupled receptor heteromers are key players in substance use disorder.
- A2A homodimers as well.
- There A2A-D1 heterodimers along with A2A-D2 R I guess - A2A-D2 Heteromers on Striatal Astrocytes: Biochemical and Biophysical Evidence
- A2A-CD73: Makes sense. Synergistic of course.
-
Ecto-5’-nucleotidase (CD73)-mediated formation of adenosine is critical for the striatal adenosine A2A receptor functions
- Confirmed with proximity ligation assays
- Moreover, CD73 KO mice displayed increased working memory performance and a blunted amphetamine-induced sensitization, mimicking the phenotype of global or forebrain-A2AR KO mice, as well as upon pharmacological A2AR blockade.
-
Ecto-5’-nucleotidase (CD73)-mediated formation of adenosine is critical for the striatal adenosine A2A receptor functions
- A2A-mGluR5: synergistic.
- A2A-D3: adenosine antagonizes affinity and signaling of D3.
- A2A-oxytocin! Heterodimer of A2A and Oxytocin Receptors Regulating Glutamate Release in Adult Striatal Astrocytes
CB1 #
-
A2A-D2-CB1 trimers as well.
-
A2A-CB1 and A2A-CB2. They are antagonistic; A2A antagonism increases CB2 signaling.
-
- Essentially absent from corticostriatal projections and striatonigral neurons, and, instead, is largely present in striatopallidal neurons
- Co-stimulation of both receptors leads to strongly reduced downstream signaling (I mean why does it have any magnitude?)
- DMR: dynamic mass redistribution - essentially a means to measure GPCR activation from light by a biosensor
- Label-free is a benefit
- Possibly facilitates Gαq signaling - just like D21?
- Gq inhibition abrogate A2A and CB1 evoked changes in DMR.
- Experiments with disrupting peptides on certain amino acids turned the heteromer into their respective classical signaling pathways.
- Lots of stuff on Huntington’s disease and how expression changes. For instance, functional A2A-CB1 heteromers are expressed in Huntington’s disease in advanced but not late disease stages.
-
- Cocaine+A2A antagonism synergizes in reducing the firing rate of cholinergic interneurons: MSN M1 AChR inhibition -> disinhibition of of Cav1.3, triggering postsynaptic Endocannabinoid release and a reduction of glutamatergic transmission via activating presynaptic CB1:
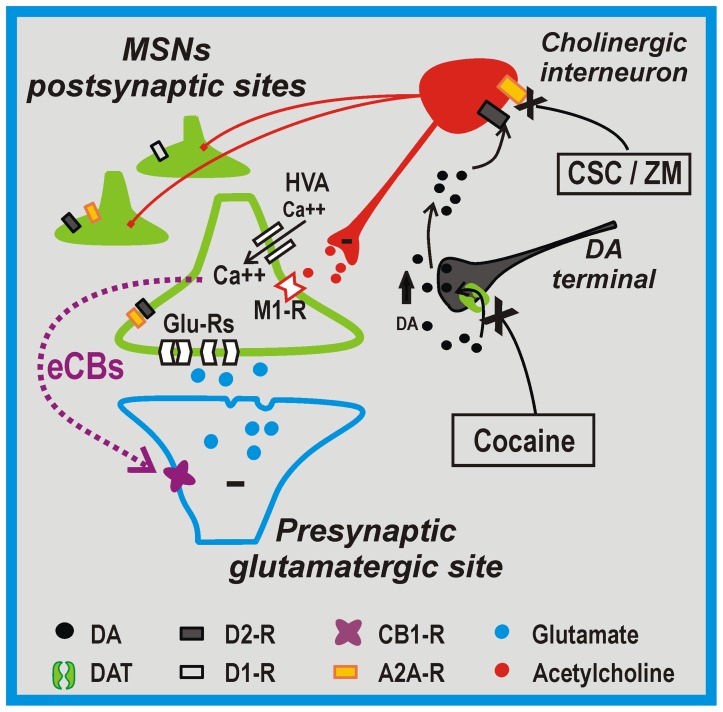
- Indeed: in the presence of pirenzepine, a M1 receptor inhibitor, the electrophysiological effects of cocaine plus A2AR antagonists modulation on glutamatergic transmission were fully occluded.
- Ironic how it’s dependent on Cav1.3 channels. Maybe it comes down to localization? It’s conflicting with the study they cite; it should follow that M1 inhibition would reduce VGCC activity.
- Cites:
Dopaminergic control of corticostriatal long-term synaptic depression in medium spiny neurons is mediated by cholinergic interneurons (2006)
- Induction of LTD: dependent on D2 on the postsynaptic membrane.
- These aspiny cholinergic Interneurons are autonomous pacemakers, leading to tonic ACh, thus tonic activation of striatal mAChR.
- Lowering M1 AChR tone promotes LTD induction by disinhibiting critical intraspine Cav1.3 Ca2+ channels.
- Previously: [The distinct role of medium spiny neurons and cholinergic interneurons in the D2/A2A receptor interaction in the striatum: implications for Parkinson’s disease]
- VTA CB1 can increase dopamine firing rate: Independent presynaptic and postsynaptic mechanisms regulate endocannabinoid signaling at multiple synapses in the ventral tegmental area
- Wtf at this point? Phasic dopamine release evoked by abused substances requires cannabinoid receptor activation
- Indeed: in the presence of pirenzepine, a M1 receptor inhibitor, the electrophysiological effects of cocaine plus A2AR antagonists modulation on glutamatergic transmission were fully occluded.
- Cocaine+A2A antagonism synergizes in reducing the firing rate of cholinergic interneurons: MSN M1 AChR inhibition -> disinhibition of of Cav1.3, triggering postsynaptic Endocannabinoid release and a reduction of glutamatergic transmission via activating presynaptic CB1:
-
Endocannabinoid signaling mediates psychomotor activation by adenosine A2A antagonists
- eCB-mediated inhibition of indirect MSN increases movement. The theory is classical that direct MSN activation is pro-locomotion and iMSN = inhibiting movement.
-
Adenosine–cannabinoid receptor interactions. Implications for striatal function (2010)
-
Potentiation of cannabinoid signaling in microglia by adenosine A2A receptor antagonists
- Microglial A2A and CB2 (heteromers also) are upregulated in AD
- Blockade of A2ARi reduces amyloid burden and improves cognition in AD.
-
A1 adenosine receptors accumulate in neurodegenerative structures in Alzheimer disease and mediate both amyloid precursor protein processing and tau phosphorylation and translocation (2003)
- High degree of colocalization for A1R and betaA4 amyloid in senile plaques and for A1R and tau in neurons with tau deposition, but without tangles, was seen.
- A1->PKC->sAPP, A1->p21 & ERK->p->Tau.
- adenosine A2A receptors, located mainly in striatal neurons in controls, appeared in glial cells in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex of patients
- Indeed, idk if it’s usually expressed there:
Adenosine A2 receptors: selective localization in the human basal ganglia and alterations with disease (1992)
- Exclusively restricted to the Basal Ganglia, specifically: caudate nucleus, putamen, nucleus accumbens, olfactory tubercle and the lateral segment of the globus pallidus.
- Not exactly, since it exists peripherally?
Novel Players in the Aging Synapse: Impact on Cognition: A2A are particularly expressed in the lungs, spleen, thymus, heart, blood vessels, muscle, and brain… whereas in the neocortex and hippocampus, they are present at residual levels.
- Plus this might be with AD patients anyways? Would need to check reference
- Not exactly, since it exists peripherally?
Novel Players in the Aging Synapse: Impact on Cognition: A2A are particularly expressed in the lungs, spleen, thymus, heart, blood vessels, muscle, and brain… whereas in the neocortex and hippocampus, they are present at residual levels.
- Parkinson’s: density of adenosine A2 binding sites was comparable to that seen in control cases.
- Huntington’s chorea: Denstiy was dramatically decreased
- Exclusively restricted to the Basal Ganglia, specifically: caudate nucleus, putamen, nucleus accumbens, olfactory tubercle and the lateral segment of the globus pallidus.
- Indeed, idk if it’s usually expressed there:
Adenosine A2 receptors: selective localization in the human basal ganglia and alterations with disease (1992)
-
A1 adenosine receptors accumulate in neurodegenerative structures in Alzheimer disease and mediate both amyloid precursor protein processing and tau phosphorylation and translocation (2003)
-
- Presynaptic: SCH-442416; Postsynaptic: KW-6002.
- SCH antagonized while KW-6002 potentiated reinforcing effects of THC!
- Previously:
Reinforcing and neurochemical effects of cannabinoid CB1 receptor agonists, but not cocaine, are altered by an adenosine A2A receptor antagonist (2011)
- Antagonist caused downward shifts of THC and anandamide dose-response curves (i.e. a decrease in effectiveness)
- MSX-3 neither promoted reinstatement of extinguished drug-seeking behavior nor altered reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior by non-contingent priming injections of THC.
- Presynaptic: SCH-442416; Postsynaptic: KW-6002.
BDNF #
- Transactivated with Trk Receptors.
- Adenosine A2A receptor activation is determinant for BDNF actions upon GABA and glutamate release from rat hippocampal synaptosomes
-
Regulation of TrkB receptor translocation to lipid rafts by adenosine A2A receptors and its functional implications for BDNF-induced regulation of synaptic plasticity
- A2A agonists increased the levels of TrkB receptors in the lipid raft fraction of cortical membranes and potentiated BDNF-induced augmentation of phosphorylated TrkB levels in lipid rafts… Lipid raft integrity was also required for the effects of BDNF on hippocampal long-term potentiation at CA1 synapses.
- Mimicked by Forskolin and blocked by PKA inhibitors… removal of endogenous adenosine or disruption of lipid rafts reduced BDNF stimulatory effects on glutamate release from cortical synaptosomes.
- Activation of adenosine A2A receptors induces TrkB translocation and increases BDNF-mediated phospho-TrkB localization in lipid raft: implications for neuromodulation
- Adenosine A2a receptors modulate TrkB receptor-dependent respiratory plasticity in neonatal rats