D21
2022-05-02: reference:
- The neurobiology of dopamine receptors: evolution from the dual concept to heterodimer complexes
- D1-D2 Receptor Heteromer as a Master Regulator for Anhedonic Depression and Addiction..pdf
- Dopamine D1-D2 receptor heteromer signaling pathway in the brain: emerging physiological relevance
D21 #
- JC takes it in eyedrop form, with his helios eyedrops for added penetration from CNC, or at least a surfextan, or else it’ll just drain into nasal passages, and says it hits super hard. Like 10x his original review. Almost jaw clenching level of dopamine, euthymic mood, dominance, smooth movement, thought acceleration, enhanced sociability, musical appreciation, and even made some breakthroughs in the gym. Also very noticeably improved visual acuity. Reality looks crispy af.
- 1mg $40. Dose is 130-250mcg. Take about every 8 days because that’s how long some kinda interaction/formtion takes place or somthing but it’s not that big a deal. AKA tat-d1.
-
 this says it all, basically.
this says it all, basically. - The heteromer flips the relationship between dopamine concentration and which receptor gets stimulated: D1 gets active in low concentrations and D2 in high cincentrations, contrary to norm. Though I’ve also heard that it essentially just nullifies dopaminergic signaling, and that splitting the dimer essentially ‘differentiates’ D1 and D2 and allows much more flexible LTP and LTD that is seen in adolescence; D21 increases with age.
- D21 is much more prevalent (~250% d21/d1 ratio compared to control) in those with Depression. Naturally then, the peptide has standard antidepressant effects. Induces calcium release by being Gq-coupled somehow.
R. Many studies will measure D1 or D2 individually, and they do no such thing. Only co-expressive cells.
- Probably driven by D1: certain in vitro thingies resulted in PIP turnover. Possibly from high concentrations activating another receptor. R
-
Differential receptor crosstalk in DRD1-DRD2 heterodimer upon phasic and tonic dopamine signals (May 2021) &
Visualization of differential GPCR crosstalk in DRD1-DRD2 heterodimer upon different dopamine levels (June 2022) looks like a refined version if biorxiv is for drafting or something
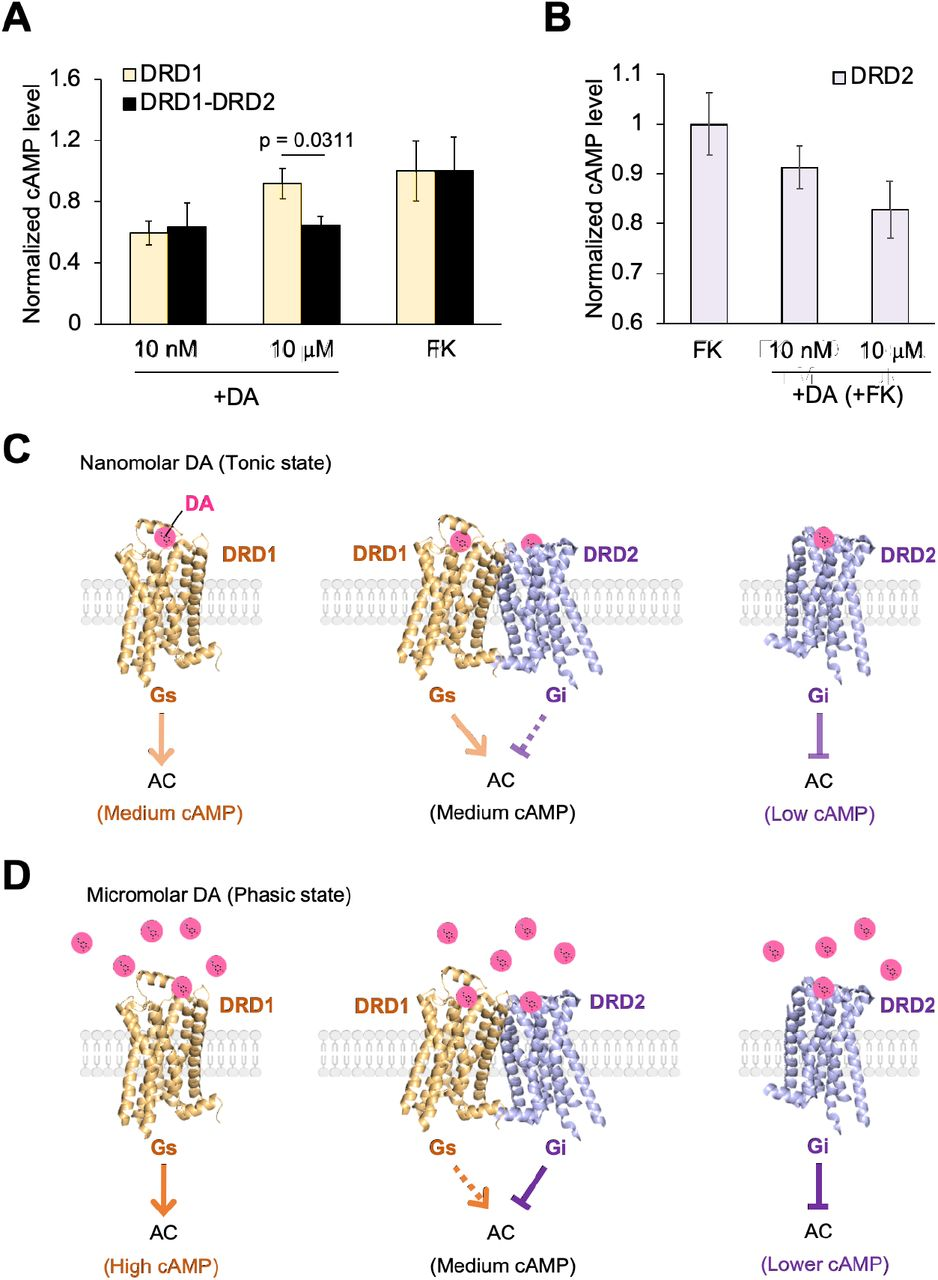
- High dopamine levels preferentially make the heteromer inhibit D1 signalling, whilst low dopamine levels make the heteromer inhibit D2 signalling:Upon treatment of 10 nM dopamine, D21 heterodimer induces a similar level of cAMP to D1 only (possibly because D2 activity in the heterodimer is inhibited at this nanomolar DA level) In contrast, at 10 µM dopamine, the cAMP level by D21 was significantly lower than the one by D1.
-
Intranasal Delivery of a Peptide with Antidepressant-Like Effect (Brown & Liu 2014)
- It doesn’t split the peptide or anything, or change protein levels, (idk, maybe Cogmetics’ does?) but simply prevents the interaction between D1 and D2 at the dimer.
- Lowered locomotor activity. Thus it is not a stimulant. However it is anti-immobility - they swam more. Yeah idfk.
- Elevates BDNF in the Prefrontal Cortex, and decreased levels are seen in major depressive disorder.
- However,
Dopamine D1-D2 receptor heteromer signaling pathway in the brain: emerging physiological relevance (Hasbi et al. 2011) suggests that D21 activation could result in transcription of BDNF in cultured neurons derived from the ventral striatum.
- There is “requisite” D1/D2 synergism for certain reward processes:
- However,
Dopamine D1-D2 receptor heteromer signaling pathway in the brain: emerging physiological relevance (Hasbi et al. 2011) suggests that D21 activation could result in transcription of BDNF in cultured neurons derived from the ventral striatum.
- There are also D1-D3 and D2-D5 heterodimers, as well as D1-NMDAR and D5-GABA-A heterodimers.
- Dopamine Negatively Regulates Insulin Secretion Through Activation of D1-D2 Receptor Heteromer
- Differential receptor crosstalk in DRD1-DRD2 heterodimer upon phasic and tonic dopamine signals
-
Dopamine D1-D2 receptor heteromer expression in key brain regions of rat and higher species: Upregulation in rat striatum after cocaine administration (Hasbi et al. 2020)
-
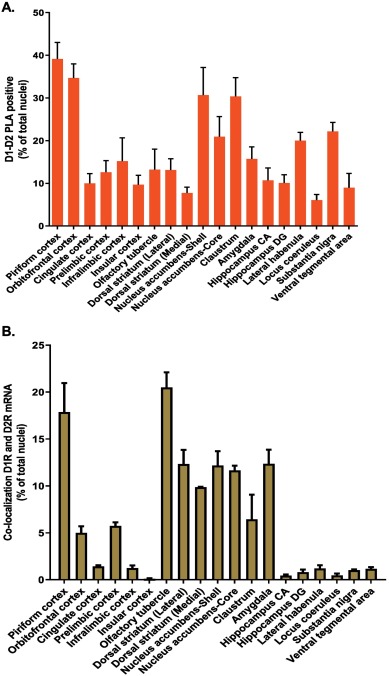 presence vs. mere mRNA. Other cool figures.
Bam says the Orbitofrontal Cortex is possibly receiving translocated d21, from areas where the difference in mRNA and presence is the inverse, such as the Olfactory Tubercle.
presence vs. mere mRNA. Other cool figures.
Bam says the Orbitofrontal Cortex is possibly receiving translocated d21, from areas where the difference in mRNA and presence is the inverse, such as the Olfactory Tubercle.
- I don’t know how common friggin’ translocation is. It kind of reminds me of ‘No Individual Particles’ honestly in that it might just be extra abstraction to imagine it that way but I think that’s neither here nor there
-
Calcium #
- Perhaps it’s been known well that D1 activates phospholipase C? D2 agonists potently enhance AA release, initiated by increasing intracellular Ca2+ or stimulating constitutive purinergic receptors - which trigger Ca2+. Naturally, all this stimulates phospholipase A2. R.
-
Calcium signaling cascade links dopamine D1-D2 receptor heteromer to striatal BDNF production and neuronal growth
- CAMK IIα increases BDNF expression.
- Rats have a lower prescence and importance of the heteromer in their brains than humans. The further up in intelligence you go across species, the more prevalent. It implies that the heteromer counteracts brain power/force in some way, and it does play the role of a negative dopamine regulator (it lowers dopamine transmission in general by lowering dopa release). In theory, society is like a Swiss army knife in making the d1/d2 heteromer appear. (wtf? lol stoner.)
-
Dopamine D1 and D2 Receptor Co-activation Generates a Novel Phospholipase C-mediated Calcium Signal (Lee et al. 2004)
- Coexpression barely changes adenylyl cyclase activity in these cells compared to D1 alone. PKA, PKC, or PI3K inhibition did not change calcium levels, but PLC inhibiton shut it down >90% (and blocked Gq-coupled P2Y receptors along the way).
- Gi/o is not directly involevd in the calcium signal. Gi and Gq crosstalk does not appear to underlie, since neither couple to Gq to begin with. Good reasoning?
- Virtually all Medium Spiny Neurons that express D1 also technically express D2.
- Coexpression did not affect the ligand binding pocket of either receptor.
- In the rat frontal cortex, interneurons only expressed D2, unlike pyramidal neurons.
- Heteromers of the CCR2 and CCR5 chemokine receptors and heteromers of the μ- and δ-opioid receptor may couple to G proteins distinct from those associated with homogeneous populations of their constituent receptors, but interestingly the cellular responses is not different from that of the individual receptors.
-
Dopamine receptor-mediated Ca(2+) signaling in striatal medium spiny neurons (Tang et al. 2004)
- ~40% MSN elicit robust repetitive Ca2+ oscillations following application of dopamine - PLC-dependent.
Cogmetics #
- This might be what he talked about as being theoretical (haven’t read it) in Hasbi et al. 2020, but indeed the heteromers are shuttled primarily to the orbitofrontal cortex after 8 days of cocaine administration. The decrease in extracellular calcium is neuroprotective.
- Working memory is impaired when D1 is prevented from binding to NMDAR. 2 hour half-life without the HA. It increases dopamine efflux and stops cocaine from working. In contrast, other papers show an increase in response from stimulants, making them more addictive!
- May be addictive (especially in those without a lot of the heteromer). Via FosB and other things. Will make other things very addictive, especially, of course, anything dopaminergic.
- Overdose would basically make behavior quite erratic. Again, childlike. One undiluted drop would make you hypomanic for days.
- D1 excites dendrites, and inhibits soma? This perhaps filters out distractions in working memory. He’s talking about the frontal cortex, at least.
- Maybe ion channel localization after depolarization
- It’s not even necessarily about the d21 cascade itself, but the fact you no longer have D1 and D2 available individually.
- Apparently this HA peptide actually dissolves D21.
- The peptide copies part of D1 that sticks to D2 in the heteromer; D2 is very sticky. It occupies the space next to D2, and both of them are unbound and liberated to act individually
- Effects of costimulation of dopamine D1- and D2-like receptors on renal function