Adenosine Receptor
links: reference: 8-25-2021
Adenosine Receptor #
A purinergic G protein-coupled Neuroreceptors.
- In an autocrine-like fashion, adenosine receptors can be found presynaptically, adjacent to nucleoside transporters. Theare are four types:
- Adenosine A1 (Gi)
- It would make sense if it were the case that A2A outnumbered A1 such that it takes until the end of the day for adenosine to bind to A1.
- A2A (Gs)
- A2B (Gs)
- The more obscure one, but nothing weird about it
- A3 (Gi)
-
Insulin/adenosine axis linked signalling pretty cool review. Focuses on muscle/vascular tone mostly
- Notice how A2 is Gs—thus they activate NOS (via p44/p42, and prostaglandin) I believe they can all be presynaptic. postsynaptic, or on astrocytes.
-
Different cellular sources and different roles of adenosine: A 1 receptor-mediated inhibition through astrocytic-driven volume transmission and synapse-restricted A2A receptor-mediated facilitation of plasticity
- Has paracrine/Astrocyte non-synaptic transmission whereby it imparts a quieting of synapses.
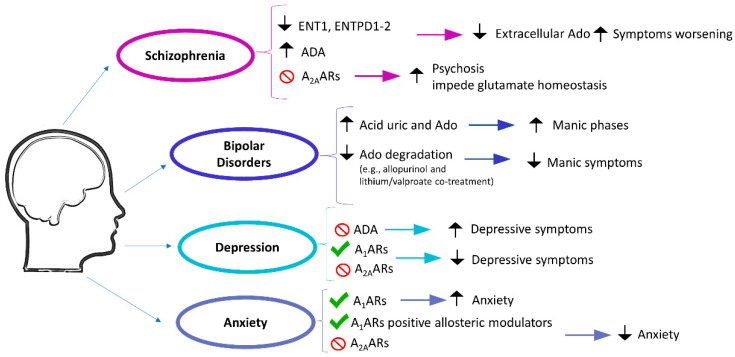
- [Adenosine Receptors in Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Fine Regulators of Neurotransmission and Potential Therapeutic Targets]
-