CB1
2021-11-18 links: Endocannabinoid reference:
Cannabinoid Receptor 1 #
Mostly Gi/o.
- Presynaptic CB1 on GABAeric neurons in the VTA, diminishes GABAergic inhibition, leading to increased dopamine release.
- The reason why stimulation doesn’t make you feel high is because there is not a basal cannabinoid tone; Endocannabinoid they are realeased phasically on demand.
- Both high and low activity impairs Memory.
-
Obesity risk is associated with altered cerebral glucose metabolism and decreased μ-opioid and CB1 receptor availability
- As opioidergic tone increases, μ-Opioid Receptor availability is reduced, potentiating Neuropeptide FF production.
- In morbidly obese subjects, increasing the plasma insulin concentration to supraphysiological levels results in acceleration of central glucose metabolism. Middle-aged subjects with peripheral insulin resistance have blunted glucose metabolism response to insulin also in brain, especially in appetite-controlling regions such as ventral striatum
- μ stimulates reward associated with food intake.
- Peripheral CB1 receptor blockade acts as a memory enhancer through a noradrenergic mechanism
-
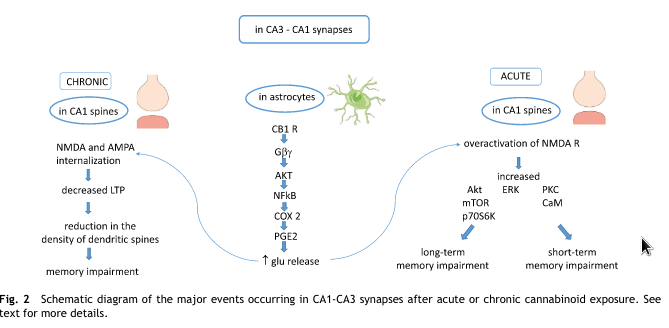
- CB1→βγ→AKT→NF-κB→COX-2→PGE2→Glutamate release→NMDA overactivation & downregulation→memory impairment.
- Acutely, glutamate release→mTOR might lead to memory impairment
5-HT2A #
- Forms heterodimers with 5-HT2A, changing it from Gq to Gi/o.