Lipid Raft
2022-08-28: reference:
Lipid Raft #
- An acyl chain = when -ic acid is replaced with -yl/-oyl or something. Their existence is apparently somewhat controversial.
- Consists of Glycosphingolipids
-
Lipid Rafts in the Maintenance of Synapses, Dendritic Spines, and Surface AMPA Receptor Stability
- we show that lipid rafts exist abundantly in dendrites of cultured hippocampal neurons, in which they are associated with several postsynaptic proteins including surface AMPA receptors. Depletion of cholesterol/sphingolipid leads to instability of surface AMPA receptors and gradual loss of synapses
- Caveolae are distinguished by the presence of caveolins. Planar lipid rafts protrude from the cell membraane and are characterized by the presence of flotillins, which attract and retain signaliung molecules into the lipid rafts.
- CNS Synaptogenesis Promoted by Glia-Derived Cholesterol
- we show that lipid rafts exist abundantly in dendrites of cultured hippocampal neurons, in which they are associated with several postsynaptic proteins including surface AMPA receptors. Depletion of cholesterol/sphingolipid leads to instability of surface AMPA receptors and gradual loss of synapses
-
Lipid raft microdomains and neurotransmitter signalling
- Two common types of lipid raft have been proposed and studied in neurotransmitter signalling: planar lipid rafts (also known as non-caveolar, or glycolipid, rafts) and caveolae
- Cytoskeletal elements such as microtubules or actin microfilaments, and the monomers or dimers that comprise them, associate with lipid rafts and might function to orchestrate neurotransmitter signalling.
- Caveolin is a palmitoylate polymer IMP
-
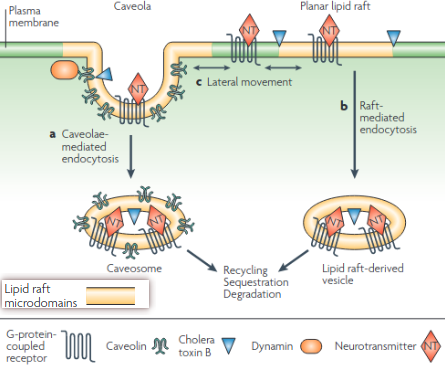
- They have similar lipid structures. The ’lipid raft signalling hypothesis’ proposes that these caveola microdomains form kinetically favorable interactions for protein complexes, or, perhaps inhibits them by separating. #Ankified
- For example, some things like α7 nAChR → Ca2+-mediated inhibition of VI Adenylyl Cyclase is dpendent on raft integrity.
- Related to NMDAR in lipid rafts mediating neurotoxicity, this claim being confounded on lipid rafts being required for calcium conductance.
- Cholesterol depletion/disruption of rafts reduces agonist binding of 5-HT1A. However, while κ-Opioid Receptor receptors are concentrated in lipid rafts, cholesterol dpletion increases maximal agonist binding, indicating that the actual G-protein occupies a different compartment (and that it was probably brought closer).
-
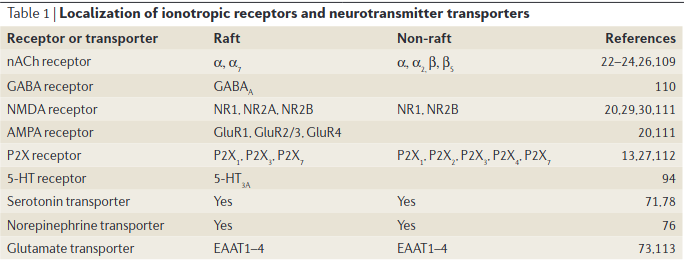
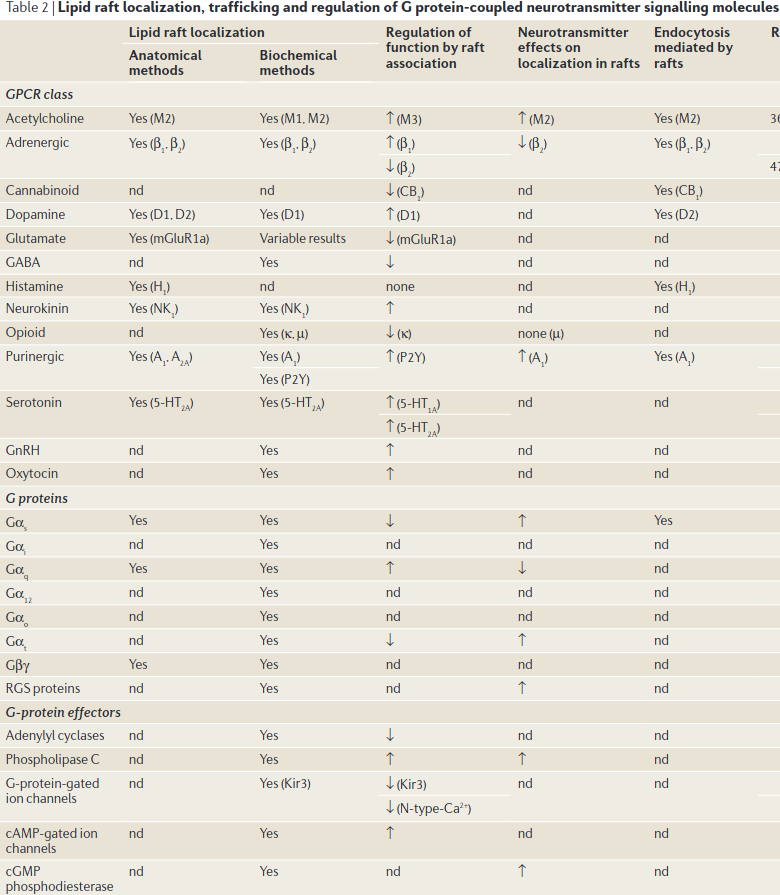
- Very interesting synthesis between membrane lipids/Glycosphingolipids and such and actin; Actin and Tubulin associate with lipid rafts.
Superlattice #
-
The superlattice model of lateral organization of membranes and its implications on membrane lipid homeostasis (Somerhaju et al. 2009)
- Superlattices = regular lateral distributions in phospholipid bilayer:
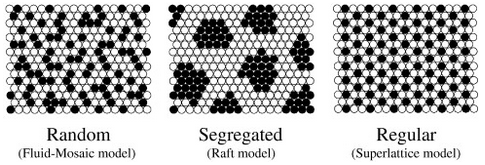
- Lateral organisation of membrane lipids: The superlattice view (Somerharju et al. 1999)
- What I’d love to know is:
- what ditcates the conformation of PUFA chains? Like you can depict DHA as straight-chained but is often depicted in all kinds of curvy-wurvy orientations.
- Makes sense that it’s a function of temperature which probably perturbs London dispersion (this is all probably related to Enthalpy). See the table in @Docosahexaenoic acid membrane properties of a unique fatty acid (Stillwell & Wassall 2003). Protein Folding may also give insights into this.
- How unsaturation contributes to superlattice formation. I thought DHA’s heavy unsaturation with its curl is what lead to sterol exclusion properties, and into lipid rafts. How does it compare to the study on palmitoyl-oleoyl-phoshpatidylcholine?
- what ditcates the conformation of PUFA chains? Like you can depict DHA as straight-chained but is often depicted in all kinds of curvy-wurvy orientations.
- Superlattices = regular lateral distributions in phospholipid bilayer:
- [LIPID RAFTS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION]
- Palmitoylation can increase a protein’s affinity for rafts, but it is not sufficient for raft association
- The classic singer-nicholson fluid mosaic model has gel-ordered, liquid-ordered, and liquid-disordered:
- Liquid-ordered phase has saturated phospholipids tightly packed with cholesterol.
- Proteins with raft affinity include glycosylphos- phatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored proteins1,7 , doubly acy- lated proteins, such as Src-family kinases or the α-sub- units of heterotrimeric G proteins8, cholesterol-linked and palmitoylated proteins such as Hedgehog 9, and transmembrane proteins, particularly palmitoylated ones.
- Proteins oligomerizing increases their affinity for rafts.
- [Functional rafts in cell membranes]
- Llipid rafts accumulate in the APICAL and axonal plasma membrane, respectively. BASOLATERAL and SOMATO- DENDRITIC MEMBRANES also contain rafts, but in smaller amounts
- Rafts are continually endocytosed.
-
Thermodynamic Comparison of the Interactions of Cholesterol with Unsaturated Phospholipid and Sphingomyelins
- The affinity of Chol to a POPC (palmitoyl-oleoyl-Phosphatidylcholine)/Sphingomyelin (1:1) membrane with 30 mol % Chol is approximately two times higher than to POPC alone; extrapolation to pure SM yields an affinity ratio of RK ∼ 5. Bringing Chol in contact with SM is highly exothermic (−7 kJ/mol for POPC/SM (1:1), and −13 kJ/mol extrapolated to pure SM, both compared to POPC). No pronounced differences were observed between egg, bovine brain, and palmitoyl SM.
- With decreasing Chol content, RK increases and ΔH becomes more exothermic, suggesting a trend toward superlattice formation. That SM/Chol-interactions are enthalpically favorable implies that the preference of Chol for SM increases upon cooling and can induce domain formation below a certain temperature. The Enthalpy gain is partially compensated by a loss in entropy in accordance with the concept of Chol-induced chain ordering, which improves intermolecular interactions (van der Waals, H-bond) but reduces conformational and motional freedom.
- So TLDR: cholesterol>POPC>sphingomyelin for enthalpy.
- The ability of cyclodextrin to extract sphingomyelin from membranes is twofold-weaker than for POPC.
-
Exploration of molecular interactions in cholesterol superlattices: effect of multibody interactions.
- Cholesterol superlattice formation reveals that although the overall interaction between cholesterol and phospholipids is favorable, it contains two large opposing components: an interaction favoring cholesterol-phospholipid mixing and an unfavorable acyl chain multibody interaction that increases nonlinearly with the number of cholesterol contacts.