κ-Opioid Receptor
links: Opioid Receptor reference: 11-10-2021
Kappa Opioid Receptor
 #
#
-
Gi-coupled PCR, coupled to Kir channels (and N-type VGCCs.). 3 subtypes (κ1, κ2, κ3)
-
The Claustrum is the region of the brain in which the KOR is most densely expressed
-
The claustrum’s proposed role in consciousness is supported by the effect and target localization of Salvia divinorum
- Crick and Koch theorized that the claustrum is a “conductor of consciousness”.
- The effect of claustrum lesions on human consciousness and recovery of function
-
The claustrum’s proposed role in consciousness is supported by the effect and target localization of Salvia divinorum
-
Primarily binds Dynorphin.
-
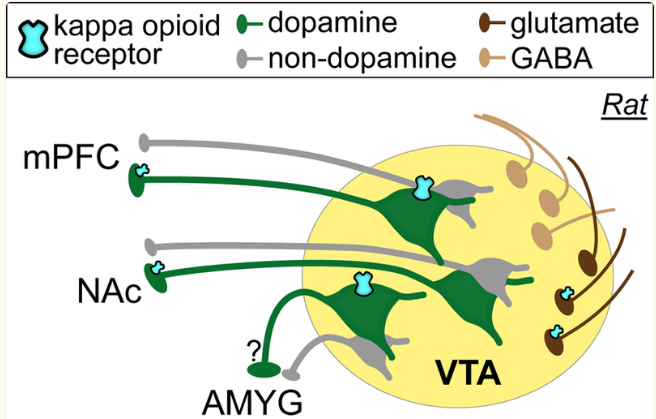
Dopaminergic Cellular and Circuit Contributions to Kappa Opioid Receptor Mediated Aversion
-
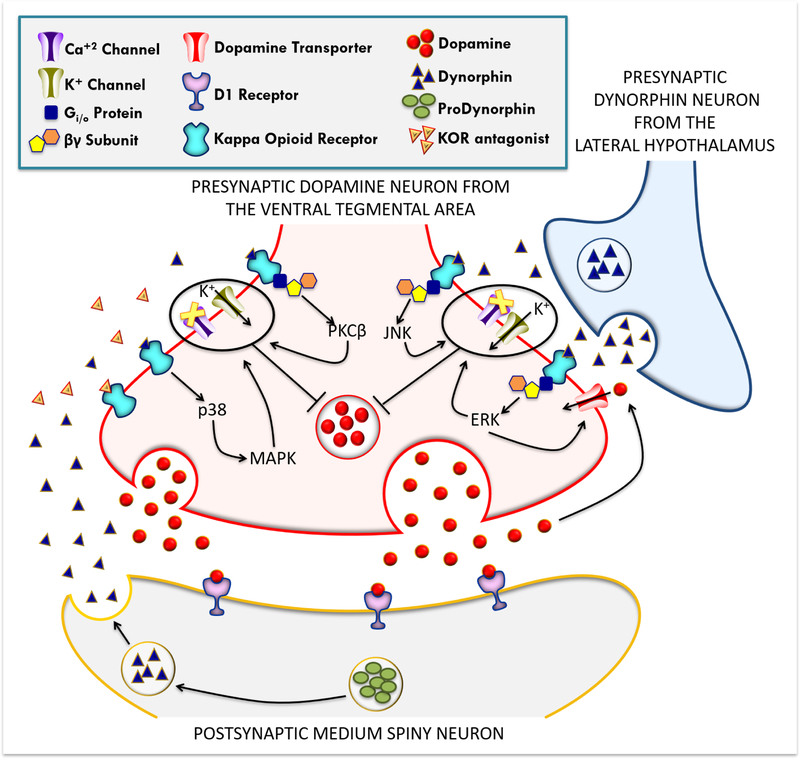
- Dynorphin binding here can apparently stimulate either p38, Protein Kinase Cβ, JNK, or ERK, which all activate GIRKs that inhibit calcium influx for dopamine exocytosis.
- ERK additionally increases DAT.
- The catalytic subunit of PP1 (one of 3) inhibits the SNARE complex of dopamine exocytosis. It’s on by default in the absence of PKA so sure.
- p38 deactivates Kir3.1 (Tyr-12 phosphorylation enhances deactivation)
-
-
Kappa Opioid Inhibition of Somatodendritic Dopamine Inhibitory Postsynaptic Currents
- The D2 IPSC is mediated by GIRK2 channels… dynorphin inhibited it, but slightly potentiated iontophoretic application of dopamine on Pars Compacta neurons.
- This implies we’re dealing with presynaptic stuff btw, because I’m sure it would inhibit EPSC all the same since it’s just exocytosis at the end of the day.
- This confirms that κ-receptors reduce dopamine release independently of membrane potential. These findings again suggest that κ-opioid receptors inhibit somatodendritic D2 IPSCs by a presynaptic inhibition, at the site of dopamine release.
- Classically the actions of opioid receptors involve the inhibition of Ca2+ conductance, activation of K+ conductance, inhibition of adenylyl cyclase, and inhibition of transmitter release.
- *…These data suggest that κ-opioid receptors do not mediate a reduction in dopamine release by selective inhibition on N-type VGCCs.
- a greater efficacy or amount of κ-receptors that couple to suppression of the IPSC in the VTA than the SNc.
- The D2 IPSC is mediated by GIRK2 channels… dynorphin inhibited it, but slightly potentiated iontophoretic application of dopamine on Pars Compacta neurons.
-
Can act via GABA-mediated repression of circuits.
-
- Chronic KOR activation increased phosphorylation of NR2B subunit of NMDA at Tyr1472 in the hippocampus, but not in the cortex. Reversed with nor-BNI or NR2B selective antagonist.
Drugs #
Given its role in mediating addictions, agonists like Naltrexone or Ibogaine can exacerbate it in the short term, but chronically, downregulation of Dynorphin removes a big part of the addictive cascade. They have been used to cure Opioid addictions like heroin.