LSD
links: Drugs reference:
- https://raypeatforum.com/community/threads/babies-experience-life-as-an-lsd-trip-as-a-result-of-their-high-metabolism.24941/
- [Trips and Neurotransmitters: Discovering Principled Patterns across 6,850 Hallucinogenic Experiences]
- drug-induced changes of conscious awareness (e.g., dissolving self-world boundaries or fractal distortion of visual perception) are linked to cortex-wide anatomical distributions of receptor density proxies. The dominant explanatory factor related ego-dissolution-like phenomena to a constellation of 5-HT2A, D2, KOR, and NMDA receptors, anchored especially in the brain’s deep hierarchy (epitomized by the associative higher-order cortex) and shallow hierarchy (epitomized by the visual cortex). 4-29-2021
LSD (Lysergic acid diethylamide)
 #
#
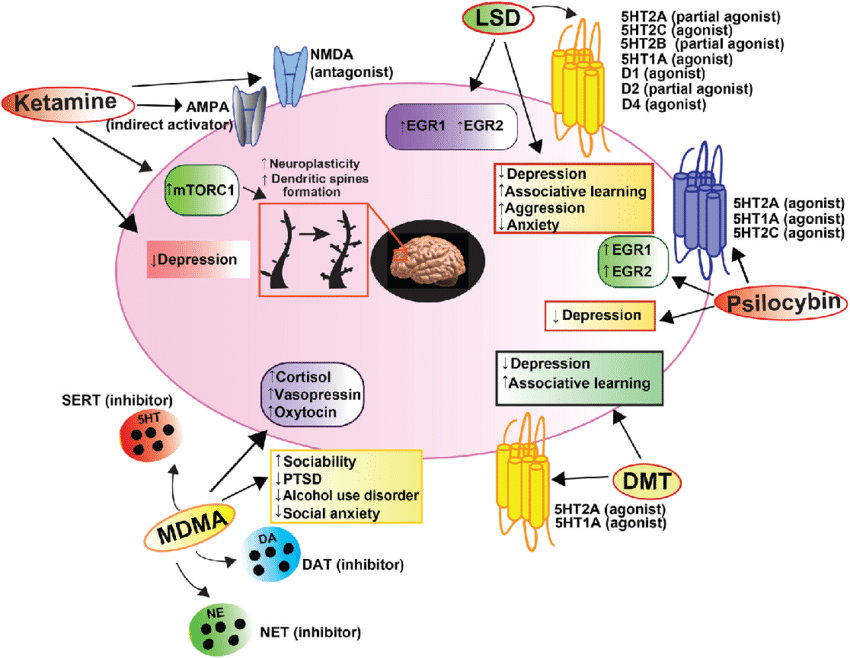
- Agonizes 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C, partial agonist of 5-HT1A.
- David Nichols in a presentation said it’s a fairly weak agonist on 5-HT2A— something like 30%.
- Histamine H2 antagonist (as are other hallucinogens). (Cyproheptadine was the most potent of all)
- Agonizes AMPAR and κ-Opioid Receptor, and antagonizes Acetylcholine -> mGluR2 antagonism -> PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway -> hippocampal synaptogenesis
- Defining the histamine H2-receptor in brain: the interaction with LSD
-
Increased thalamic resting‐state connectivity as a core driver of LSD‐induced hallucinations
- LSD‐induced functional connectivity measures between the thalamus and the right fusiform gyrus and insula correlated significantly with subjective auditory and visual drug effects
- An important model suggested that hallucinogens disrupt thalamic gating of external and internal signals, leading to increased passage of information across the cortex: Serotonin research: contributions to understanding psychoses (good stuff)
- LSD‐induced functional connectivity measures between the thalamus and the right fusiform gyrus and insula correlated significantly with subjective auditory and visual drug effects
-
Hallucinogens in Mental Health: Preclinical and Clinical Studies on LSD, Psilocybin, MDMA, and Ketamine
-
- Psyhcedelics Promote Structural and Functional Neuroplasticity
-
https://raypeatforum.com/community/threads/lsd-antagonizes-serotonin-and-glutamate-excitation.8854/
-
White FJ. Comparative effects of LSD and Lisuride…
- Increases whole brain concentrations of 5-HT, but reduces synthesis and metabolism of it.
- Central H1 antagonist.
- Decreases 5-HIAA.
- Increases Noradrenaline turnover.
- Weak Dopamine agonist compared to Lisuride, even antagonizing at higher doses by increasing DA synthesis (How does that work? Autoreceptor binding affinity?)
- Increases Homovanillic Acid levels.
-
- Facilitated activation of locus coeruleus neurons by sciatic nerve stimulation. https://serendipstudio.org/bb/neuro/neuro98/202s98-paper3/Frederickson3.html
- LSD has a higher affinity for all the 5-HT receptors than serotonin - but it has a lower potency. This explains how it exhibits “antagonistic” actions while technically being an agonist. Are there other molecules like this? It seems strange how all these psychedelics just bind to 5-HT. Can this happen to other monoamines, or even something like acetylcholine.
- 5-HT2 antagonists do not decrease the effects of LSD.
-
67.02mg/L water solubility.