PPAR-α
2022-08-15: reference:
PPAR-α #
- Increases hepatic Fatty Acid Oxidation via upregulating Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase (and generally speaking the transport and catabolism of Fatty Acids.) and decrease circulating triglycerides. Unlike PPAR-γ, I believe it suppresses Lipogenesis.
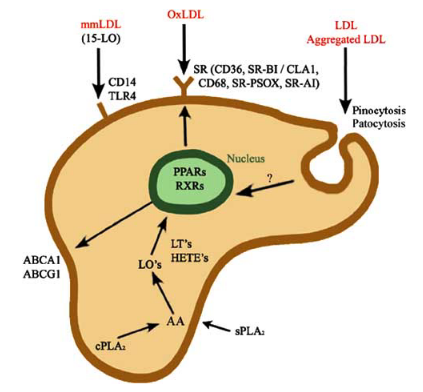
- Inhibits the formation of ‘foam cells’, fat/Cholesterol-laden M2-like Macrophages (now it’s coming together with PPAR-γ…)
- Natural ligands include ω-3/PUFAs, like AA. Necessary for ketogenesis, it is activated under conditions of energy deprivation.
- Inhibits Glycolysis and promotes Gluconeogenesis.
- Lauric Acid is its ’natural ligand’? Lauric Acid Beneficially Modulates Apolipoprotein Secretion and Enhances Fatty Acid Oxidation via PPARα-dependent Pathways in Cultured Rat Hepatocytes
- Transcription factor for various CYP enzymes (CYP1A1, 1A2, 1B1, etc.)