Heme Oxygenase
2022-05-31: reference:
Heme Oxygenase #
Located in endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, nucleus, and membrane.
Busts Heme down to ferrous iron + biliverdin, which is converted to Bilirubin.
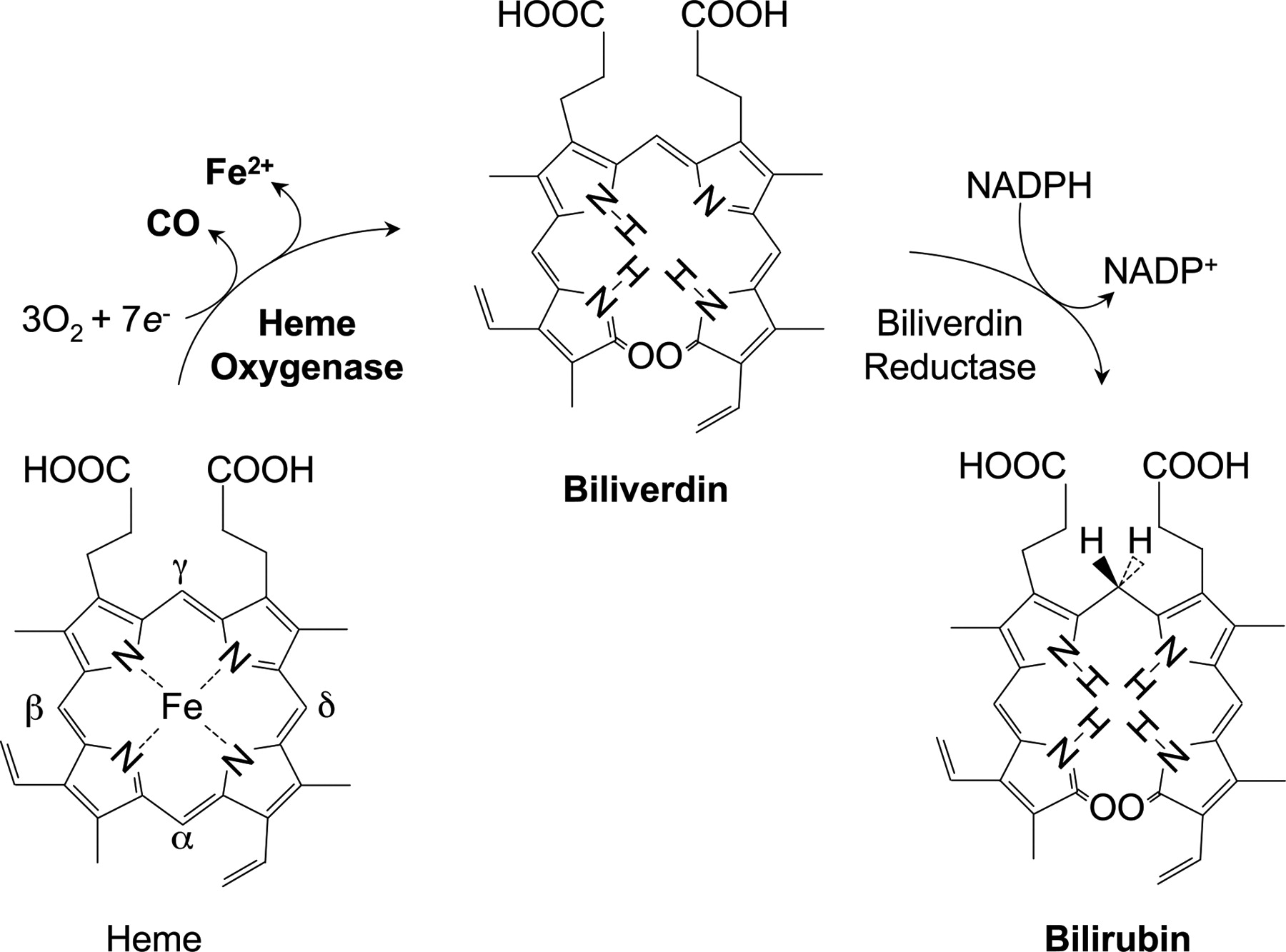
- I think Pax is pro-heme oxygenase.
-
Protective role of microglial HO-1 blockade in aging: Implication of iron metabolism
- Since HO produces free iron, it’s naughty. It is activated by Endotoxin. Results in increase of iron deposits, ferroptosis, oxidative stress, cognitive decline, etc.
-
The sinister face of heme oxygenase-1 in brain aging and disease
- By converting pro-oxidant heme to the antioxidants, biliverdin and bilirubin, HO-1/biliverdin reductase may help restore a more favorable tissue redox microenvironment. Contrariwise, heme-derived carbon monoxide and iron may amplify intracellular oxidative stress and exacerbate the disease process
- Sustained Hmox1 induction promotes oxidative mitochondrial membrane damage, iron sequestration and mitophagy (macroautophagy).
- The HO-1 mediated gliopathy renders nearby neuronal constituents vulnerable to oxidative injury and recapitulates ‘core’ neuropathological features of many aging-related neurodegenerative and some neurodevelopmental brain disorders
- Sustained Hmox1 induction promotes oxidative mitochondrial membrane damage, iron sequestration and mitophagy (macroautophagy).
- By converting pro-oxidant heme to the antioxidants, biliverdin and bilirubin, HO-1/biliverdin reductase may help restore a more favorable tissue redox microenvironment. Contrariwise, heme-derived carbon monoxide and iron may amplify intracellular oxidative stress and exacerbate the disease process