Somatostatin
links: Peptide Hormone reference:
- The role of neuropeptide somatostatin in the brain and its application in treating neurological disorders
- Somatostatin Interneurons Facilitate Hippocampal-Prefrontal Synchrony and Prefrontal Spatial Encoding 11-10-2021
Somatostatin #
AKA Growth Hormone-inhibiting hormone. In the Pancreas, it inhibits the flow of other pancreatic hormones.
- Secreted by delta cells, which are found in the antrum, Duodenum, and Pancreas islets. Acts locally in the GI trct, reducing secretion of gastrin, secretin, etc.
- Increased in Schizophrenia and positively correlated with positive symptoms. Can cause deficits in Prepulse Inhibition. Its receptor localizes in the Mesolimbic Pathway and Striatum.
- Opposes the action of Substance P R
- The dogwasher special:
- Somatostatin Interneurons can express GABA but they also express SST. SST opposes the actions of GABA and promotes the inhibition of Parvalbumin interneurons which impart inhibition onto pyramidal cells. SST increases the efficiency of glutamate and the “fidelity” of neurotransmission.
- SST increases both muscarinic and nicotinic acetylcholine currents.
- He claims glutamate neurotoxicity is due to the starvation of glutamate neurons of glu and other excitatory AAs like I guess NMDA for example.
- Decline in SST = increased synorphin signalling/opioidergic tone hypothesis of brain aging.
- Opioids activate SST interneurons, suppressing parvalbumin interneuron activity on pyramidal neurons, disinhibiting pyramidal cell activity leading to reward: Morphine coordinates SST and PV interneurons in the prelimbic cortex to disinhibit pyramidal neurons and enhance reward
- In disorders such as autism, PV interneurons far outnumber those of SST leading to overinhibition.
- Decline in SST = increased D21 formation though GABA B, increasing D2, reducing NMDA via cholinergic deafferentation, and increasing mTOR signalling.
- Somatostatin dysfunction is the root cause of all neurodegenerative diseases and mental disorders including depression
- Hypothalamic inflammation via endotoxins, ceramides, SFA, is a lead cause of diabetes. This is all these pathologies are ultimately mediated by a decline in insulin sensitivity and SST interneurons
- Somatostatin inhibitory interneurons are one of three populations of gabaergic interneurons within the brain that send gamma (GABA?) currents to pyramidal cells The foundations for optimal human health are grounded upon somatostatin interneurons especially within the hypothalamus
- The only GABAergic interneurons that express α7 nAChR, meaning it mediates the rewarding effects of cholinergic signaling.
-
Somatostatin down-regulates the expression and release of endozepines from cultured rat astrocytes via distinct receptor subtypes
- Agonists also inhibited cAMP formation dose-dependently, i.e. reduced Forskolin-induced endozepine release.
-
The role of neuropeptide somatostatin in the brain and its application in treating neurological disorders
-
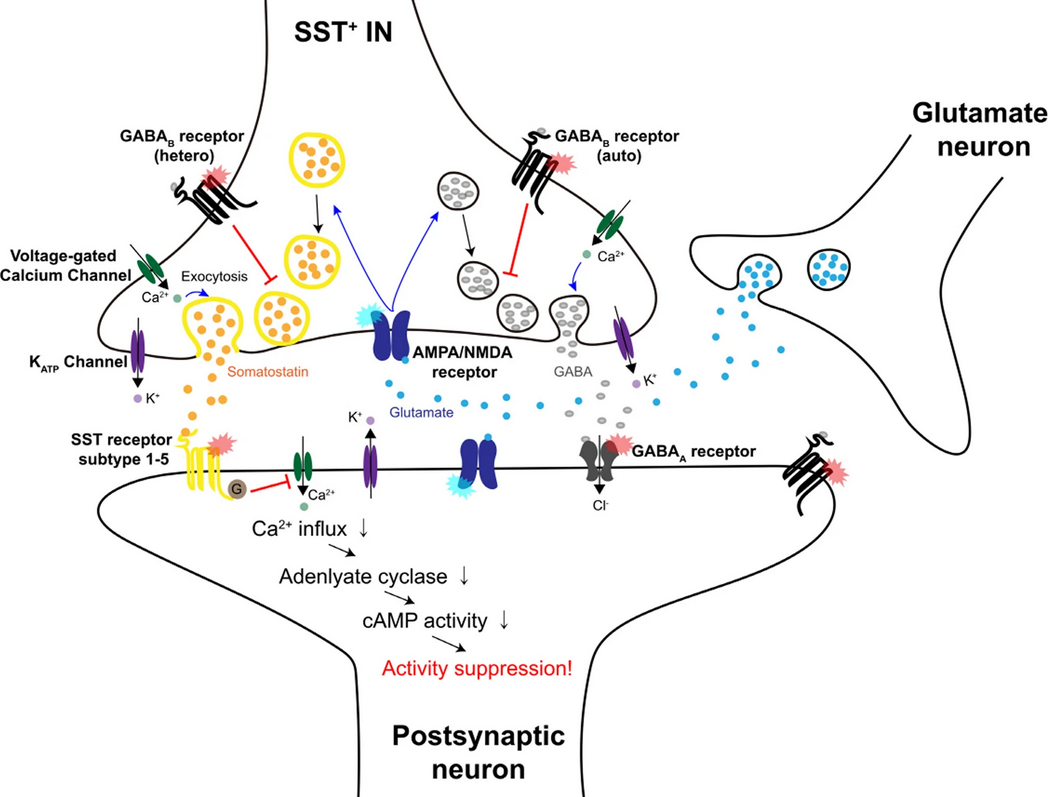
- Presynaptic GABA-B activation is dis-inhibitory, preventing (Ca2+-mediated) exocytosis of SST or GABA. There’s presynaptic AMPA/NMDA that does the opposite.
-
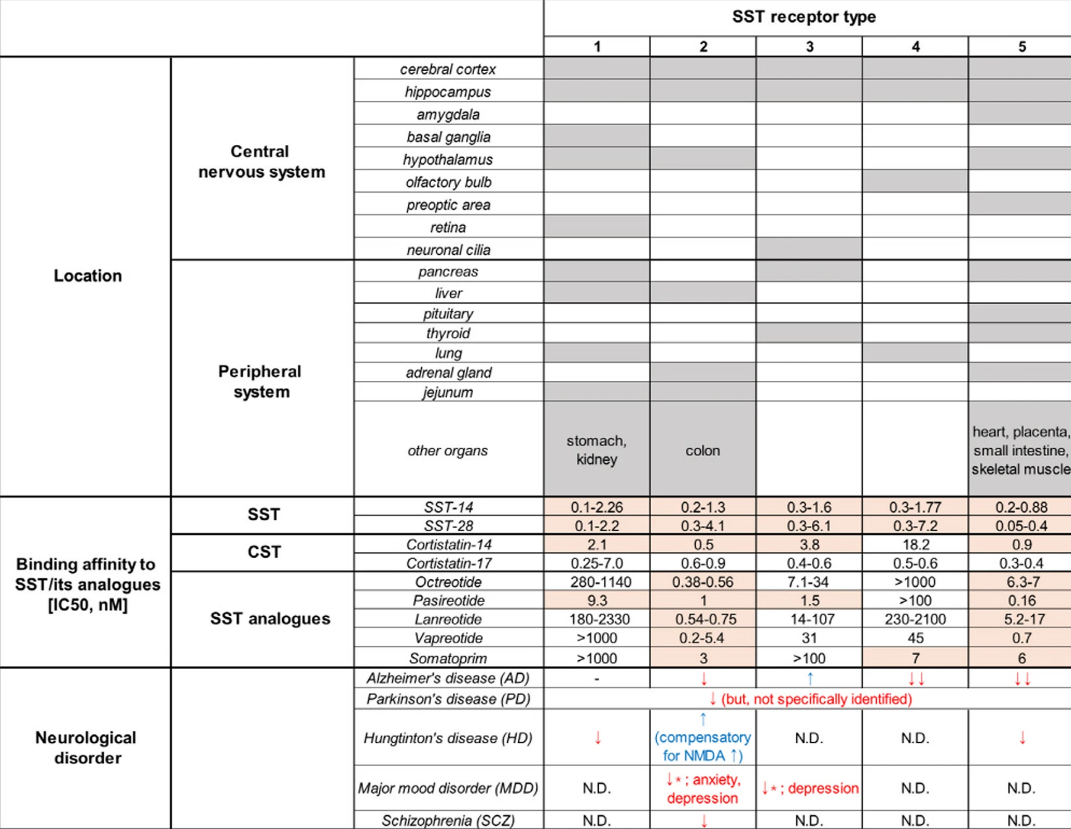
- SSTR2 seems to be the principal receptor in the cortex; deep layers: Localization of the somatostatin receptor SST2A in rat brain using a specific anti-peptide antibody etc.
-
-
Somatostatin Interneurons Facilitate Hippocampal-Prefrontal Synchrony and Prefrontal Spatial Encoding
- Inhibiting SOM but not PV interneurons during the encoding phase of the task impaired working memory accuracy.
- Depleting Hypothalamic Somatostatinergic Neurons Recapitulates Diabetic Phenotypes in Brain, Bone Marrow, Adipose, and Retina
- The Somatostatin 2A Receptor Is Enriched in Migrating Neurons during Rat and Human Brain Development and Stimulates Migration and Axonal Outgrowth