NR2B
2022-03-06: reference:
- some BRB stuff jus to get rid of the tab spam (these look really good though - they’re all connected somehow in some train of understanding so take good care of them!)
- NMDA receptors: Recent insights and clinical correlations
- Differential Roles of NR2A and NR2B-Containing NMDA Receptors in Cortical Long-Term Potentiation and Long-Term Depression
- Targeting the NMDA receptor subunit NR2B for treating or preventing age-related memory decline
- Flux-Independent NMDAR Signaling: Molecular Mediators, Cellular Functions, and Complexities
-
Memory Enhancement by Targeting Cdk5 Regulation of NR2B
- Cogmetics’ peptide is “SIP”.
NR2B (GRIN2B) (GluN2B) #
- NMDAR subunit. Humans use it better than rats/monkeys according to Bam, whatever that means. Guess I have to look up the architectural differences. We all have hippocampi and I think that’s all we’re concerned with here. There is probably literature on what he’s talking about or I can just ask him to elaborate
- Mice with the CDK5 knockout had nearly 100% more NR2B surface proteins than control, since knockout reduces Calpain-mediated NR2B degradation.
-
Bam: consciousness magnets and GRIN he claims he developed it for use alongside TMS/cc-PAS for strengthening specific networks (‘potentially up to 7x’???), such as medial anterior thalamus and PFC (OFC/dlPFC), which is associated with consciousness (that’s where Anesthesia works a la Hammeroff)
- In the area of the Thalamus where the end of the loop of the information flow with the beginning of information flow (wtf), there’s way more information coming back in than going out. Improve information processing by making it reflexive.
- Bam: nr2b and autism if anything, in Autism, it’s more likely there’s lack of NR2B, leading to excessive synapses etc.
Phosphorlyation #
-
BDNF acutely increases tyrosine phosphorylation of the NMDA receptor subunit 2B in cortical and hippocampal postsynaptic densities
- Not NR2A, though.
- Ser1116: CDK5. Disruption of this complex increases surface expresion. This is the MOA of cogmetics’ peptide.
- Ser1303: CAMK IIα, Protein Kinase Cα. Inhibits interaction with CAMK IIα (wtf?) and induces injurious Ca2+ influx, leading to neuronal death.
- Ser1323: PKC
- Y1474: increases CAMKII binding, endocytosis, LTP in amygdala. Fyn
- Tyr1472: Endocytosis. Fyn; and dephosphorylated by STEP, which also dephosphorylates Fyn itself
- Tyr1336:
Synaptic shift to NR2A #
- @Global view of transcriptome in the brains of aged NR2B transgenic mice (Li et al. 2013)
- @Co-agonists differentially tune GluN2B-NMDA receptor trafficking at hippocampal synapses (Ferreira et al. 2017)
-
Subtype-Dependence of NMDA Receptor Channel Open Probability (Chen et al. 1999)
- They used HEK cells.
- Our results indicate that peak open probability is significantly higher (twofold to fivefold) for NR2A than NR2B.
- Open probabilty modulates the amplitude of calcium transients, as well as their spatial distribution.
-
NR2B subunit in the prefrontal cortex: A double-edged sword for working memory function and psychiatric disorders
- the molecular composition of prefrontal neurons suits the operating characteristics of this structure
-
A specialized NMDA receptor function in layer 5 recurrent microcircuitry of the adult rat prefrontal cortex
- Levels only decline ~10% in the PFC.
-
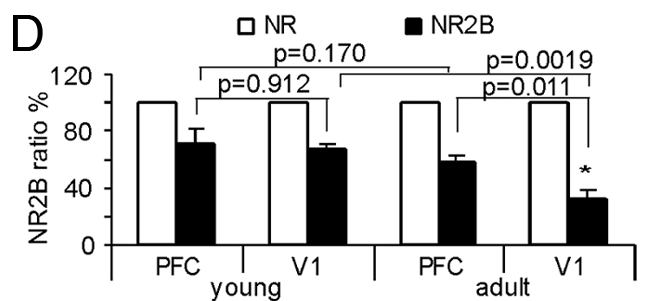
- NMDA receptor subunit composition controls synaptic plasticity by regulating binding to CaMKII
-
Expression of NMDA receptor Nr1, NR2A, and NR2B subunit mRNAs during development of the human hippocampal formation (2003): n=34 total, so take this for what you will…
-
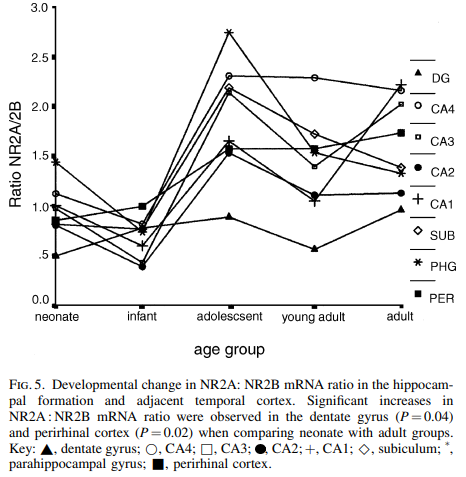 Surprinslgy only a few areas spiked up from young adult (20-24) to adult (34-55). Adolescent = 14-18.
Surprinslgy only a few areas spiked up from young adult (20-24) to adult (34-55). Adolescent = 14-18.
-
-
Differential Roles of NR2A and NR2B-Containing NMDA Receptors in Cortical Long-Term Potentiation and Long-Term Depression (Massey et al. 2004)
- LTD can be readily induced in adult cortex by the activation of NMDAR after inhibition of glutamate uptake.
- I guess this might be another way of framing the rationale depicted in
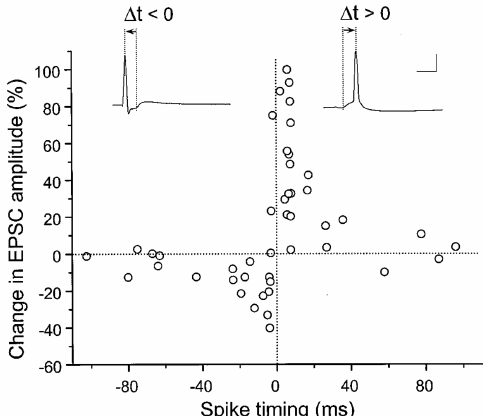 , where no glutamate uptake is the same as ‘firing before the presynaptic’?
, where no glutamate uptake is the same as ‘firing before the presynaptic’?
- I guess this might be another way of framing the rationale depicted in
- De novo LTD requires the activation of NR2B-containing NMDAR, whereas LTP requires activation of NR2A-containing NMDARs. Surprisingly another form of LTD, depotentiation, requires activation of NR2A-containing NMDARs.
- LTD can be readily induced in adult cortex by the activation of NMDAR after inhibition of glutamate uptake.