Omega-3
2022-02-08 links: PUFA reference:
- [Polyunsaturated fats, membrane lipids and animal longevity]
Omega-3 #
- Ray Peat says that they may lower inflammatory markers in studies because they’re immunosuppressant, but don’t actual heal and reduce the need for inflammation.
Types #
-
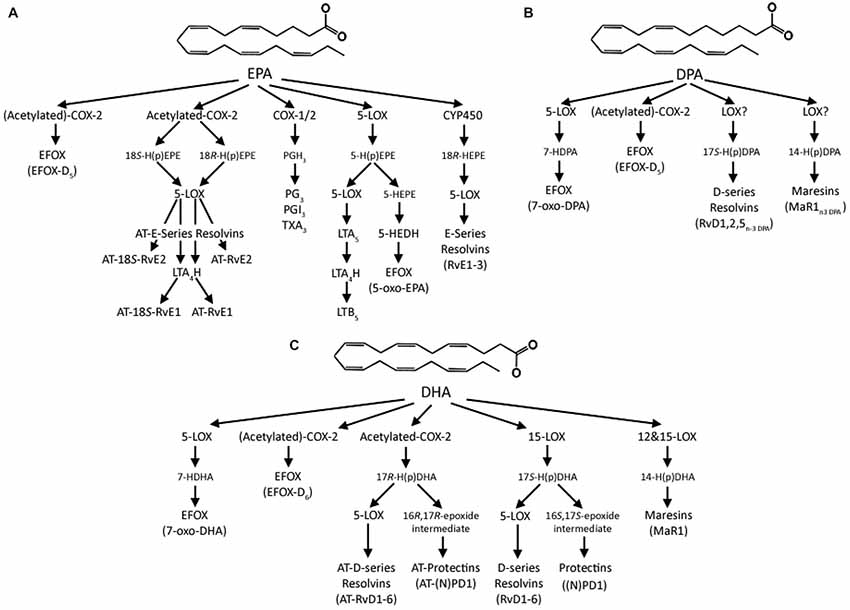
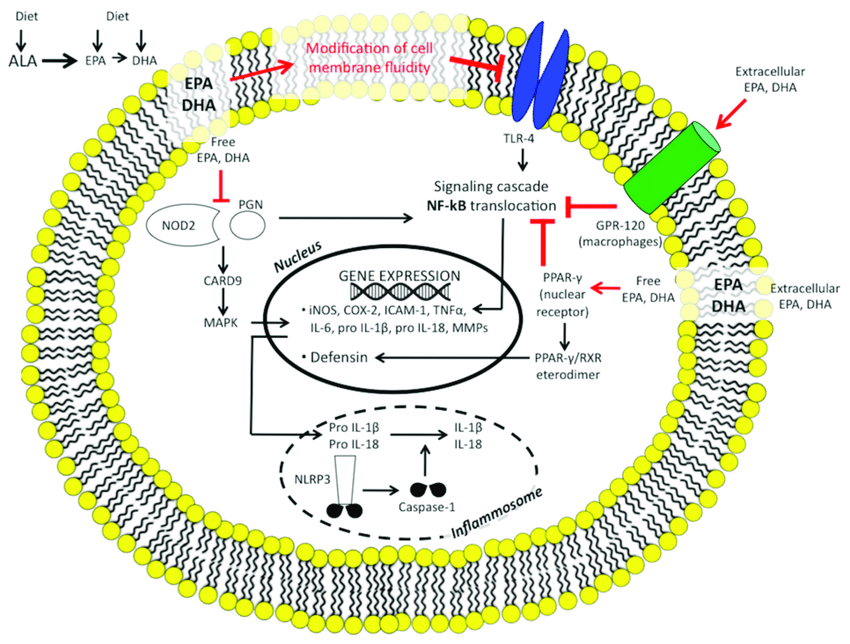
- So yeah when it comes to eicosanoids there’s a lot of classes to deal with: Prostaglandin, Thromboxane, Lipoxin, Resolvin, Leukotriene, Maresin, Protectin, and other weird species of this or that lipid.
Etc research #
Let’s keep it clean by having acid-specific papers go to their own page.
-
ω-3 are actually about twice as unstable as ω-6 by the way, since they have more double bonds.
-
https://raypeatforum.com/community/threads/is-omega-3-fish-oil-bad.24798/ Travis has some posts here. He is of the opinion that ω-6 should be completely avoided, but that trace DHA/ALA does have its merits, with such amounts being trivial to obtain.
-
DHA/EPA inhibit Calcium ATPase in the cerebral cortex, dampening neuronal activity. R
-
Saturated fat to the rescue:
-
Dietary saturated fatty acids down-regulate cyclooxygenase-2 and tumor necrosis factor alfa and reverse fibrosis in alcohol-induced liver disease in the rat
- All this really proves is that no shit, saturated fats are essential. Who argues they aren’t?
- 1: Fish oil-ethanol, 2,3,4: fish oil-ethanol, then switched to dextrose +: 2: fish oil, 3: palm oil, 4: MCT. All for six weeks, while 5, 6: fish oil and fish oil-dextrose for eight weeks.
- The most severe inflammation, fibrosis, and highest levels of Endotoxin, lipid peroxidation, and mRNA for COX-2 and TNF-α were detected in 1 and 5.
- After ethanol was discontinued, minimal histological improvement in 2 but near normalization of the histology, including regression of fibrosis, in 3 and 4. (Histological improvement was associated with the aforementioned 4 markers)
- Dietary saturated fatty acids: a novel treatment for alcoholic liver disease
-
The effect of dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) on acute rejection and cardiac allograft blood flow in rats
- Diet A (MO) contained 19.5% menhaden oil and 0.5% safflower oil; diet B (SO) was 20% safflower oil; diet C (BT) was 20% beef tallow rich in n-9 and sat. fat.
-
Dietary saturated fatty acids down-regulate cyclooxygenase-2 and tumor necrosis factor alfa and reverse fibrosis in alcohol-induced liver disease in the rat
Development #
Excess Omega-3 Fatty Acid Consumption by Mothers during Pregnancy and Lactation Caused Shorter Life Span and Abnormal ABRs in Old Adult Offspring #
- Dietary ω-3 supplementation can increase infant birth weight and prolong pregnancy (thereby reducing incidence/severity of preterm births)
Dangers #
-
-
-
Can cause Pansteatitis (yellow fat disease) when deficient in Vitamin E.
- Lipofuscin accumulation in the mesenteric lymph node did not depend on vitamin E deficiency."
-
- Associated with increased lipid peroxidation in most studies. Vitamin E co-administration is unreliable for prevention of the lipid peroxidation.
-
Effect of long-term fish oil supplementation on vitamin E status and lipid peroxidation in women
- Increase in plasma lipid peroxide through mo 2 of supplementation. After 2 mo, older women had significantly higher lipid peroxide levels than young women. The lipid peroxide:TG ratio, which declined by mo 3, was still significantly higher than baseline.
-
- 10g of MaxEpa (3g n-3) or placebo olive oil for 2x8 weeks. | VLDL: -22, -16 | LDLt: -2, -6 | HDLt: -4, +8 | Triglyceride: -18, -11 | ApoA1: -2, 0 |
- The diabetic subjects in the present study were all hypertriglyceridaemic on admission.
- Neither MaxEPA nor placebo caused significant change in mean blood glucose concentration compared to baseline levels. However, there was a general trend towards increased values after MaxEPA and reduced values after placebo.
- Insulin sensitivity changed (-15% vs +15%)
-
- For 6 weeks, 600 mg marine oil (150mg DHA + 30mg EPA) or control (600mg sunflower oil).
- Proliferative responses of lymphocytes to several mitogens were significantly decreased in MO, slightly lowering of cytosolic cyclic nucleotide (cAMP and cGMP) phosphodiesterase activity, increase of particulate PDE, slight increase in intracellular CN.
- Glutathione peroxidase activity significantly depressed. Consider @Diets rich in saturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids metabolic shifting and cardiac health (Diniz et al. 2004) where an ω-3 based diet increased it quite significantly compared to the SFA-oriented diet.
-
Why Fish Oil Fails: A Comprehensive 21st Century Lipids-Based Physiologic Analysis (2014)
- Retracted as a result of an undeclared competing interest on the part of the manuscript’s author. Classic.
- https://raypeatforum.com/community/threads/why-fish-oil-fails.8234/
-
I’m not a fan of studies of negation or whatever, but stoodies have shown ω-3 intake has:
Immunosuppressive effects of fish oil in normal human volunteers: correlation with the in vitro effects of eicosapentanoic acid on human lymphocytes (Virella et al., 1991) #
- 2.4g EPA/day for 6 weeks or olive oil placebo. n=4 and 2 respectively. 23 week follow-up.
- All the parameters apparently affected by fish oil ingestion were also affected by the incubation of normal lympocytes wih EPA in vitro.
- In conclusion, low doses of fish oil may have a mild immunosuppressive effect affecting both T and B cell functions.
- This interest was prompted by multiple reports of the downregulating effects of fish oil and EPA on the synthesis of PGE2, Thromboxane, and (LTB4)
- Mice whose fat source was exclusively fish oil produced less PGE2 and PGI2 and showed decreased susceptibility to the development of collagen-induced arthritis.
- EPA in vitro depress neutrophil chemotaxis, the superoxide burst, and (PAF) release (2-11).
- See the study on atlantic salmon where DHA increased superoxide and othter inflammatory markers. Hmm
- A decrease of both COX-2 and lipoxygenase activities in neutrophils obtained from healthy volunteers receiving fish oil supplementation for 6 weeks (3) and decreased chemiluminescence and superoxide production by phagocytosing PMN obtained from individuals that had ingested cod liver oil for 6 weeks (14).
- Fish oil supplementation may reduce the release of other important mediators of inflammation, including PAF (11), (IL-I), and (TNF-α (15).
- Okay okay okay. Lots of hype but let’s see what this study’s conclusions are
Cancer #
- Dietary omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids promote colon carcinoma metastasis in rat liver (Griffini et al., 1998)
-
Effects of dietary n-3-to-n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid ratio on mammary carcinogenesis in rats (Sasaki et al., 1998)
- An increase in the n-3/n-6 ratio did not suppress the incidence or reduce the latency of mammary tumor development.
- As the n-3/n-6 ratios were elevated, the total number and weight of tumors increased gradually.
- Greaty lowered PGE2 concentration (~800ng/g?) in 1.03 ratio vs. 0.01 (90ng/g?), but stayed constant when exceeded 1.03.
-
Plasma phospholipid fatty acids and prostate cancer risk in the SELECT trial
- Compared with men in the lowest quartiles of LCω-3PUFA, men in the highest quartile had increased risks for low-grade (HR = 1.44, 95% CI = 1.08 to 1.93), high-grade (HR = 1.71, 95% CI = 1.00 to 2.94), and total prostate cancer. Higher linoleic acid (ω-6) was associated with reduced risks of low-grade (HR = 0.75, 95% CI = 0.56 to 0.99) and total prostate cancer.
-
Serum phospholipid fatty acids and prostate cancer risk: results from the prostate cancer prevention trial
- DHA was positively associated with high-grade disease… Oleic Acid and Linoleic Acid were linearly and inversely associated with risk of high-grade prostate cancer.
Byproducts #
- When they undergo Lipid Peroxidation, they’re converted into hydroperoxides and endoperoxides.
-
Contribution of peroxidized cardiolipin to inactivation of bovine heart cytochrome c oxidase
- Lipid-soluble peroxides tetr-butyl hydroperoxide and peroxidized Cardiolipin each react with bovine Cytochrome C Oxidase and cause a loss of electron transport activity.
- Then the breakdown products, reactive aldehydes, i.e:
-
Contribution of peroxidized cardiolipin to inactivation of bovine heart cytochrome c oxidase
Susceptibility to peroxidation #
-
Lipid peroxidation during n-3 fatty acid and vitamin E supplementation in humans
- In those supplemented with n-3 fatty acids, EPA and DHA increased in plasma phospholipids and plasma Malondialdehyde and lipid peroxides increased. Vitamin E intake did not prevent the increase in lipid peroxidation during menhaden oil supplementation.
-
Effect of 6 Weeks of n-3 fatty-acid supplementation on oxidative stress in Judo athletes
- Some Judo athletes: A significant interaction effect between supplementation and time on Triglycerides was noted, with values significantly lower in the n-3 long-chain-PUFA group after supplementation. Elevated MDA and Rmax. Significantly greater Nitric Oxide and oxidative stress increase with exercise in the n-3 group. No interaction effects for retinol and α-tocopherol.
- Mitochondria: omega-3 in the route of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species This review discusses the role of mitochondria in ROS generation and the mechanisms by which it regulates ROS production. The susceptibility to peroxidation of PUFAs by ROS raises the question of the adverse effects of ω-3 PUFA dietary supplementation…
- @Diets rich in saturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids metabolic shifting and cardiac health (Diniz et al. 2004)
- Incorporation of marine lipids into mitochondrial membranes increases susceptibility to damage by calcium and reactive oxygen species: evidence for enhanced activation of phospholipase A2 in mitochondria enriched with n-3 fatty acids (Malis et al., 1990)
- EVEN IN SALMON THEMSELVES!!
Dietary n-3 HUFA affects mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation capacity and susceptibility to oxidative stress in Atlantic salmon (Kjaer et al., 2008)
- 11%, 21, and 55% n-3 with DHA or EPA. Group fed highest level of DHA had higher expressions of PPAR-β and the FA beta-oxidation genes acyl-CoA oxidase (ACO) and Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase. The high n-3 groups had reduced activity of mitochondrial Cytochrome C Oxidase and beta-oxidation capacity, together with increased activities of Superoxide Dismutase and Caspase 3 activities.
- In the group fed the highest level of n-3 HUFA, decreased percentages of major phospholipids in the mitochondrial and microsomal membranes of the liver were also apparent. The percentage of mitochondrial Cardiolipin was 3.1 in the highest n-3 group compared to 6.6 in the intermediate group. These data clearly show an increased incidence of oxidative stress in the liver of fish fed the high n-3 diets.