Cardiolipin
2022-02-08 links: reference:
Cardiolipin #
- A Phospholipid typically rich in Linoleic Acid (it is occupied by C18:n in most animal tissues.)
-
Double bonds of unsaturated fatty acids differentially regulate mitochondrial cardiolipin remodeling
- *Intact OA(18:1) was incorporated to CL; LA(18:2) and ALA(18:3) were desaturated and elongated to long chain fatty acid before the incorporation; GLA(18:3) and SDA(18:4) were unfavorable for the CL incorporation. *
-
Double bonds of unsaturated fatty acids differentially regulate mitochondrial cardiolipin remodeling
- Constitutes ~20% of the Inner Mitochondrial Membrane’s lipid composition and is almost exclusively found there; it’s vital for cristae formation.
-
First-in-class cardiolipin-protective compound as a therapeutic agent to restore mitochondrial bioenergetics
- Promotes curvature in lipid membranes due to its conical structure:
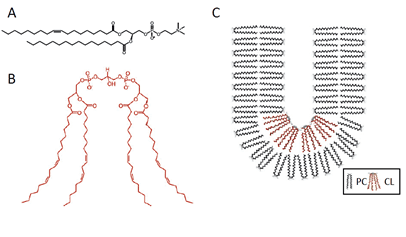
-
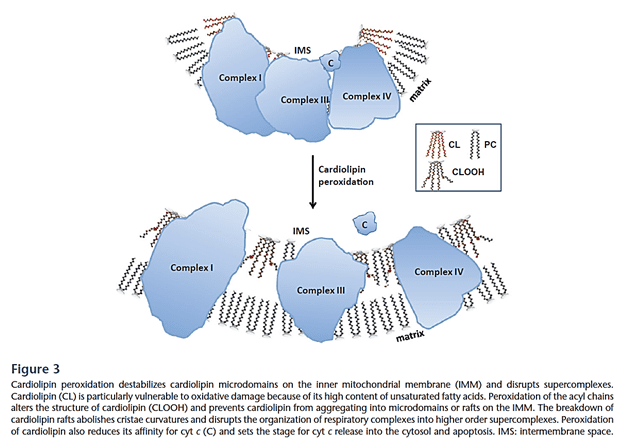
- Peroxidation causes Cytochrome C Oxidase to dissociate from the Inner Mitochondrial Membrane/ETC, and I believe serves as a major signal for triggering Apoptosis once released into the cytosol.
- Promotes curvature in lipid membranes due to its conical structure:
- Saturation of acyl chains converts cardiolipin from an antagonist to an activator of Toll-like receptor-4