Electron Transport Chain
links: reference:
- Pure gold from Amazoniac: https://bioenergetic.forum/topic/1778/on-cellular-organization-and-respiration/12?_=1716858791392&lang=en-US 8-25-2021
Electron Transport Chain #
- AKA electron transport-linked phosphorylation. The production of ATP in the inner membrane of the mitochondria via enzymes that oxidize nutrients. You hear all about ATP being cleaved for the precious Phosphates, but this is how it gets anabolically constructed, aside from the 2 each from glycolysis and TCA. This bad boy makes 34: 3 ATP is formed from each NADH + H+, and 2 ATP per FADH2.
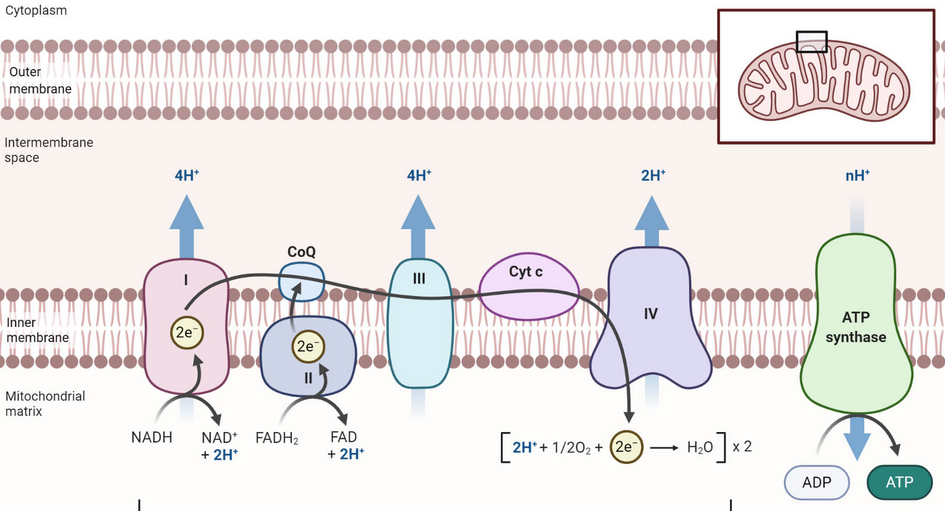
- Complex I: NADH ubiquinone oxidoreductase
- 2x NADH/FADH + $\ce H^+$ + Ubiquinone $\ce{->}$ NAD$^+$ + Ubiquinol (CoQH2). These hydrogens on CoQ are transported outside the mitochondria.
- Fe-S stabilized
- Complex II: Succinate Dehydrogenase: FADH2 -> FAD + 2H+
- Complex III: Cytochrome BC1 complex/CoH2-Cytochrome C reductase
- Complex IV: Cytochrome C Oxidase $\ce{O2 + 4e^- + 4H^+ -> 2H2O}$
- Oxygen here is an electron acceptor. Another analogy to Photosynthesis.
- Two Hemes (cytochrome a and a3), two Copper centers (CuA and CuB)
- Don’t forget UCP which imports protons.
Cofactors #
-
- This chapter talked about stuff like: A high SFA diet in obese insulin-resistant rats leads to greater tissue oxidative stress (increased ROS) with a shift toward hepatic and skeletal mitochondrial fission
Redox #
- The sublte difference between oxidation state and charge is that, mainly in inorganic I suppose, is coordination complexes (neutral ligands binding to central metal atom), the “charged” atom is really not regarded as such in these assemblies since the charge can become delocalized.
- Why oxi-? No idea. But oxidation is loss in electrons, reduction is gain: OIL RIG.
- For instance, $\ce{CO2 = C^4+O^{2-}O^{2-}}$. One must consider which half of the periodic table these element’s valence find theirselves. Hydrogen of course wants to lose an electron and thus is considered oxidized in organic compounds. Carbon with 4 valence could be either, thus it’s dependent on what it’s bound to.
- So, you can induce from $\ce{H+}$ and $\ce{O^{-2}}$ that methanol’s ($\ce{C^?H3^{3+}O^{2-}H+}$) carbon must be: -2.