Caffeine
links: reference:
- Interesting thoughts on high-dose caffeine for MPB: https://raypeatforum.com/community/threads/all-my-hair-loss-ideas-over-the-years-summarized.39520/
- Caffeine is a Natural “Sun Screen” 6-6-2021
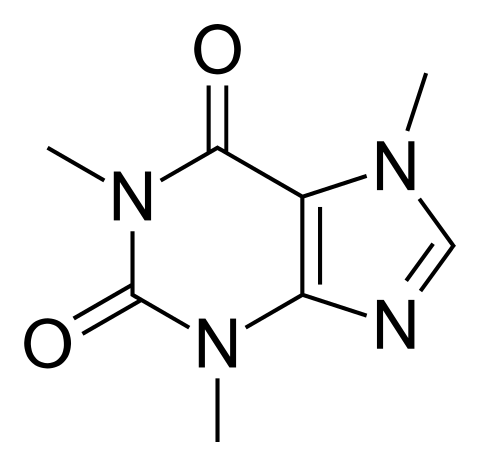
Caffeine
 #
#
- Antagonizes: A1 (12 μM) and A2A (2.4) A2B (13) and A3 (80) Adenosine Receptors.
- Indeed, the Adenosine A1 antagonism gives a depressant effect, hence selective A2A inhibitors hitting the scene like Istradefylline.
- Antagonizes the IP3 receptor, competitive antagonist of the ionotropic Glycine Receptor, and voltage-independent activator of the ryanodine receptors.
- Antagonizing Adenosine A1-D1 heterodimers increases release of dopamine in the dorsal Striatum and Nucleus Accumbens core (not shell).
- Adenosine is a vasodilator?
- Moderate inhibition of Acetylcholinesterase R R
- Increases BDNF in the Hippocampus
- Activatives Histaminergic neurons?
- Suppressess TRPA1
- Prevents or even reverses various forms of Fibrosis in the liver. R
- Reduces atherogenesis R
- Caffeine Caused a Widespread Increase of Resting Brain Entropy (2018)
- Caffeine increases striatal dopamine D2/D3 receptor availability in the human brain
- Caffeine inhibits exercise-induced increase in tryptophan hydroxylase expression in dorsal and median raphe of Sprague-Dawley rats Red Ginseng also does this. Idk mechanism
- Enhances Estrogen metabolism/detox
R
- By competing for the Cytochrome P450 oxidase system, can inhibit clearance of Estrogen from the Liver? R
- Caffeine does not entrain the circadian clock but improves daytime alertness in blind patients with non-24-hour rhythms
- Caffeine reduces low-frequency delta activity in the human sleep EEG
- Ergogenic effects of caffeine are mediated by myokines - via being an Ca2+ ionophore andor AMPK activator, enhancing secretion of Myokines.
- [Caffeine enhances acetylcholine release in the hippocampus in vivo by a selective interaction with adenosine A1 receptors.]
-
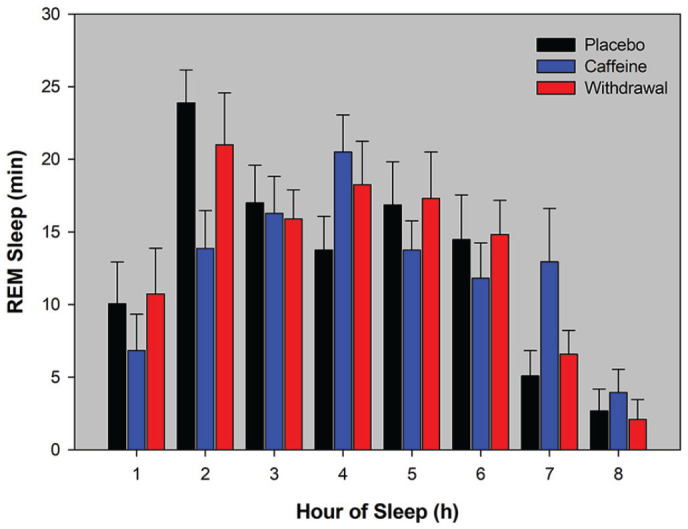
Regular Caffeine Intake Delays REM Sleep Promotion and Attenuates Sleep Quality in Healthy Men
- 20 male coffee consumers who reported 478 +- 102.8 mg/day: they were given 3x150 mg for 10 days, or 3x150 mg caffeine for 8 days then placebo (for the last 2 days I suppose)
-
-
The effect of caffeine on working memory load-related brain activation in middle-aged males
- Load-related encoding activation was greater in the DLPFC, and lower in the thalamus.
- [Adenosine A2A, but not A1, receptors mediate the arousal effect of caffeine]
- Increased wakefulness in wild-type and A1 knockout, but not in A2A knockout.
- Activates the Integrated Stress Response?
Tolerance #
-
Chronic Caffeine Alters the Density of Adenosine, Adrenergic, Cholinergic, GABA, and Serotonin Receptors and Calcium Channels in Mouse Brain
- Saw no A2A upregulation!
- In platelets, neutrophils, etc. it is upregulated, but that’s different from the brain. What’s more significant is other studies on the brain.
- [A1 and A2A adenosine receptors and A1 mRNA in mouse brain: effect of long-term caffeine treatment (1997)]
- Upregulated A2A in the striatum
- [A1 and A2A adenosine receptors and A1 mRNA in mouse brain: effect of long-term caffeine treatment (1997)]
- In platelets, neutrophils, etc. it is upregulated, but that’s different from the brain. What’s more significant is other studies on the brain.
- 5-HT1 and 5-HT2: +26-30%
- mAChR & nAChR: +40-50%
- Benzodiazepine-binding site: +65%, and slightly decreased affinity.
- Density of cortical nitrendipine-binding sites in Calcium Channels: +18%.
- Saw no A2A upregulation!
Metabolism #
- Into: 84% Paraxanthine, 12% Theobromine, and 4% theophylline.
- Have also heard: paraxanthine: ~68%, theobromine: ~23%, theophylline: ~9%
Dose #
- ~5 hour half life.
-
https://raypeatforum.com/community/threads/optimal-dose-of-caffeine-in-humans.7710/
- 3mg/kg twice a day (~220x2 for me. Fair). 6mg/kg wasn’t any better or worse but it raised noradrenaline
- The cortisol response from caffeine after 3 days is nearly abolished, while coffee inhibits cortisol synthesis from cortisone