Botany
2022-08-23: !Biology reference:
- https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Botany/From_Growing_to_Biology%3A_Plants_(Hacisalihoglu)/01%3A_Chapters
- A Photographic Atlas for Botany (Morrow)
Botany #
-
Structure
- Cells & Tissues
- Roots
- Stems
- Leaves
-
Physiology & Regulation
- Photosynthesis & Respiration
- Chemoautotrophs extract energy from inorganic chemical compounds to synthesize sugars.
- Environmental Responses
- Nutrition and Soils
- Hormones
- Salicylic Acid is part of the plant acquired immune response.
-
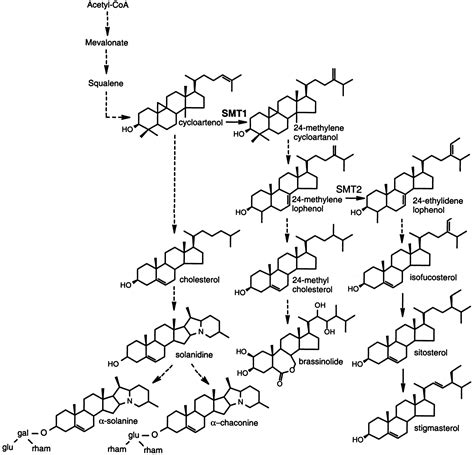
- Transport
- Development
- Photosynthesis & Respiration
Biodiversity #
-
- Horizontal gene transfer is the introduction of genetic material from one spcies to another by mechanisms other than parent->offspring “vertical” gene transmission.
- Many prokaryotes siomply uptake DNA. Bacteria uptake a bacteriophage. Rice and millet plants use transposons (“jumping genes” discovered in 1983)
- Aphids obtain the ability to synthesize carotenoids (desaturase enzyme) and become red by some kind of fungal infection,
- Agrobacterium insert part of their owngenome into a plant, and make it produce a gall thing.
- Many prokaryotes siomply uptake DNA. Bacteria uptake a bacteriophage. Rice and millet plants use transposons (“jumping genes” discovered in 1983)
- In the Endosymbiotic Theory, mitochondria, plastids, etc. were once prokaryotes that incorporated themselves into the eukaryotic cell and differentiated its DNA into the nucleus. This is why Mitochondrial DNA is a separate thing (it’s also only inherited from the mother since it degrades in the sperm in the fertilized egg).
- There are fibrous roots, like trees, and taproots that is a mtain root with little branching - this is seen in Carrots, turnips, beets, which are just food-storing roots. Some plants have root nodules with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, includng legumes.
- Structures that produce or release sugars for the growing plant are referred to as sources. Their storage point, i.e. fruits, seeds, roots, are sinks.
Taxonomy/Phylogeny #
- Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of a specific group of a species.
- So the clades on wikipeida are in a top-down order. It’s just that there are tons of subclaseses - for some reason all this variety happens mostly between order and phylum.*
-
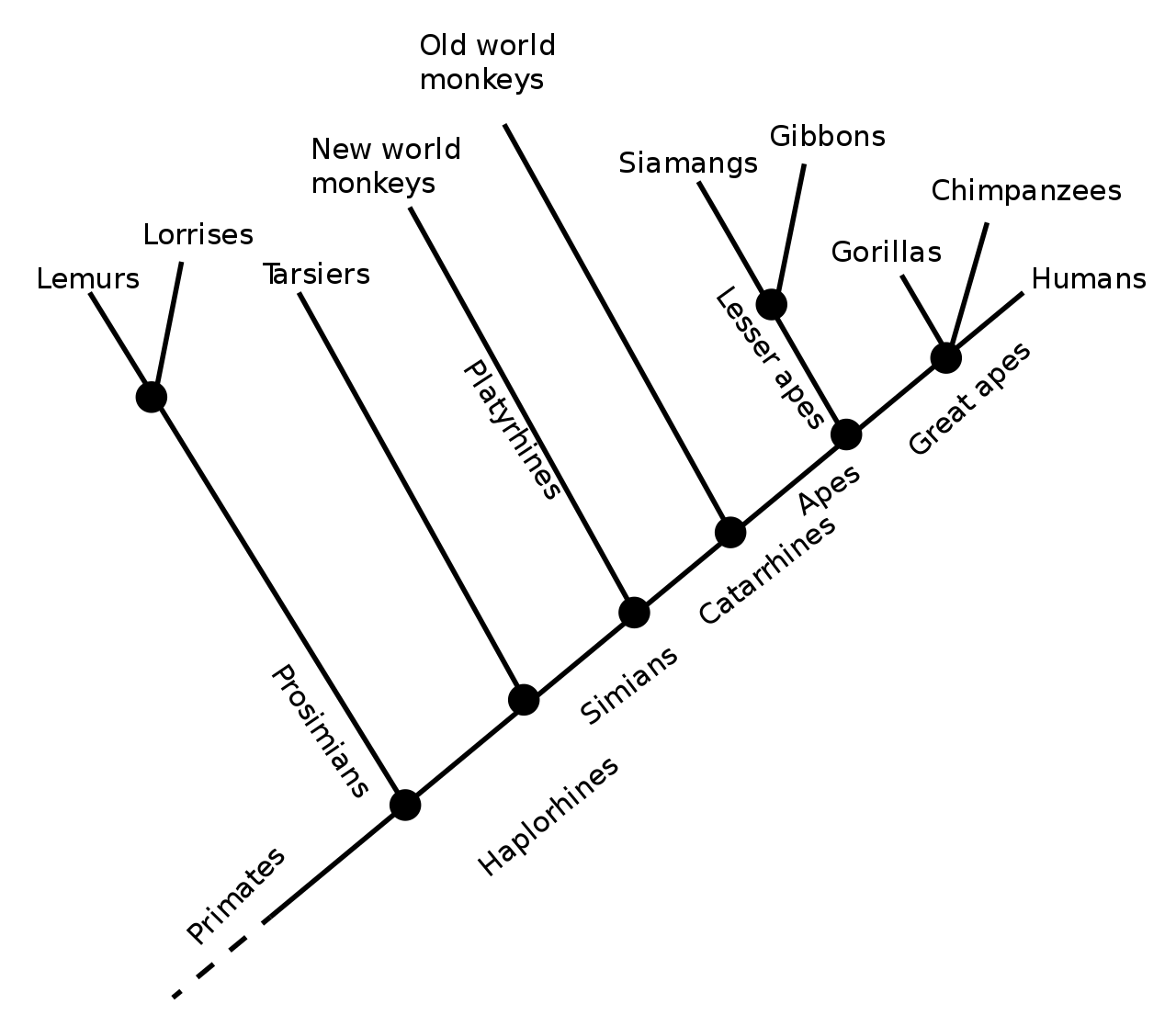
- All apes are catarrhines, but not all catarrhines are apes, etc.
- Creating a Phylogenetic Tree from gene sequences
-
- So like, Phylae have multiple clades.
-
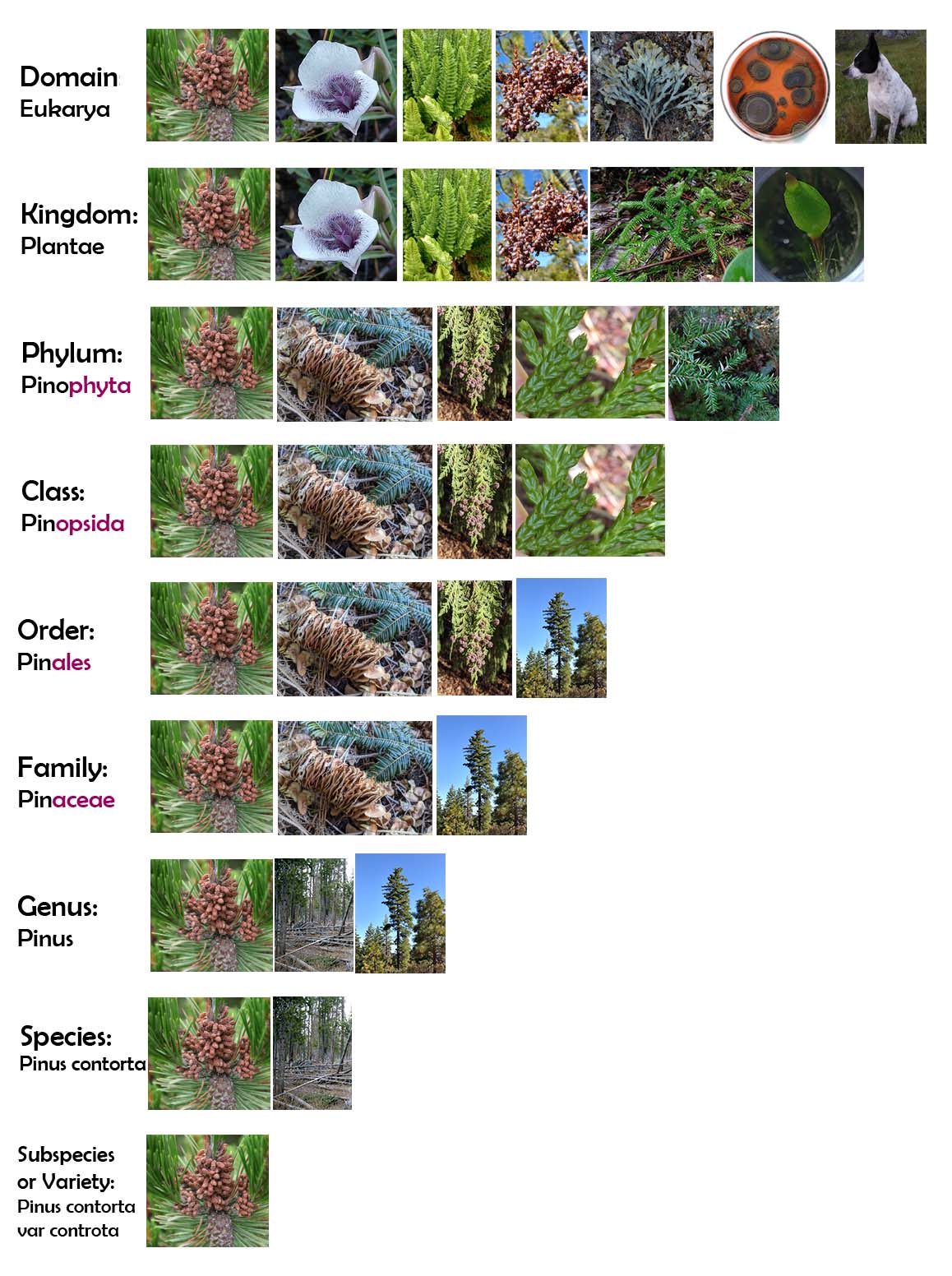

- These affixes are only for plants btw.
-

- DNA sequencing revolutionized the construction of phylogenies. I’m excited that our dear VEGF is so different between species!
Big Tree #
-
Life (2 empires: prokaryote and eukaryote), then (3 Domains)
- Archaea (Unicellular; prokaryotes) (became accepted in 1990)
- Psuedopeptidoglycan cell walls
- Their DNA structure differs from that of bacteria
- (‘Eu’)Bacteria (Usually unicellular; prokaryotes)
- Peptidoglycan + sometimes LPS cell walls.
- Eukarya (Usually multicellular)
- (3 main Kingdoms): Animalia, Fungi, and Plantae:
- Kingdom Protista is unicellular.
- Protazoa
- Parallel to these domains are the 5 ‘dominiums’ which adds viruses/viroids and prions (part of the controversial ‘superdomain’ of non-cellular life)
- Archaea (Unicellular; prokaryotes) (became accepted in 1990)
-
Archaea and Prokarya coevolved during the early stages of life. Apparently archaea were the first. Eukarya they split off from Archaea.
-
Clade: Tracheophyta (vascular)
- C.: Spermatophytes (seed-bearing)
- C.: Angiospermae (Flowering/fruiting plants) - All flowers become fruits. ‘Angio’ = vessel (for the seed) - that is to say, fruit.
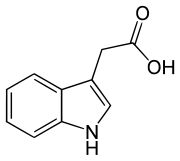 Auxins are hormones (all have carboxyls; usually indoles) that stimulate the wall of the ovary to develop into the fruit; it can be supplemented for commercial use.
Auxins are hormones (all have carboxyls; usually indoles) that stimulate the wall of the ovary to develop into the fruit; it can be supplemented for commercial use.
- C.: Eudicots (two seed leaves upon germination):
 (left: monocot)
(left: monocot)
- C.: Rosids
- Order: Fabales
- Family: Fabacaea (legumes)
- Subfamily: Faboidae
- Genus: Lens
- L. Culinaris: Lentil
- Pisum
- P. sativum: Pea
- (L. Sativus: cultivated, planted)
- P. sativum: Pea
- Phaseolus (Bean)
- P. vulgaris: kidney, pinto, navy beans (AKA white bean or pea bean)
- Vigna
- V. radiata (Mung bean)
- Genus: Lens
- Subfamily: Faboidae
- Family: Fabacaea (legumes)
- Brassicales
- Sapindales
- Rutaceae
- Aurantioideae
- Citrus:
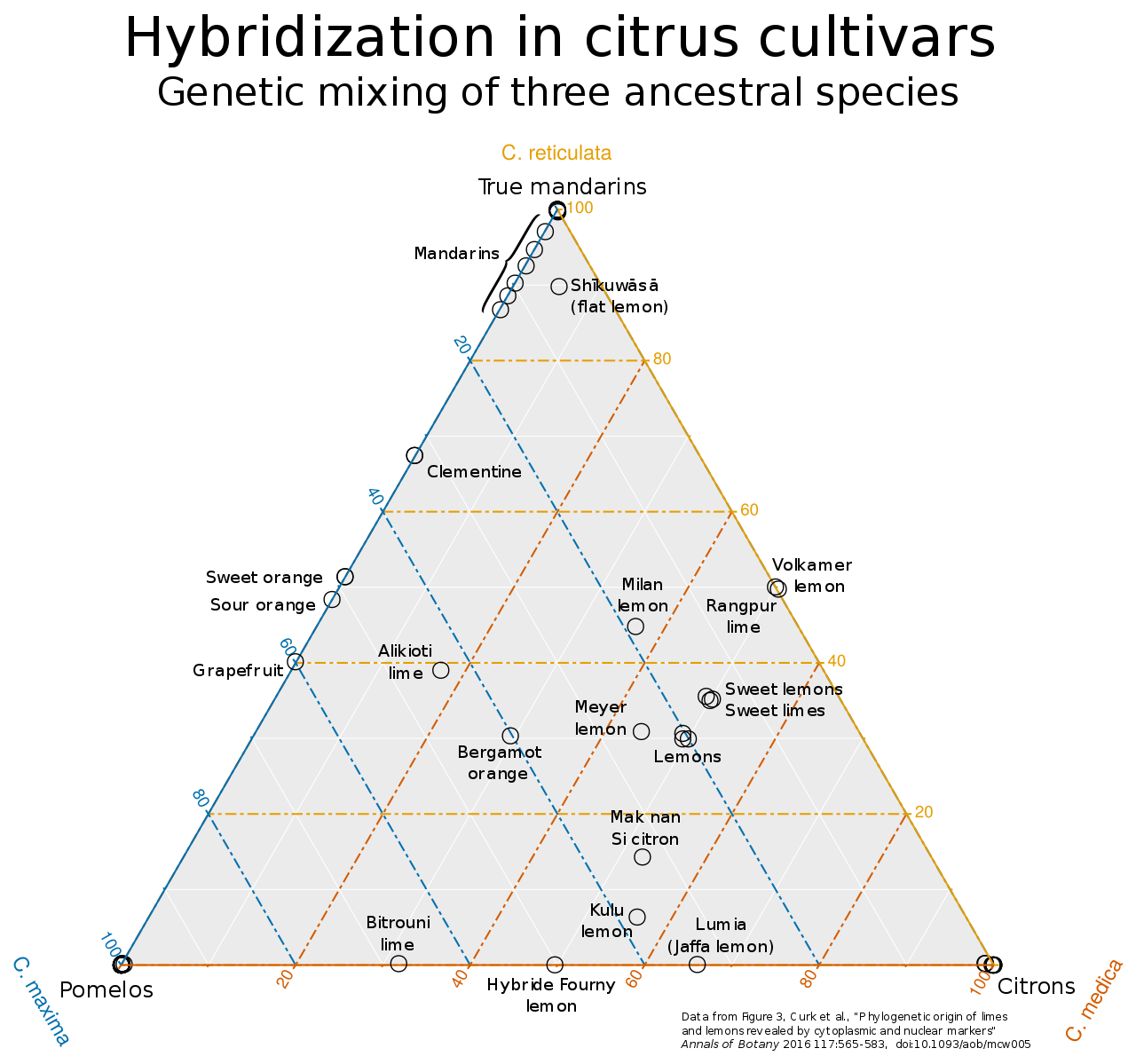
- Citrus:
- Aurantioideae
- Anacardiaceae: these fruits are “dupes” that have a fruit surrounding a big kernel.
- Mangifera
- M. indica Mango. Indica = L. Indicate, uncover, etc.
- Mangifera
- Rutaceae
- Vitales
- Vitaceae
- Vitis:
- V. labrusca, etc.: Grape
- Vitis:
- Vitaceae
- Order: Fabales
- Caryophyllales: many are succulent, i.e. cactuses, beets, as well as carnivorous plants.
- Malvales
- Malvaceae
- Helicteroideae
- Tribe: Durioneae
- Durio (9 different species: Durian)
- Tribe: Durioneae
- Theobroma
- T. Cacao
- Helicteroideae
- Malvaceae
- Rosales
- Rosaceae
- Fragaria: Strawberry
- F. ananassa: Common garden Strawberry
- Fragaria: Strawberry
- Moraceae
- Ficus
- F. carica: Fig. Apparently one of the first plants cultivated by humans: before 9000 BC.
- Artocarpus
- A. heterophyllus: Jackfruit, the largest fruit of all trees
- Ficus
- Cannabaceae
- Rosaceae
- Myrtales
- Lythraceae
- Punica
- P. granatum: Pomegranate
- Punica
- Lythraceae
- Asterids
- Ericales
- Ericaceae
- Vaccinium
- Vaccinium sect. Cyanococcus: Blueberry
- Vaccinium Oxycoccus: Cranberry
- Vaccinium
- Ericaceae
- Solanales
- Solanaceae: Nightshades. Its
4 most famous alkaloids are Solanine, Tropanes (yeah like Tropisetron), Nicotine, and Capsaicin.
- Solanum (where the Glycoalkaloid action gets real)
- Nicotianeae
- Nicotiana: Tobacco plants
- Capsiceae
- Capiscum: chili peppers.
- Convolvulaceae
- Ipomoea
- I. batatas: Sweet potato
- I. tricolor: Motrning Glory
- This as well as some others contain ergine AKA d-lysergamide for LSD. (I think Hoffman used fungi)
- Ipomoea
- Solanaceae: Nightshades. Its
4 most famous alkaloids are Solanine, Tropanes (yeah like Tropisetron), Nicotine, and Capsaicin.
- Lamiales
- Lamiaceae: Quite Estrogenic. Includes mint, oregano, basil, rosemary, sage, thyme, lavender, catnip, salvia, etc.
- Gentianales
- Rubiacaea
- Coffea
- C. arabica
- Coffea
- Rubiacaea
- Ericales
- C.: Rosids
- Monocots (Seeds contain only one embryonic leaf)
- C.: Eudicots (two seed leaves upon germination):
- Gymnospermae: Seed-producing plant (γθμνός = naked, i.e. without a fruit/ovary covering it). Includes Ginkgo and other boring stuff
- C.: Angiospermae (Flowering/fruiting plants) - All flowers become fruits. ‘Angio’ = vessel (for the seed) - that is to say, fruit.
- C.: Spermatophytes (seed-bearing)
Fungi #
- Biodiversity All 1.5 million+ are eukaryotes. Yeast is the only single-celled fungus. They do not photosynthesize. They aerobically respirate, but yeast of course ferments.
- White button mushrom = Agaricus bisporus
- Kingdom: Eucomycota
- Can be sexual, asexual. or both.
- A fungus’ role in a plant’s rhizosphere - the roots that connect fungi with a plant’s - are mycorrhizae. Fungi receive glucose, while exchanging minerals and water with the plant.
- WTF. Leaf cutter ants feed leaves to Leucoagaricus gongylophorus to digest cellulose and feed them “gongylidia”. They guard it and tend to the fungi.,
Viruses #
- Not even included in the tree of life, since they have no cells, but they do have a DNA or RNA genome, which is surrounded by a protein capsid or a phospholipid membrane.
- They work by entering a host cell and changes the genome accordingly in order to replicate form new virus particles (virions).
- Bacteria-infecting viruses = bacteriophages/phages.
Protists #
Eukaryotes. Neither animals, fungi, nor plants. Included are amoeba, algae, invertebrates, slime molds, protozoans, etc.
Algae #
- Molecular evidence supports that all Archaeplastida are descendants of an endosymbiotic relationship between a heterotrophic protist and a cyanobacterium
Plant Cells #
- It seems the main differences are as follows:
- Cell wall. Consists of cellulose
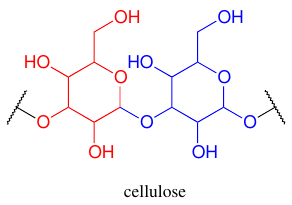 pectin, and hemicelluloses, and other polymers like lignin, suberin, cutin.
pectin, and hemicelluloses, and other polymers like lignin, suberin, cutin.
- Algae have cell walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides like agar and even carrageenan! Fungi have cell walls made of chitin.
- Plastids:
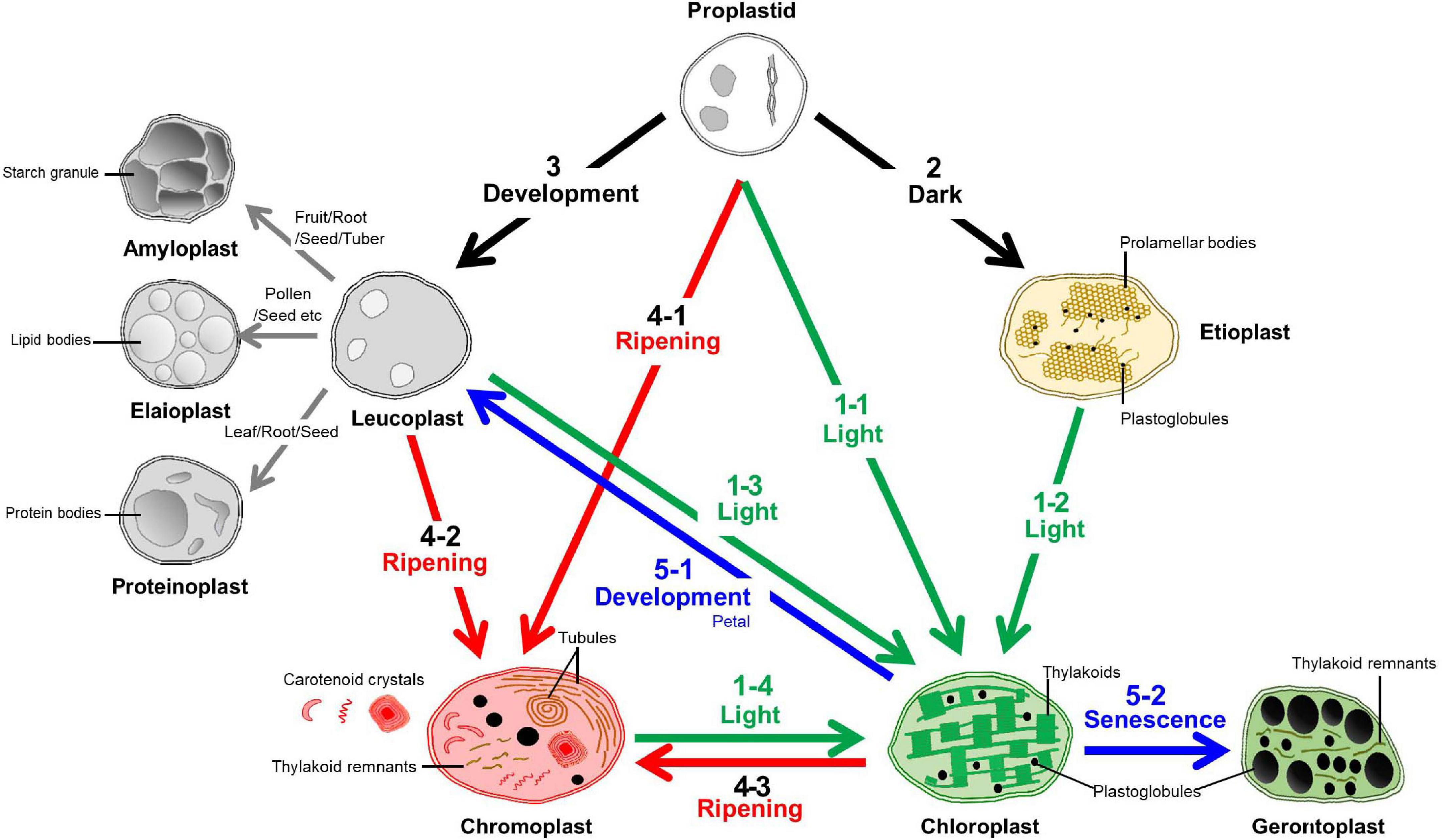
 R
R
- Amyloplasts store Starch.
- They are actually considered endosymbiotic cyanobacteria.
- Chloroplasts store their pigments in interconnected sacs called thylakoids. Chloroplasts contains its own DNA+ribosomes and is double membraned - just like the Mitochondria.
- A large permanent vacuole - which are usually absent in animal cells. It’s a sap that contains enzymes and stuff in solution. They’re basically just big vesicles. It controls the water concentration.
- When a plant wilts, its vacuoles are emptying and becomes hypertonic.
- Photosynthesis makes their own food; animal cells do not do this
- No movement; square. It will bend and has strong tensile strength.
- Usually no lysosomes.
- Cell wall. Consists of cellulose
Growing/Harvest #
- Knowing the last frost date of the year is important - when the air is <= 32°F/O°C which is when the more tender plants are killed. 24°F and under is damaging to most everything.
- Or, you plant in late summer before the first frost. In Michigan, the first fall frost is on the end of October. The last spring frost is the end of April.
- Containerized plants need to be two zones hardier than your winter since the roots lack protection.
Permaculture Tips #
- https://www.permaculturenews.org/2016/01/15/guidelines-for-perennial-polyculture-design/
- https://permaculturelegacy.wixsite.com/website/post/my-favorite-permaculture-books-of-all-time-part-1 this dude knows what he’s talking about
- There are 7 layers for a polyculture: overstory trees, understory trees, bushes, herbaceous (flowers, strawberries), ground crops, roots, vines.
- Therefore yeah, put peach trees over strawberries for instance.
- Aromatic confusers for pests like garlic (garlic mustard)
- Similarly, chives are insecticides. Their roots expel it into hydroponic water
- Basils are “sacrificial plants” for grasshoppers and other insects.
- Rabbits love clover. Put onions, garlic, dill, thyme right behind it so that they fuck off and go no further.
- Mulch (woodchips, hay, straw, sawdust, palm leaves) over the soil to protect it from frost
Hydroponics #
- Greens can be mass produced with hydroponics. They don’t take long at all to grow.
- yewtu.be/watch?v=YxFiMz81q1U
- Mad scientist’s homestead is parking size, off-grid system (vertical farming)