Capsaicin
links: reference: 4-30-2021
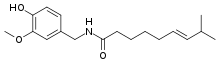
Capsaicin
 #
#
An anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant.
- Derivative of Homovanillic Acid.
- I think its sole receptor is TRPV1.
-
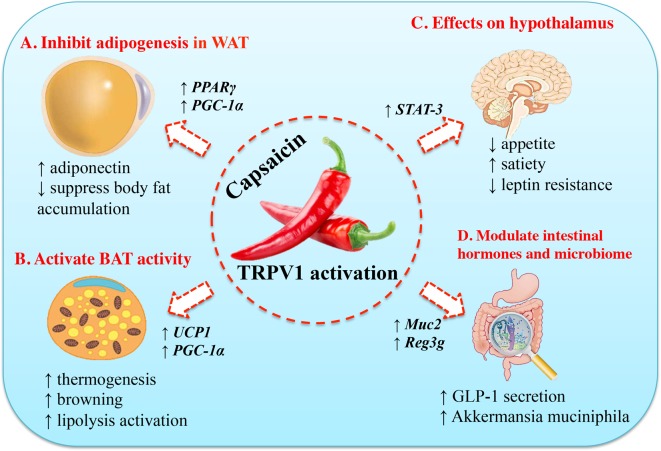
Acute Effects of Capsaicin on Energy Expenditure and Fat Oxidation in Negative Energy Balance
- Causes in increase in catecholamines and is neuroprotective; prevents dopamine neural regeneration.
- It does not effect birds, unlike mammals.
- Cold milk is effective at relieving the burning sensation due to Casein’s detergent effect. More soluble in fat or alcohol than water.
-
Mechanisms of depletion of substance P by capsaicin
- Capsaicin depletes sensory nerves of their Substance P.
- Capsaicin interferes with the retrograde transport of NGF to the cell bodies of sensory nerves. Decreased availability of NGF at the site of neural protein synthesis leads to decreased synthesis of Substance P.
- Dietary capsaicin and its anti-obesity potency: from mechanism to clinical implications (2017)
-
Study on the Effect of Capsaicin on the Intestinal Flora through High-Throughput Sequencing
- Caused weight gain in males by lowering Akkermansia.
- too much is net gut mucin-degrading while too little is associated with bowel syndromes since Akkermansia protects our gut lining in optimal levels (MoA may be recycling of degraded mucin that gastric epithelial lining uses in the form of short-chain fatty acids).