Sialic Acid
2022-08-28: reference:
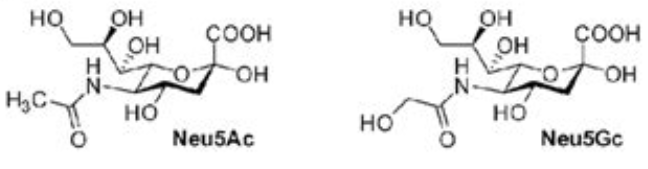
Sialic Acid (N-Acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac/NANA)
 #
#
- NANA is the ‘primary’ sialic acid. The terminal sugar in some glycoproteins like Fibrinogen.
- Inhibits IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, etc. Activates PPAR-α
- Exogenous supplement of N-acetylneuraminic acid improves macrophage reverse cholesterol transport in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
-
Sialic acid is an essential nutrient for brain development and cognition (50 pages!)
- Essential component of brain Gangliosides and polysialic acid chains that modify NCAMs.
- Polysialyation occurs on NCAM.
- High in human breast Milk, predominately in the form as Neu5Ac (N-acetylneuraminic acid) but formulascontain quite a low level consisting of both Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc (N-glycolylneuraminic acid)
- Essential component of brain Gangliosides and polysialic acid chains that modify NCAMs.
-
Molecular mechanism underlying sialic acid as an essential nutrient for brain development and cognition
-
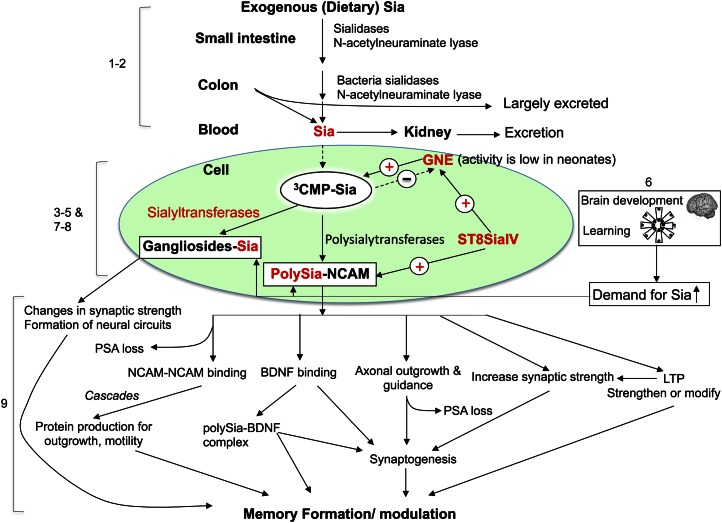
- The concentration of Sia in brain gangliosides significantly correlated with ganglioside ceramide, DHA, and total (n-3) fatty acids in breast-fed, but not in formula-fed, infants.
-
Effects of essential fatty acid deficiency during late gestation on brain N-acetylneuraminic acid metabolism and behaviour in the progeny (1980)
- Maize oil vs hydrogenated coconut oil for 2 weeks before mating and 2 weeks of gestation:
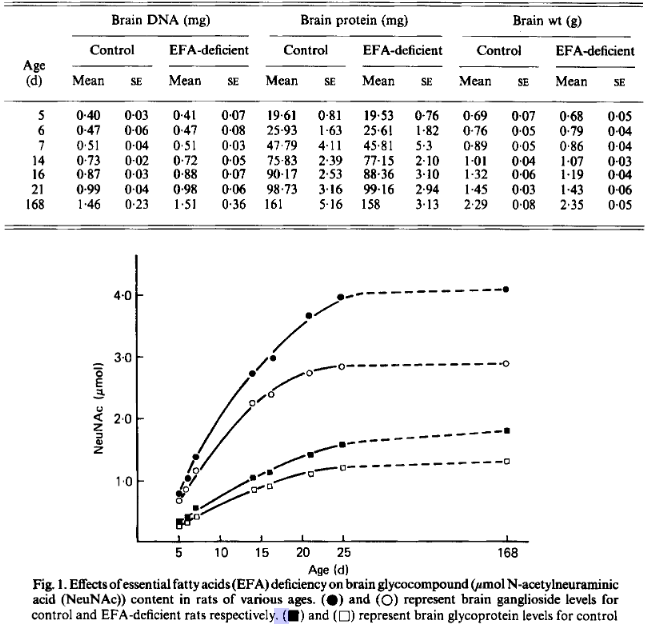
- Maize oil vs hydrogenated coconut oil for 2 weeks before mating and 2 weeks of gestation:
-
Effects of essential fatty acid deficiency during late gestation on brain N-acetylneuraminic acid metabolism and behaviour in the progeny (1980)
-
-
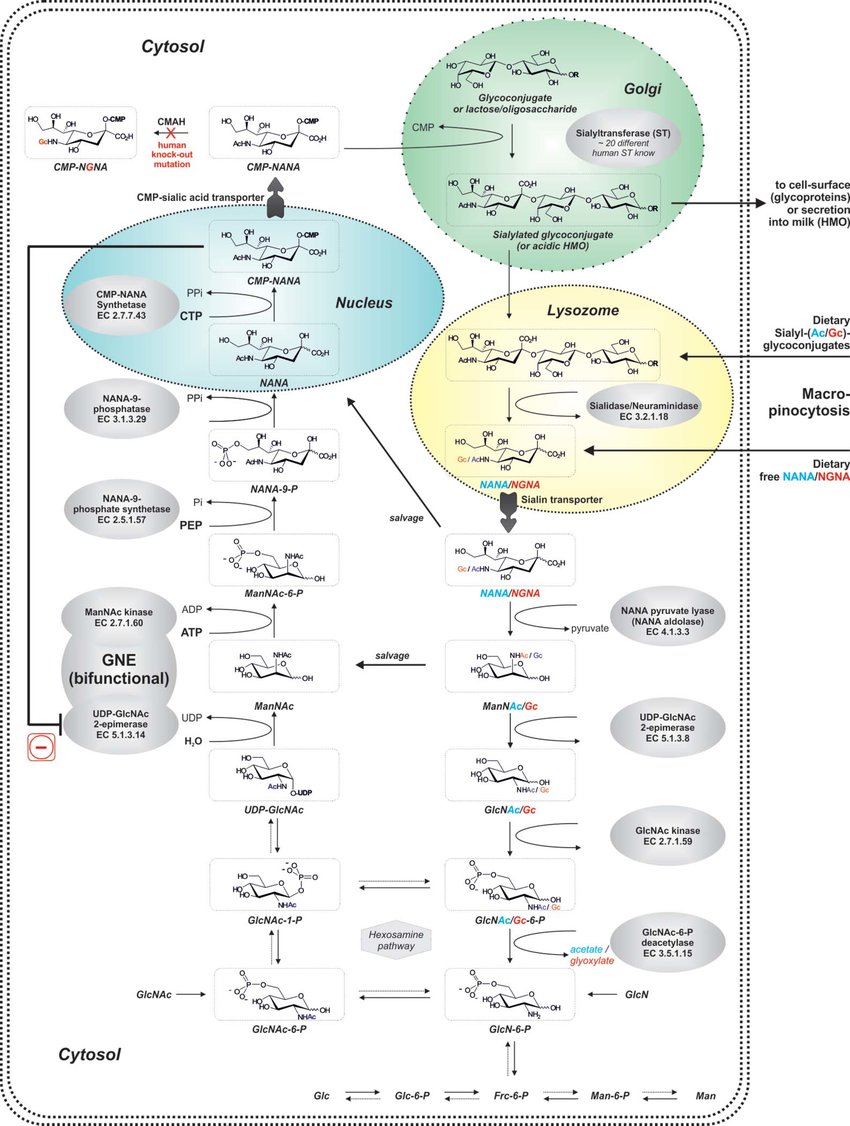
The role and potential of sialic acid in human nutrition
- ~65% of sialic acids are located in ngliosides, ~32% in glycoproteins, the remaining 3% occurring as free sialic acid. Very concentrated in the brain compared to other regions, though it is found in almost all tissues in vertebrates, with neural cell membranes having 20x SA than other membranes.
- Sialic acid (pKa 2.2-3.0) contributes to the negative charge of the membrane (R: Rosenberg - Biology of the Sialic Acids (1995) (400pgs))
- The negative charge is responsible for its repulsive effects, preventing cell aggregation. This can be disrupted by positively-charged substances like Ca2+, which electrostatically bind to sialic acid on gangliosides (which are colocalized with calcium pumps.)
- They perhaps act as an extracellular storage mechanism for calcium? Neuraminidase application increases postsynaptic activity (not unlike LTP) by releasing Ca2+.
- In the presence of calcium, gangliosides aggregate around membrane-associated peptides (like BDNF)
- The negative charge is responsible for its repulsive effects, preventing cell aggregation. This can be disrupted by positively-charged substances like Ca2+, which electrostatically bind to sialic acid on gangliosides (which are colocalized with calcium pumps.)
- NCAM is synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum and polysialyation takes place in Golgi compartments.
- Gangliosides can be exogenously administered i.p.. tf?
- After intake, it’s probably cleaved by Neu5Ac lyase into N-acetylmannosamine + pyruvic acid, which is the used for SA(-containing compound) resynthesis. It’s highly permeable to intestinal cell walls in rats with ~90% absorption.
-
Uptake, metabolism and excretion of orally and intravenously administered, 14C- and 3H-labeled N-acetylneuraminic acid mixture in the mouse and rat
- Older animals did not show significant brain incorportion of SA after acute dosing.
- Higher circulating SA in T1/2 diabetes.
-
Dietary sialic acid supplementation improves learning and memory in piglets
- Spplementary sialic acid was associated with faster learning, higher concentrations of protein-bound sialic acid in the frontal cortex, and 2–3-fold higher mRNA levels of 2 learning-related genes, GNE (UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase) and ST8SIA4.
- Maternal Neu5Ac Supplementation During Pregnancy Improves Offspring Learning and Memory Ability in Rats (Bian et al. 2021)
- Sialic Acid and Sialylated Oligosaccharide Supplementation during Lactation Improves Learning and Memory in Rats (Oliveros et al. 2018)
- Exogenous supplement of N-acetylneuraminic acid improves macrophage reverse cholesterol transport in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
- Novel biological function of sialic acid (N-acetylneuraminic acid) as a hydrogen peroxide scavenger
-
- Decreased sialyltransferase in Alzheimer’s
- Down-regulation of glutamate release from hippocampal neurons by sialidase
Polysialic Acid (PSA) #
-
Polysialic acid in the plasticity of the developing and adult vertebrate nervous system
- PSA is highly voluminous due to its hydration. The fact it’s a ‘slippery eel’ makes it hard for proteins to bind to it and would require an enzyme to also have affinity (avidity) for the Immunoglobin domains.
- BDNF-induced Choline Acetyltransferase activation is dependent on a reudction of PSA expression. PSA effects on ChAT seems to involve BDNF (this is not observed in its absence) and NCAM.
- Polysialic acid limits choline acetyltransferase activity induced by brain-derived neurotrophic factor… in developing cholinergic neurons.
- [Polysialic Acid in Brain Development and Synaptic Plasticity]
- Sialic acids are added onto the oligosaccharide chain via two complementary sialyltransferases, ST8SIA2 (STX) and ST8SIA4 (PST). I dunno how they differ.
- There are like 20 of them bro. It’s mostly just age and location of expression, I think. STSIA4 persists in adulthood whereas ST8SIA2 is more for prenatal and early postnatal development.
- Implicated in neural tube closure.
- Valproic acid increases the polySia to NCAM ratio, while Retinoic Acid accelerates polysialylation of NCAM, at least in cell culture experiments, by augmenting ST8SIA4 but decreasing ST8SIA2 mRNA levels.
- The major, but not the only carrier of polysialic acid is NCAM.
-
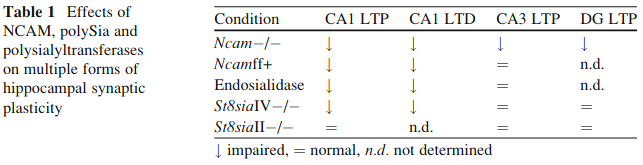
- Ranges from 8-90 sugar units.
- Comprises ~10% of total protein-bound neuraminic acid in the developing brain
- Post-training intrahippocampal injection of synthetic poly-α-2,8-sialic acid-neural cell adhesion molecule mimetic peptide improves spatial long-term performance in mice
- SNPs in NCAM1 and ST8SIA2 (not A4) are associated with Schizophrenia
- Sialic acids are added onto the oligosaccharide chain via two complementary sialyltransferases, ST8SIA2 (STX) and ST8SIA4 (PST). I dunno how they differ.
-
Polysialic acid regulates chain formation by migrating olfactory interneuron precursors
- Olfactory interneuron precursors in the rostral migration stream migrate in chains and through long distances to the olfactory bulb. The migration is inhibited when polysialic acid moiety of NCAM is removed.
- Polysialic acid may prevent cells in chains from interacting too tightly.
- Polysialic acid regulates cell contact-dependent neuronal differentiation of progenitor cells from the subventricular zone
-
PSA-NCAM is required for activity-induced synaptic plasticity
- Treatment of the cultures with endoneuraminidase-N selectively removed PSA from NCAM and completely prevented induction of LTP and LTD without affecting cellular or synaptic parameters.
-
Membrane oligo- and polysialic acids short but complex
- *Biological roles of poly/oligoSia are based on its ability to modulate repulsive and attractive interactions between two molecules, and its ability to modulate membrane surface charge density, pH at the membrane surface, and membrane potentials.
-
Polysialic acid chains exhibit enhanced affinity for ordered regions of membranes
- That is to say, in the presence of Lipid Rafts.
Neu5Gc #
-
SIALIC ACIDS AND AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE
- Sialic acid-recognizing Ig superfamily lectins or Siglecs are a family of cell surface proteins largely expressed in hematopoietic cells… mostly inhibitor receptors that bind to sialic acid-containing ligands and recruit tyrosine phosphatases to C-termini.
- Not found in humans; synthesized by an enzyme which humans lack: via CMAH (cytidine 5′-monophosphate-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase.) That C2O2H3 thing is a ‘glycolyl’ group but if I look that up, sialic acid stuff are the only results really.
- It is found in apes though. I think the lack of this enzyme is what makes it inflammatory as the immune system may create antibodies. Makes me wonder what gene editing would do?
-
A red meat-derived glycan promotes inflammation and cancer progression
- Quite high in beef and goat cheese for some reason, but none in butter or poultry and low in whole milk. Doesn’t seem to be found in plants.
- Nope, they found Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc in corn in some australian study.
- Quite high in beef and goat cheese for some reason, but none in butter or poultry and low in whole milk. Doesn’t seem to be found in plants.
-
Why does multiple sclerosis only affect human primates?
- We propose the concept that long-term ingestion by human primates of the foreign Neu5Gc, via red meat consumption, is an ignored environmental risk factor for Multiple Sclerosis.
-
A red meat-derived glycan promotes inflammation and cancer progression
- Cow’s milk is 27% Neu5Gc, the remaining 73% is Neu5Ac. It is 0.47mmol/L sialic acid compared to 3.72 in human milk. As well as 0.025 g/L free oligsaccharides compared to 24 in human milk.
- It is found in apes though. I think the lack of this enzyme is what makes it inflammatory as the immune system may create antibodies. Makes me wonder what gene editing would do?
Supplementation #
2-3 grams daily.
- Suspiciously cheap ($.23/g): https://vitamondo.net/n-acetylneuraminic-acid-memory-immunity-sialic-acid/
- Ridiculously expensive ($3.8/g in 100mg capsules): https://nextvalley.com/shop/sialic-acid/
- Instead of size it’s “Smell” and we got $148 for 100g: https://www.aliexpress.com/item/3256804012823090.html?algo_exp_id=dcd340fe-2f71-4ad8-9a8d-05f11bce83f4-5&pdp_ext_f=%7B%22sku_id%22%3A%2212000028354645892%22%7D&pdp_npi=2%40dis%21EUR%2154.58%2149.67%21%21%21%21%21%402100bb4916611828588891885e0f7e%2112000028354645892%21sea&curPageLogUid=kC5bpzFhUd0X&gatewayAdapt=4itemAdapt
- ($1.67/g) https://www.aliexpress.com/item/3256804394935088.html?algo_exp_id=dcd340fe-2f71-4ad8-9a8d-05f11bce83f4-6&pdp_ext_f=%7B%22sku_id%22%3A%2212000029707387278%22%7D&pdp_npi=2%40dis%21EUR%2120.45%2120.45%21%21%2119.07%21%21%402100bb4916611828588891885e0f7e%2112000029707387278%21sea&curPageLogUid=fnWZIWPJuOEK&gatewayAdapt=4itemAdapt 10g $16.69