NCAM
2022-04-28: reference:
NCAM (Neural cell adhesion molecule) (CD56) #
- Glycoprotein. As the name suggests it’s for cell-cell adhesion, plasticity, etc. in neurons/glia, lymphoid cells, etc. and skeletal muscle. NCAM1 associates with FGFR to induce neurite outhgrowth.
-
Aβ-dependent reduction of NCAM2-mediated synaptic adhesion contributes to synapse loss in Alzheimer’s disease
- Amyloid β binds to NCAM2 and induces their removal from synapses. This cleavage is increased in Alzheimer’s.
- Knockdown of NCAM2 expression or incubation with NCAM2-ED induces disassembly of GluR1-containing glutamatergic synapses in cultured hippocampal neurons.
-
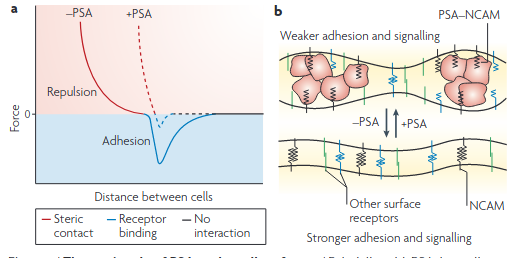
PSA–NCAM: Synaptic functions mediated by its interactions with proteoglycans and glutamate receptors (Senkov et al. 2012)
-
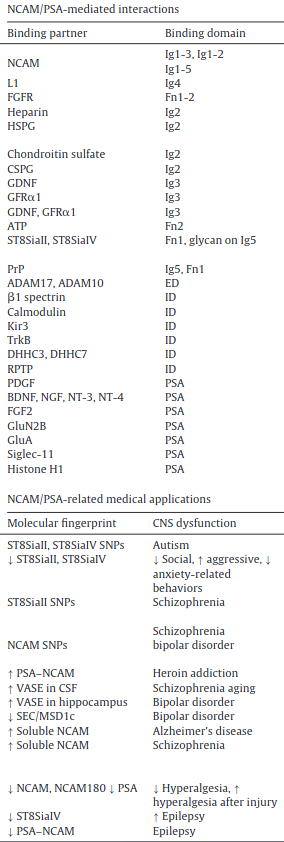 not sure what the extracellular domain is precisely.
not sure what the extracellular domain is precisely.
- Degradation of transmembane isoforms of NCAM occurs via enzymatic cleavage by metalloproteinases ADAM10 and ADAM17/TACE, whereas GPI-anchored NCAM-120 is cleaved by a phosphatidylinositol-specific Phospholipase C
- Interacts with extracellular matrix (ECM) molecules like Chondroitin/heparan sulfate proteoglycans. (A proteglycan is a class of heavily-glycosylated proteins.) They bind to the Ig2 domain and PSA promotes their binding, perhaps acting as a mediator between cell-cell and cell-ECM adhesion?
- HSPGs incrporated in the ECM promote synaptogenesis.
- Interacts with extracellular matrix (ECM) molecules like Chondroitin/heparan sulfate proteoglycans. (A proteglycan is a class of heavily-glycosylated proteins.) They bind to the Ig2 domain and PSA promotes their binding, perhaps acting as a mediator between cell-cell and cell-ECM adhesion?
- PSA-NCAM in the synaptic cleft promotes LTP and surface expression of AMPAR/NMDAR.
- PSA-NCAM or PSA alone inhibits eNMDAR - I’m guessing somehow physically-kinetically.
- [Neural cell adhesion molecule-associated polysialic acid inhibits NR2B-containing N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and prevents glutamate-induced cell death (Hammond et al. 2006)]
- A bit worrying if not restricted to extrasynaptic NR2B. In vitro.
- [Neural cell adhesion molecule-associated polysialic acid inhibits NR2B-containing N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and prevents glutamate-induced cell death (Hammond et al. 2006)]
- *Another important posttranslational modification of NCAM is palmitoylation, mediated by DHHC3 and DHHC7, which is necessary for targeting of NCAM to Lipid Rafts and NCAM signaling in lipid rafts via Fyn and FAK. Co-signaling via this pathway and FGFR is required for NCAM-mediated neurite outgrowth.
-
Increase in polysialyltransferase gene expression following LTP in adult rat dentate gyrus
- In vivo induction of LTP in adult rat dentate gyrus is followed by a rapid and sustained (up to 4 h) NCAM polysialylation by activation of ST8SiA2 and ST8SiA4 gene expression
-
PolySialic Acid #
-
-
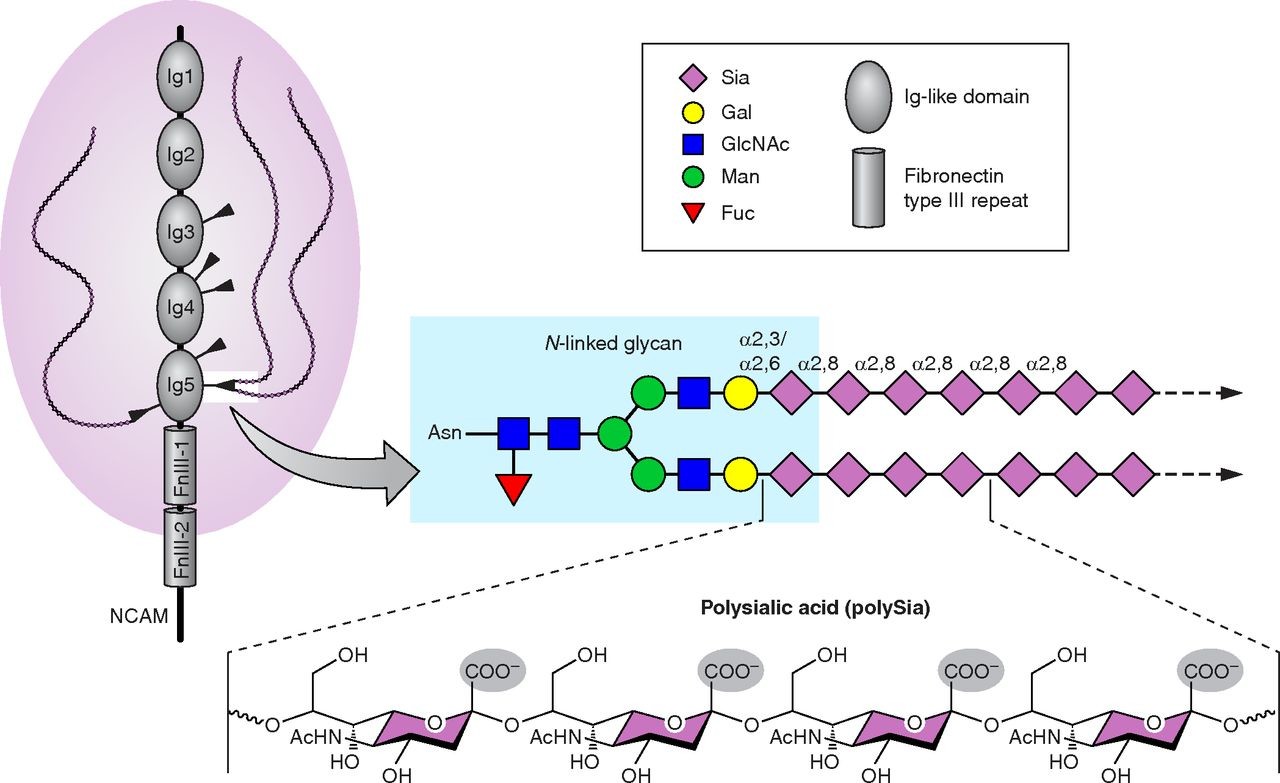
- Depicted is all 6 possible N-glycosylation sites, with those bottom two being polysialyatable.
- Fibronectin type III domain…
- Immunoglobin domains are pretty damn prevalent, including but not limited to all the proteins in the Immunoglobin superfamily. I have no idea if there’s something special or immune-related about the Ig folds.