RTK
2022-04-13: reference:
RTK #
 ,
,
-
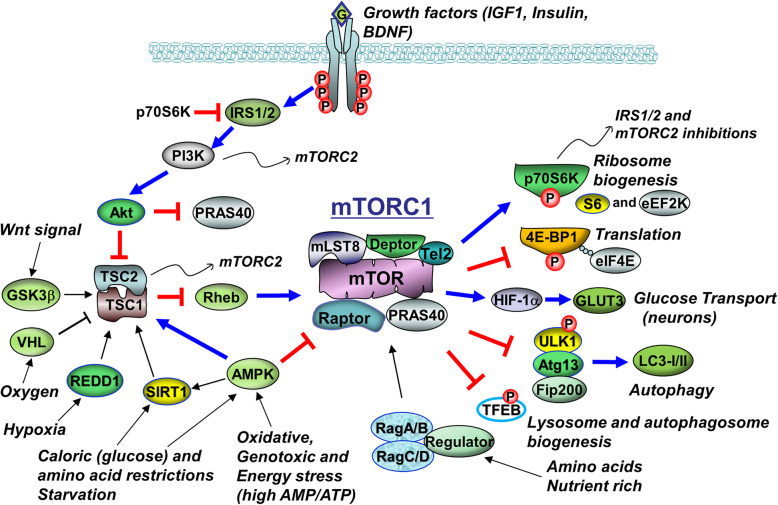
This is NOT representative of every RTK, especially when you consider all the isoforms, but many of them do activate PI3K. I swear they basically all activate PI3K, Ras-RAF… and STAT-.
-
A single unit with an extracellular ligand-binding domain. After binding, adjacent units form dimers: The cytoplasmic protein kinase domains then activate, and uses ATP to autophosphorylate the other unit on the Tyrosine residues.
- Pretty sure the dimerization is covalent; apparently the inslin receptors form disulfides. Thus Methionine/Cysteine concentration is something to consider (cysteine-rich regions are characteristic of all RTK classes).
- After phosphorylation, proteins including PI3K and Ras bind.
-
Considering there’s 20 subclasses, I think I’ll worry about what they activate rather than RTK generally…
- Their cascades can activate MAPKs.
Classes #
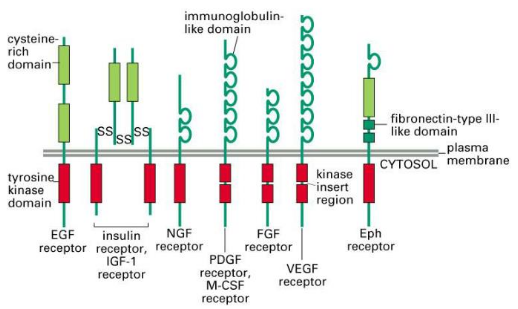 They all bind to Peptide Hormones.
They all bind to Peptide Hormones.
- I (EGF receptor family) (ErbB family (ErbB-1 to -4))
Ligand EGFR HER2 HER3 HER4 EGF + - - - TGF-α 1 + - - - NRG1 - - + + neuregulin 2 - - + + neuregulin 3 - - - + neuregulin 4 - - - + - II (Insulin Receptor family)
- Comes pre-dimerized out of the box!
- III (PDGF receptor family)
- IV (VEGF receptors family)
- V (FGF receptor family)
- VI (CCK receptor family)
- VII (Neurotrophin/NGF receptor family)
- VIII (HGF receptor family)
- IX (Eph receptor family)
- X (AXL receptor family)
- XI (TIE receptor family)
- XII (RYK receptor family)
- XIII (DDR receptor family)
- XIV (RET receptor family)
- XV (ROS receptor family)
- XVI (LTK receptor family)
- XVII (ROR receptor family)
- XVIII (MuSK receptor family)
- XIX (LMR receptor)
- XX (Undetermined)