REM
links: Sleep reference:
- https://men-elite.com/2020/02/18/how-to-optimize-sleep-for-better-life-performance/
- Effects of Diet on Sleep Quality
- https://supermemo.guru/wiki/NREM_and_REM_sleep 4-16-2021
REM #
- REM is actually the deepest form of sleep, which is why it’s called ‘paradoxical sleep’. What constitutes deepest? Not sure, considering the brain rhythms are most similar to waking.
- The release of Noradrenaline, Histamine (I think) and Serotonin are inhibited.
- Dopamine, Glutamate, and orexin are elevated, while during deep sleep, GABA, Adenosine, and Glycine are active.
- Carb oxidation is highest during REM.
- I think it’s related to activation of the parts of the brain related to sensory processing as opposed to the frontal lobe and is probably associated with acetylcholine/prolactin/low blood sugar. Low REM sleep means these stress hormones are low and CO2/blood sugar/progesterone is high
- Dreams are more likely to occur when the majority of slow waves (type II slow waves) are small, sparse, and shallow, especially in posterior brain regions and the content of dream experiences is more likely to be reported if, in addition, high-amplitude slow waves (type I slow waves) occur in frontocentral brain regions and are followed by high-frequency increases.
-
The (gamma) power to control our dreams
- Namely, in frontal or temporal regions of the brain. Associated wit conscious awareness and executive function.
- Induction of self awareness in dreams through frontal low current stimulation of gamma activity
- Initiated by glutamatergic REM-on neurons in the sublaterodorsal region.
Acetylcholine #
Highest out of any state of consciousness. REM and dreams are separate but temporally overalpping phenomena.
- Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptors Chrm1 and Chrm3 Are Essential for REM Sleep - becomes almost undetectable.
-
Circadian variation in the acetylcholinesterase activity of specific rat brain areas
- For RATS, AChE activity is highest during the light phase and lowest during the dark phase of the cycle in all the brain areas studied except the adenohypophysis, cerebellum, hippocampus and hypothalamus.
- But remember: rats are nocturnal. So for humans, in other words: Hippocampal etc. acetylcholine levels are REM>wakefulness>SWS.
- For RATS, AChE activity is highest during the light phase and lowest during the dark phase of the cycle in all the brain areas studied except the adenohypophysis, cerebellum, hippocampus and hypothalamus.
-
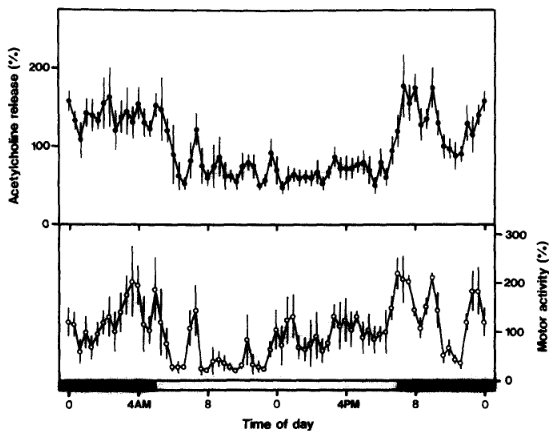
Acetylcholine release in the rat hippocampus as measured by the microdialysis method correlates with motor activity and exhibits a diurnal variation
-
-
Memory consolidation during sleep: a neurophysiological perspective (Buzsaki 1998) Buzsaki has a handful of these. #
-
Neuromodulation: acetylcholine and memory consolidation (Hasselmo 1999)
-
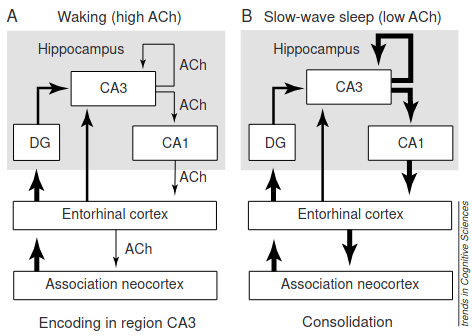
- This reminds me of the Executive Network vs the Default Mode Network, basically. I mean, how could there not be a hippocampal component?
- So yeah, it’s kind of weird how connections are formed by suppressing hippocampus->cortex information flow, but perhaps that’s consolidation without conscious control.
- ‘Association cortex’ is actually just areas not involved in primary sensory or motor processing. I think the temporal lobe/Perirhinal Cortex is what we’re dealing with.
-
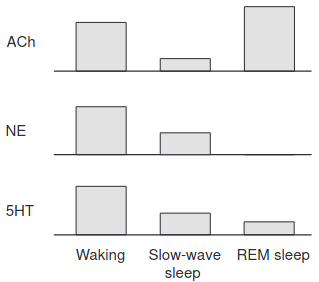
- 1st is taken from High acetylcholine levels set circuit dynamics for attention and encoding and low acetylcholine levels set dynamics for consolidation
- Neocortical information -> Entorhinal Cortex -> DG -> CA3.
- This type synaptic modification forms intermediate-term representation and binding of different elements of an episodic memory, with Ach suppressing connections of CA3->CA1.
- During deep sleep or ‘quiet waking’, memories are reactivated in the CA3 during ‘sharp waves’, which flow backwards: from the CA3 -> CA1 -> Entorhinal -> Neocortex.
- This enables ‘slow consolidation’ (formation of separate traces) of long-term episodic memory. Might underlie modification of semantic memory within circuits of the association neocortex.
-
-
High acetylcholine levels set circuit dynamics for attention and encoding and low acetylcholine levels set dynamics for consolidation (Hasselmo 2004) #
-
Neurocognitive aging: prior memories hinder new hippocampal encoding
-
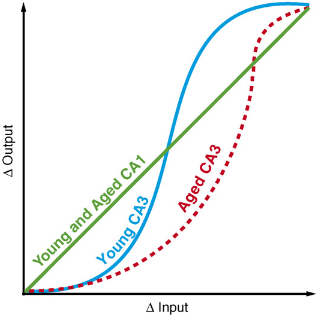
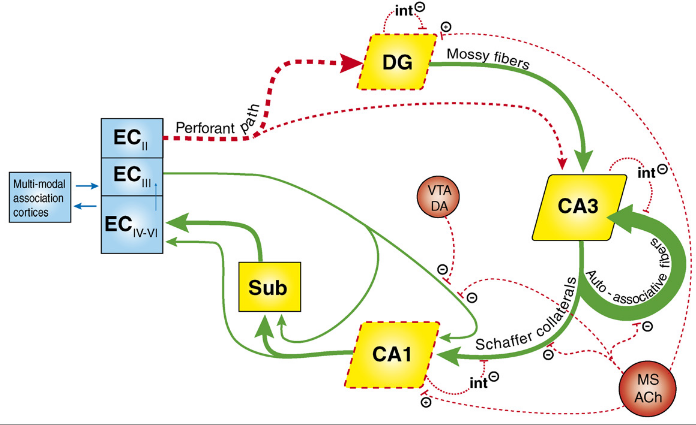 - The broken red lines are deteriorated in aging.
- The broken red lines are deteriorated in aging.
- I didn’t even know the Entorhinal Cortex had layers. Wish I knew what kind of DA neurons from the VTA inhibit the flow of information from EC-3 to CA1.
- Looks like muscarinic acetylcholine might even inhibit flow of information from the Dentate Gyrus to the CA3.
- Pattern Completion is also impaired:
-