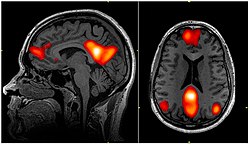
Default Mode Network
2022-03-04: As opposed to the Executive Network reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Default_mode_network
Default Mode Network
 #
#
-
You can see it’s primarily the Dorsomedial Prefrontal Cortex, Posterior Cingulate Cortex, Precuneus, and angular gyrus.
- There are also a few subnetworks:
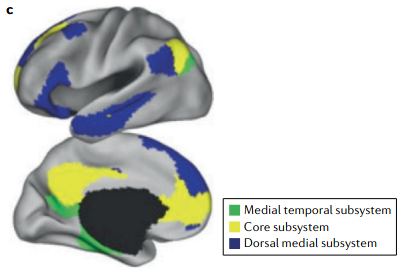
- There are also a few subnetworks:
-
The Unique Cytoarchitecture and Wiring of The Default Mode Network
- This is such a brilliant lecture for some reason. Casey Paquola - time to watch all her lectures.
- Basically to start, the DMN isn’t just task-negative: it’s activated during memory-related tasks, social cognition, etc., and they all depend on integration of internal and external information. That is one of the main functions of the DMN, as an association area.
- But not all tasks, of course. The DMN was first discovered through its tendency to deactivate in response to external task demands:
A default mode of brain function
- Furthermore, in RS-FMRI, in her words the “principal axis of differentiation”, there’s 2 kinds of gradients. One anchored by the DMN, the other anchored by sensory regions.
-
Situating the default-mode network along a principal gradient of macroscale cortical organization (Marguiles et al. 2016)
- Topographically, you can see it’s practically optimized to be maximally distant geodesically from the sensorimotor cortex.
- The default mode network in cognition: a topographical perspective (Smallwood, Marguiles et al., 2021)
-
Situating the default-mode network along a principal gradient of macroscale cortical organization (Marguiles et al. 2016)
- Furthermore, in RS-FMRI, in her words the “principal axis of differentiation”, there’s 2 kinds of gradients. One anchored by the DMN, the other anchored by sensory regions.
- But not all tasks, of course. The DMN was first discovered through its tendency to deactivate in response to external task demands:
A default mode of brain function
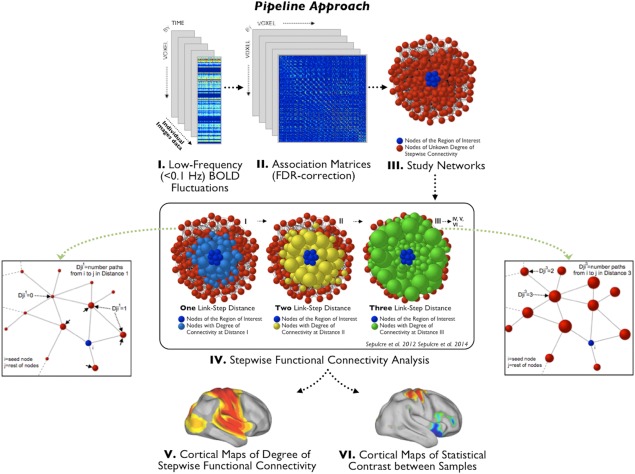
- Instroducing *stepwise fuectional connectivity:
Integration of visual and motor functional streams in the human brain (Sepulcre, 2012)
 (not the DMN here btw)
(not the DMN here btw)
- Later: Stepwise Connectivity of the Modal Cortex Reveals the Multimodal Organization of the Human Brain (Sepulcre et al., 2012)
-
Sensation‐to‐cognition cortical streams in attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder (Carmona,, et al. 2015)
- fMRI is used to calculate the connnectivity association matrix, then a binary connectivity matrix is computed.
-
- fMRI is used to calculate the connnectivity association matrix, then a binary connectivity matrix is computed.
-
From sensation to cognition (Mesulam 1998)a pretty seminal work regarding the Cortical Hierarchy.
- Decreasing laminar differetiation (that is, less diverse cell types) the more inward one goes.
- She references Gacia-Cabezas et al. where they talk about this model which is like a second-tier abstraction of the layers of the Cerebral Cortex.
-
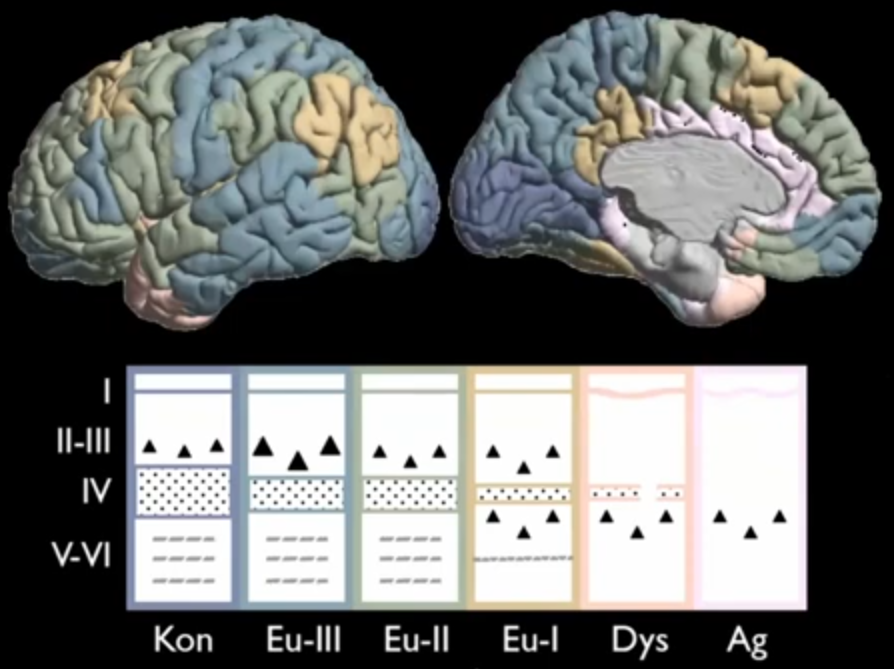
- Paquola found that the DMN overrepresents Eu-I - heteromodal.
- There’s 6 different “phenotypes” or whatever for which layers are populated in every given area (with what each layer itself is normally populated. of course). Koniocortex, Eulaminate III, II, I, Dysgranuolar, and Agranular.
-
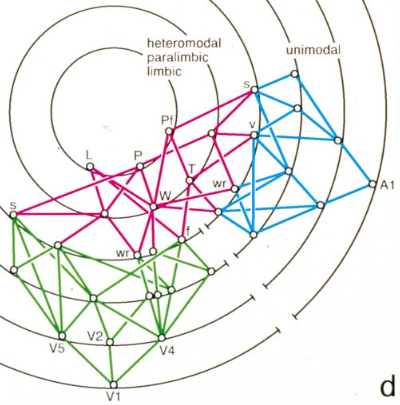
- Level 1 is occupied by the primary sensory cortex.
- Small empty circles represent macroscopic cortical areas or ‘nodes’, one to several centimetres in diameter. Nodes at the same synaptic level are reciprocally interconnected by the black arcs of the concentric rings.
- Coloured lines represent reciprocal monosynaptic connections from one synaptic level to another.
- Green = visual, blue = auditory, red = transmodal.
- I’m pretty sure both these models are describing the exact same thing: the innermost rings correspond to high-order, heteromodal processing, and thus the koniocortex, while the innermost rings are unimodal and associated with the sensory areas, with a lack of the Granule Cells associated with layer IV.
- (This makes sense since IV mainly receives thalamic afferents - what is the need?)
-
- Decreasing granularity the more outwards you go from V-VI to I.
- This provides a cytoarchitectural proxy for proximity to the external world vs. the internal milieu.
- Sensory information undergoes extensive associative elaboration and attentional modulation as it becomes incorporated into the texture of cognition.
- This process occurs along a core synaptic hierarchy which includes the primary sensory, upstream unimodal, downstream unimodal, heteromodal, paralimbic and limbic zones of the cerebral cortex
- The association cortex
- This process occurs along a core synaptic hierarchy which includes the primary sensory, upstream unimodal, downstream unimodal, heteromodal, paralimbic and limbic zones of the cerebral cortex
- A review based on this study:
Representation, inference, and transcendent encoding in neurocognitive networks of the human brain
- Here he seeks to emphasize the pallel (rather than serial), flow of information in the other direction.
- Consciousness appeared to be constructed from bottom up, one sensation at a time, through a process mirroring the progression from “simple” to “complex” and “hypercomplex” visual neurons delineated by Hubel and Wiesel. The frontal lobes were occasionally placed at the apex of this pyramid, as an obligatory portal into consciousness, reminiscent of the Cartesian theater where information from multipl esources was ushered into the pineal gland to be appre-hended by an immaterial soul.
-
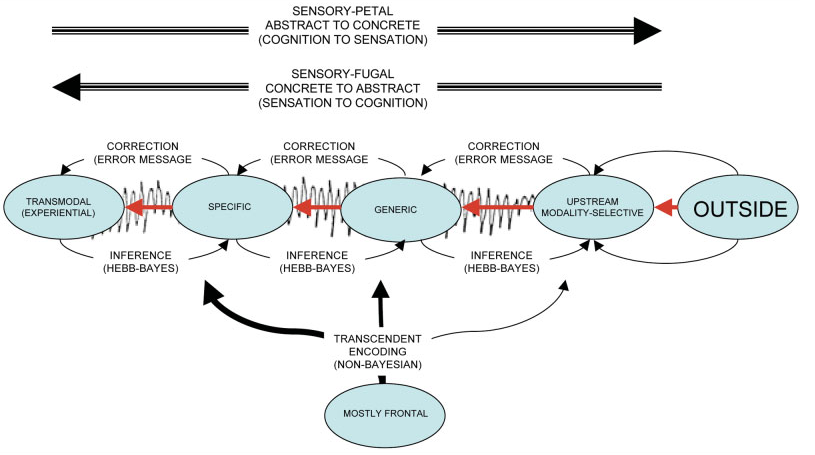
- In Bayesian brain: the cortex is poised to minimize uncertainty triggered by sensory stimuli, and association areas function to dampin this uncertainty by inferring their causesf their sensory inputs according to Bayes’ law and based on patterns established through Hebbian principles of coactivation in the course of past exposures to similar events
- Essentially, along each step of the sensory-fugal process, it triggers probabilistic predictions, and then the
- A theory of cortical responses (Friston 2005)
- In Bayesian brain: the cortex is poised to minimize uncertainty triggered by sensory stimuli, and association areas function to dampin this uncertainty by inferring their causesf their sensory inputs according to Bayes’ law and based on patterns established through Hebbian principles of coactivation in the course of past exposures to similar events
- Here he seeks to emphasize the pallel (rather than serial), flow of information in the other direction.
- In many models, the DMN is the apex of a Cortical Hierarchy of processing.
-
The Default Mode Network in Autism #