GRK
2022-04-21: reference: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6389790/ https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0005273606003774?via%3Dihub#fig1 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arrestin
GRK (GPCR kinase) #
- GRK1: Rhodopsin kinase
- I guess it’s just selective for rhodopsin.
- GRK2: β-adrenergic receptor kinase 1
- The RGS-homology (RH) domain of GRK2 and GRK3 binds to heterotrimeric G protein subunits of the Gq family, but despite these RH domains being unable to act as GTPase-activating proteins like traditional RGS proteins to turn off G protein signaling, this binding reduces Gq signaling by sequestering active G proteins away from their effector proteins
- GRK3: β-adrenergic receptor kinase 2
- GRK4: Polymorphism associated with hypertension
- Most high expression at the mRNA level
- GRK5: Polymorphism associated with cardioprotection
- GRK6:
- GRK7: Cone opsin kinase
- Non-visual GRKs are inhibited by Calmodulin, (as opposed to recoverin)
- GRK2 and GRK5 phsophorlyate PDGF and IGF
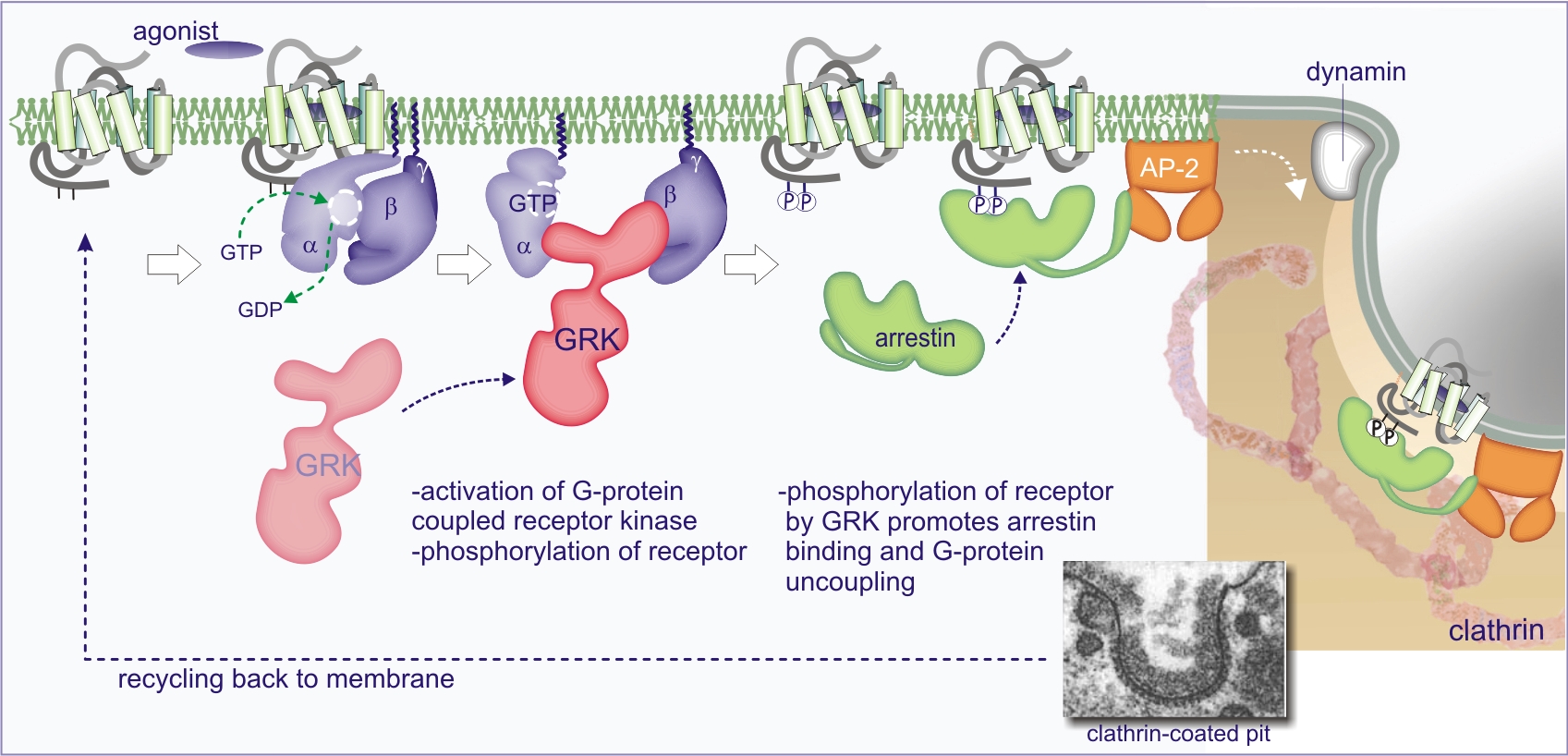
- The C-terminus of GPCR contains serine/threonine residues which are phosphorlyated by GRK after Gα-GTP activates it, increase the affinity for β-Arrestin binding:
- Which prevents G-protein coupling and instead recruits other proteins: *Several GPCRs can signal in a G-protein independent way via the arrestin adaptor proteins (see Section 2.5) to activate GSK-3β, ERK, or MAPK.
- Phosphorlyation targets the receptor for Clathrin-mediated endocytosis, which recycles the receptor back to the membrane. Seems complicated just for some dephosphorylation.
- Yeah, Gα-GDP is said to inhibit the phosphorylation of the attached receptor, but that might just be by, yknow, not being Gα-GTP.
-
The G protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK) interactome: Role of GRKs in GPCR regulation and signaling #