Ceramide
2022-08-11: reference:
Ceramide
 #
#
-
-
-
 is this comprehensive, or what? Not sure
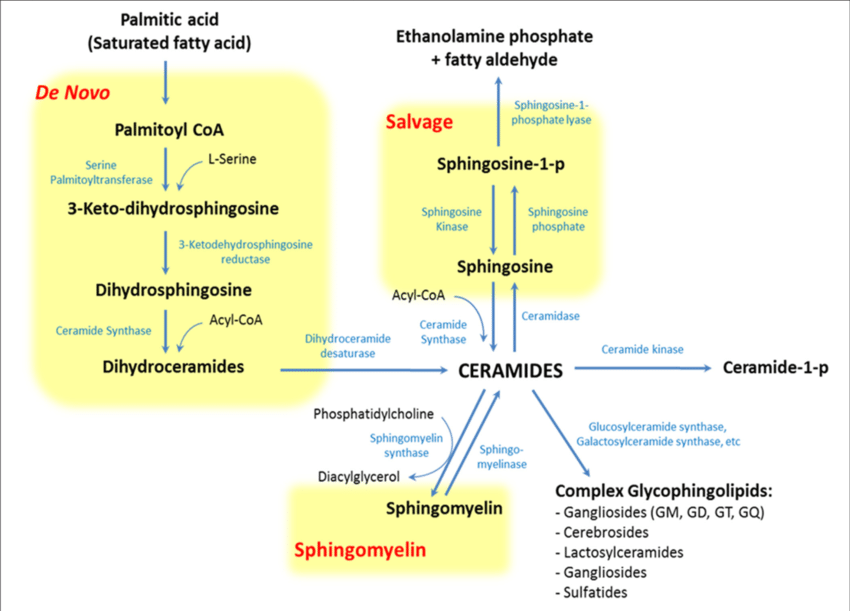
is this comprehensive, or what? Not sure - (They skipped 3-keto-dihydrosphingosine -> Sphinganine)
- There are 6 Ceramide Synthase subtypes each with fatty acid specificity:
- CerS1: Specifically Stearic Acid. Basically only in brain and skeletal muscle.
- CerS2: C20-26. Highest expression of all CerS in oligodendrocytes/Schwann cells.
- Indeed, this de novo synthesis of ceramide is the rate-limiting step of the synthesis of all the complex sphingolipids, sphingomyelin, and so on.
-
-

-
In schizophrenia’s structural sphingolipid abnormality, myelin-associated glycoprotein and myelin/oligodendrocyte glycoprotein are segregated from the lipid raft.
-
-
Similarly, The Role of Ceramides in Insulin Resistance (2019)
-
Ceramide function in the brain: when a slight tilt is enough
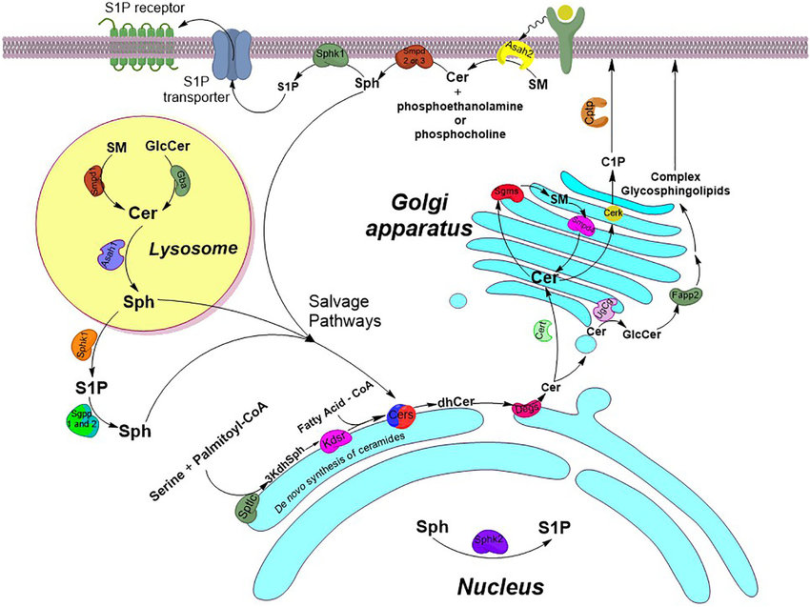
- De novo synthesis of ceramides takes place on the cytoplasmic face of the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum and in mitochondria.
-
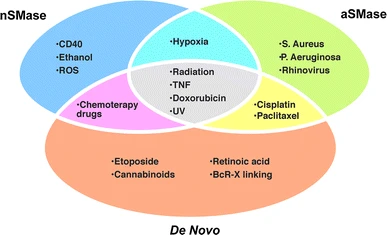 all these things stimulate. The study describes most of these things as ‘inducers of cell death’. Ceramide production results in cell deaht.
all these things stimulate. The study describes most of these things as ‘inducers of cell death’. Ceramide production results in cell deaht.
-
Ceramide channels and mitochondrial outer membrane permeability
- They permeabilize the Outer Mitochondrial Membrane
- The dogma in early mitochondrial research was that channels had to be small and highly selective.
- It is uncertain in which direction the influence is, but it synergizes with BAX in permeabilizing the MOM.
-
Bioactive sphingolipids in the modulation of the inflammatory response
- SphK1 and CERK1 are probably effectors of cytokine-mediated Prostaglandin generation in inflammatory conditions.
- It was shown that S1P pathway but not C1P pathway mediated IL-1β-mediated COX-2 induction.
- Ceramide-1-phosphate activates cPLA2.
- PLA2/COX-2 colocalized with the golgi and perinuclear regions in response to S1P/C1P treatment.
- LPS treatment produces rapid rise of ceramide in Macrophages. LPS as well as ceramide analogues induce TNF-α secretion. However, the fact that LPS but not ceramide analogues stimulated interferon activity suggested that ceramide induced only a subset of LPS-induced genes.
- SphK1 and CERK1 are probably effectors of cytokine-mediated Prostaglandin generation in inflammatory conditions.
-
Ceramide-1-phosphate (via ceramide kinase). This facilitates localization of p-Phospholipase A2 to the trans-Golgi
- Indeed it locazlies to the COX-2-localization site on the Outer Mitochondrial Membrane
-
Autophagy in the light of sphingolipid metabolism
- Promotes Ca2+-dependent Liposomeal fusion, enhancing vesicle fusion.
- C1P levels increase during phagocytosis, indicating that C1P may promote fusion between phagosomes and lysosomes
Neurodegenerative Disease #
-
Triangulated mal-signaling in Alzheimer’s disease: roles of neurotoxic ceramides, ER stress, and insulin resistance reviewed.
- Ceramide accumulation appears to be bidirectional with oxidative/ER stress and neuroinflammation.
-
Amyloid-β peptide induces oligodendrocyte death by activating the neutral sphingomyelinase–ceramide pathway
- Activates neutral sphingomyelinase - but not Acid Sphingomyelinase…
- Blocking ceramide degradation with Oleoylethanolamine exacerbated Aβ cytotoxicity.
- Addition of sphingomyelinase (from bacteria) induced Oligodendrocyte death.
- Astrocytic ceramide as possible indicator of neuroinflammation (In frontotemporal lobar dmentia Pick’s disease)
- Association between Plasma Ceramides and Phosphatidylcholines and Hippocampal Brain Volume in Late Onset Alzheimer’s Disease
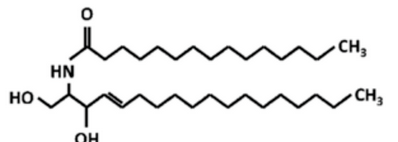
- I swear they can be as short as 14 carbons or as long as 26.
- Aging-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction mediated by ceramide signaling inhibits antitumor T cell response
Phytoceramide #
- Phytoceramide has an extra hydroxyl group.
- Administration of Phytoceramide Enhances Memory and Upregulates the Expression of pCREB and BDNF in Hippocampus of Mice