Apolipoprotein E
2022-02-08 links: Apolipoprotein reference: https://wiki.apoe4.info/wiki/Main_Page#Thiamine
Apolipoprotein E #
- Higher affinity with LDL Receptor with 2<3<4. Blocks insulin receptor?
- Produced by Astrocytes. The principal Cholesterol carrier/lipoprotein in the brain, required for transport of it between astrocytes and neurons via ApoE receptors like LRP.
- That being said, they’re all around the body, not just the brain. The liver, for instance.
- Increased DHA uptake with 2/3/4:
- Association of Docosahexaenoic Acid Supplementation With Alzheimer Disease Stage in Apolipoprotein E ε4 Carriers: A Review
- Association of Serum Docosahexaenoic Acid With Cerebral Amyloidosis
-
The effect of APOE genotype on the delivery of DHA to cerebrospinal fluid in Alzheimer’s disease
- After 18 months of DHA supplementation, participants at the lowest Aβ42 tertile had significantly lower CSF DHA levels, and lower CSF-to-plasma DHA ratios.
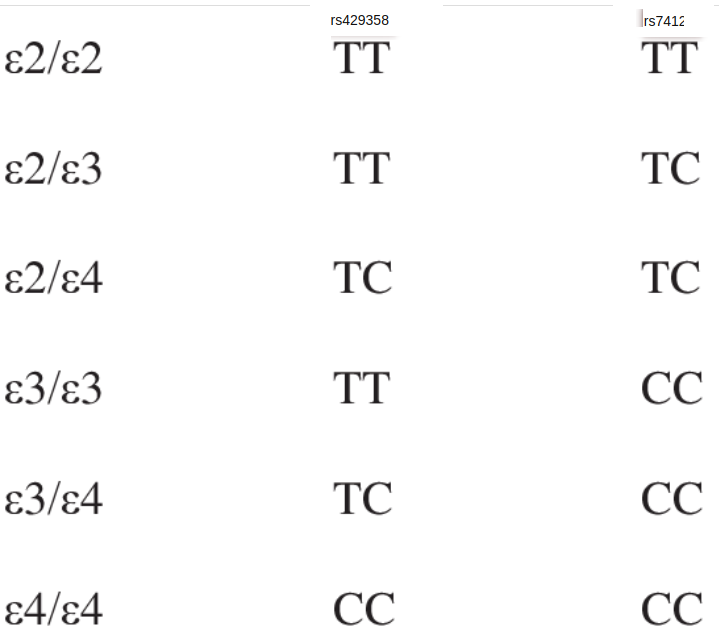
Genetics
 #
#
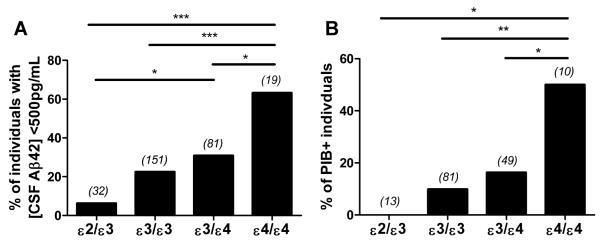
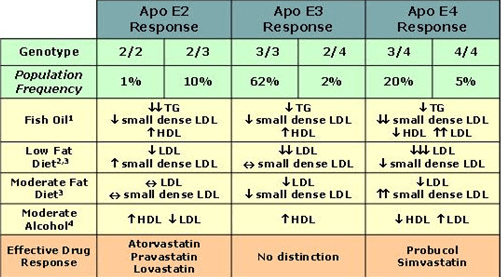 For 2/3/4, prevalence in the Alzheimer’s population is respectively 3.9%, 59.4%, 36.%.
For 2/3/4, prevalence in the Alzheimer’s population is respectively 3.9%, 59.4%, 36.%.
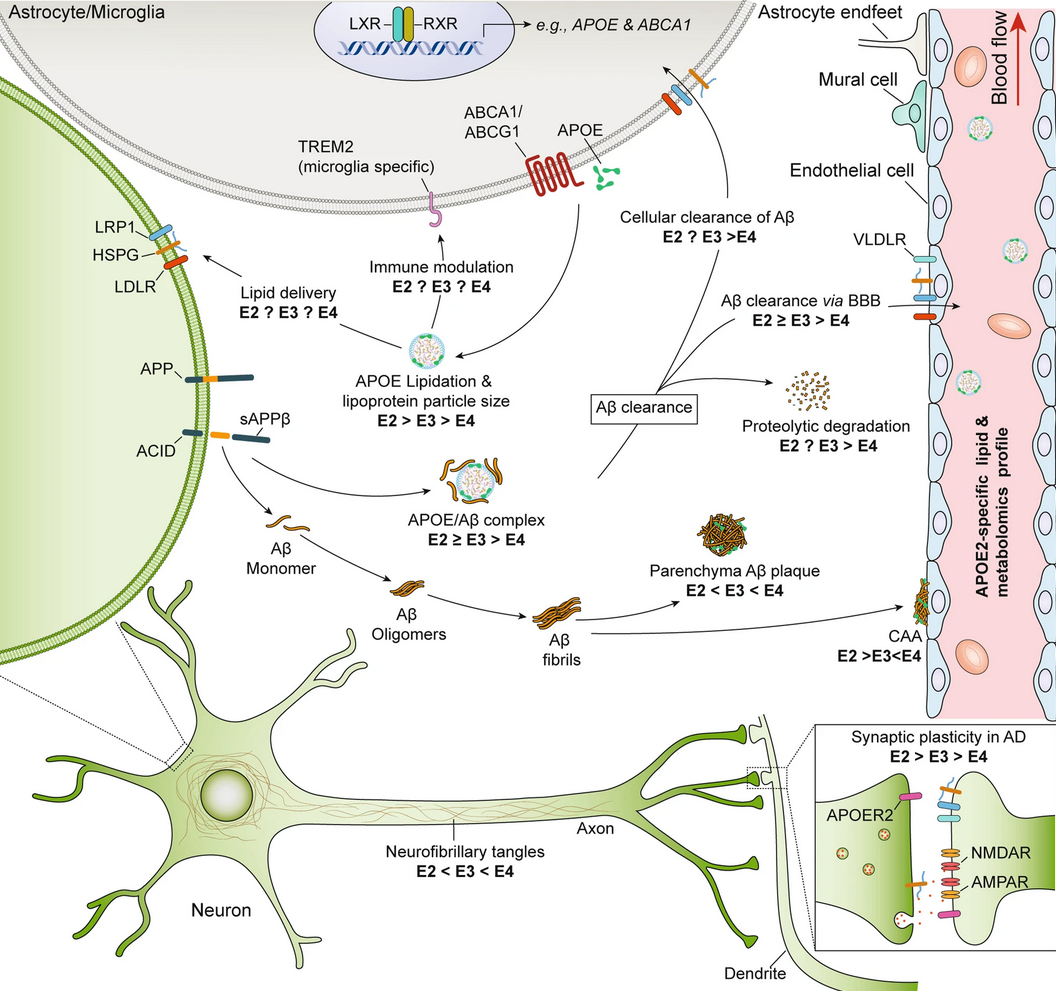
The Role of APOE4 in Disrupting the Homeostatic Functions of Astrocytes and Microglia in Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease #
-
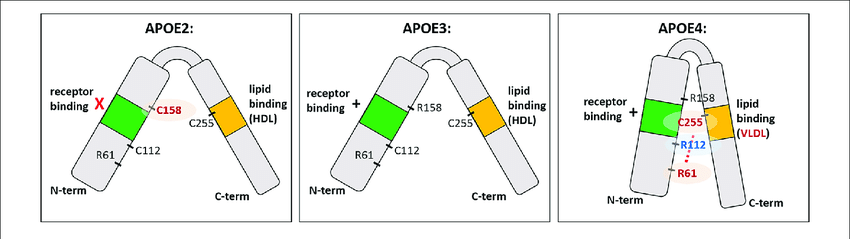
- So this tiny lipid binding region means it sucks at properly importing cholesterol into neurons, and binding to Aβ for export, since it can really only bind VLDL.
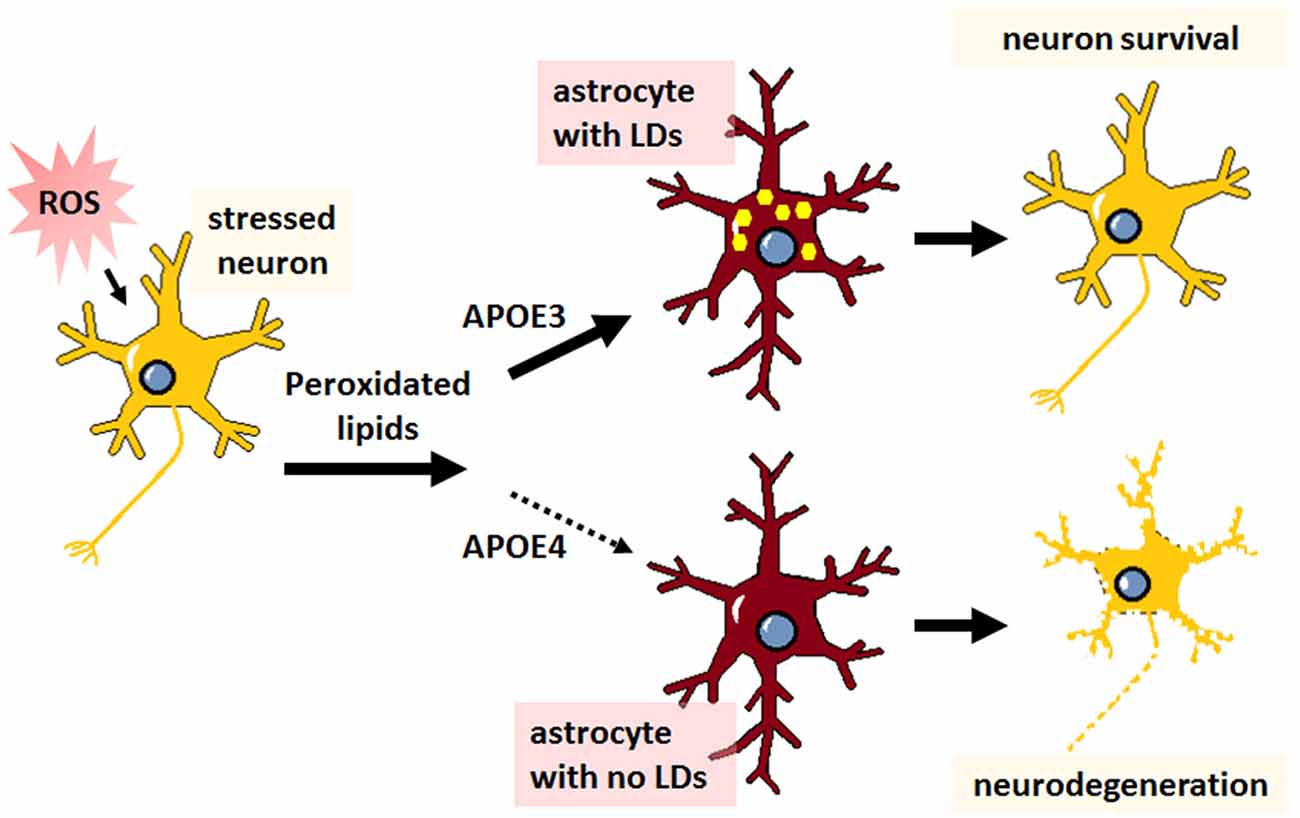
- The export of peroxidated lipids from neurons to astrocytes (lipid droplet formation) is impaired with ApoE4, leading to neurodegeneration:
 .
.
- Note that this is not cholesterol (though the previous figure does suggest an analogous phenotype with it) This study cites plenty of others with conflicting, paradoxical claims.
- ApoE4 leads to a ‘DAM (disease-associated microglial) transcriptomic phenotype’, which is apparently what the majority of GWAS alzheimer’s genes are implicated in causing.
- Aged (22 months) mice expressing APOE4 exhibit decreased insulin signaling in cortex and hippocampus: Apolipoprotein E4 Impairs Neuronal Insulin Signaling by Trapping Insulin Receptor in the Endosomes
-
Human ApoE Isoforms Differentially Modulate Brain Glucose and Ketone Body Metabolism: Implications for Alzheimer’s Disease Risk Reduction and Early Intervention
- Middle-aged (6 months) female APOE4 mice are deficient in the uptake and utilization of glucose in the brain, with compromised respiratory capacity and decreased PPAR-γ signaling
- Downregulated IGF-1, IRS-1, and GLUT4.
- Certain brain regions tend to preferentially use aerobic glycolysis ,and as the brain ages, there is a shift towards oxidative phosphorylation to meet energy requirements. This aging-related increased reliance on OxPhos has been proposed to lead to elevated ROS and peroxidated lipids
- Regional aerobic glycolysis in the human brain This cite, and reelated studies, seem juicy
-
Inhibition of glycogenolysis in astrocytes interrupts memory consolidation in young chickens &
Glycogen is a preferred glutamate precursor during learning in 1-day-old chick: biochemical and behavioral evidence
- This seems obvious, but then I realize this gives a major role for GSK-3β in driving neurodegeneration: Impairment in long-term memory formation and learning-dependent synaptic plasticity in mice lacking glycogen synthase in the brain
- Glycogenolysis disrupts LTP in young but not old rat hippocampus: . Glycogen Phosphorylase is predoinantly expressed in astrocytes, but in old animals is expressed in neurons, and neuronal Brain Glycogen accumulation triggers Apoptosis, so this upregulation is probably to keep neuronal glycogen stores low.
- Glycogen is still protective for neurons in low levels during Hypoxia.
- They go on to say that this protection provided by glycogen is likely indeed for lactate, a la the ANLS.
-
Altered Energy Metabolism Pathways in the Posterior Cingulate in Young Adult Apolipoprotein E ɛ4 Carriers
- Like the only thing that wasn’t increased was MCT1/MCT4, go figure: surely leads to a deficit in lactate secretion.
- The DMN relies on aerobic glycolysis in young,m healthy brain… the increased neuronal activity and decreased capacity of astrocytes to keep up with such activity in APOE4 carriers might then be expected to burn out glycogen stores early, effectively accelerating an aging-associated metabolic phenotype reliant on OxPhos.
-
Neuronal hyperactivity due to loss of inhibitory tone in APOE4 mice lacking Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology (Nuriel et al. 2017)
- In aged mice:
- Entorhinal Cortex hyperactivity in aged mice, associated with decreased background synaptic inhibition in layer II entorhinal Pyramidal Neurons.
- In aged mice:
- Default Mode Network is highly metabolically active and is one of the earliest regions to deteriorate in AD and in normal aging, and
-
Distinct patterns of brain activity in young carriers of the APOE-epsilon4 allele
- young APOE4 carriers exhibit increased activity in the DMN before any signs of disease (looks miniscule)
- The encoding task produced greater hippocampal activation in epsilon4-carriers relative to noncarriers. (more noticeable)
- Novel allele-dependent role for APOE in controlling the rate of synapse pruning by astrocytes ε2>ε3>ε4 phagocytotic capacity.