Apolipoprotein
2022-02-08 links: reference:
Apolipoprotein #
- Apolipoproteins are protein that forms lipoproteins via binding lipids, transporting them in blood, lymph, and CSF.
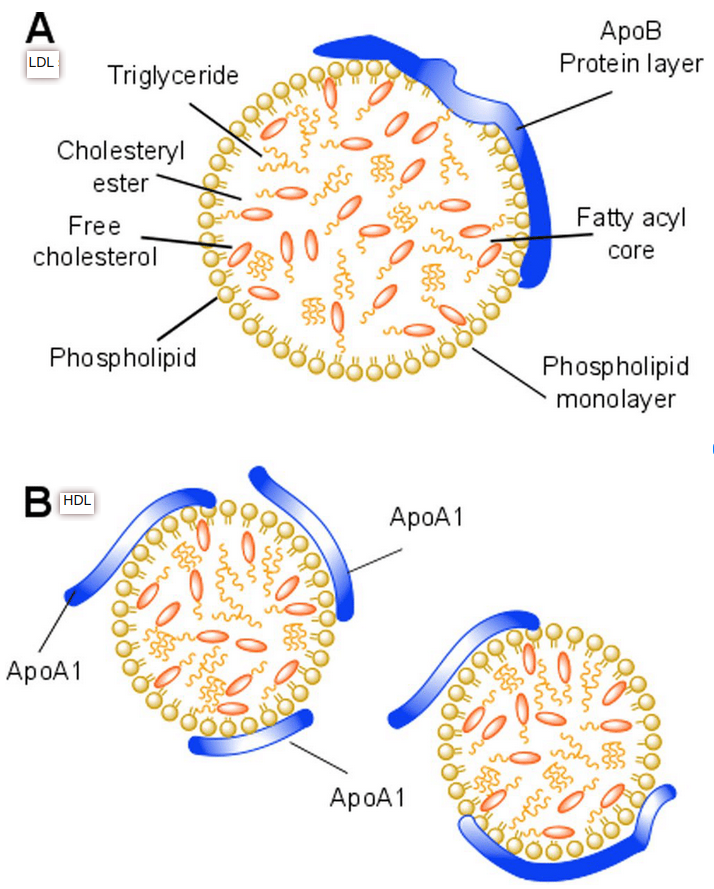 The apolipoproteins serve as enzyme activators, ligands for cell receptors, and provide structural stability.
The apolipoproteins serve as enzyme activators, ligands for cell receptors, and provide structural stability.
Classes #
- Apolipoprotein A: (NOT to be confused with Lipoprotein(a))
- ApoA-1: Major component of HDL. Activtes Lecithin and cholesterol acyltransferase. Chylomicron
- ApoA-2: HDL, chyomicron
- ApoA-4: Secreted with Chylomicrons but transfers to HDL
- ApoA-5
- Apolipoprotein B: Integral.
- ApoB-100: Major component of LDL. Synthesized in liver. Also VLDL/IDL
- ApoB-48: Chylomicron
- Apolipoprotein C: Peripheral
- ApoC-I: VLDL, HDL, chylomicron
- ApoC-II: VLDL, HDL, chylomicron
- ApoC-III: VLDL, HDL, chylomicron
- ApoC-IV:
- Apolipoprotein E: VLDL, HDL, Chylomicrons and their remnants
- Apolipoprotein D: Subfraction of HDL
- Apolipoprotein E:
- Apolipoprotein F:
- Apolipoprotein H:
- Apolipoprotein L:
- Apolipoprotein M: