TGF-β
2022-02-19 links: reference:
TGF-β (Transforming growth factor beta) #
Not to be confused with TNF-β. Isoforms are TGF-β 1-3.
-
Activates PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway, RhoA
-
Role of TGF-beta2 in the human hair cycle (2004)
- TGF-β2 suppresses proliferation of epithelial cells and stimulates synthesis of certain caspases. Then TGF-b2 triggers the intrinsic caspase network and subsequently epithelial cells are eliminated through apoptotic cell death.
- The ‘caspase network’ is gone into at length. They are essential in programmed cell death.
- The study goes into TGF-β at large. The distinction to ‘2’ I guess is minimal
- TGF-β2 suppresses proliferation of epithelial cells and stimulates synthesis of certain caspases. Then TGF-b2 triggers the intrinsic caspase network and subsequently epithelial cells are eliminated through apoptotic cell death.
-
TGF-β profoundly skewed the transcriptional program induced by the Wnt/β-catenin activator… impairs Fibroblast ability to support epithelial repair likely through multiple mechanisms, including modulation of secreted growth factors. R
-
Primary factor that drives fibrosis in most, if not all, forms of chronic kidney disease R
-
Increased concentrations are seen in blood/CSF of Alzheimer’s patients.
-
Decreased levels are seen in patients with Multiple Sclerosis, explainable by its role in regulating apoptosis of Th17 cells, which secrete TNF-α, inducing demyelination of oligodendroglial R. This study showed TGF-β induces oligodendrocyte growth outright?
-
Reduces subcutaneous fat, thus having a positive role in skin aging. Blocks conversion of dermal fibroblasts into fat cells.
-
Inverse relationship with IGF-1 production. Which doesn’t make much sense with M2 microglia.
Receptors #
- Activated TGF-β (can?) form(s) a Serine-Threonine Protein Kinase complex that binds to TGF-β receptors.
-
Type I: (activin-like receptors) #
2024-11-24:
TGF-β #
- Type II: after ligand binding, these phosphorylate→activate the type I receptors, which then autophosphorylate and bind to Smad2/3.
-
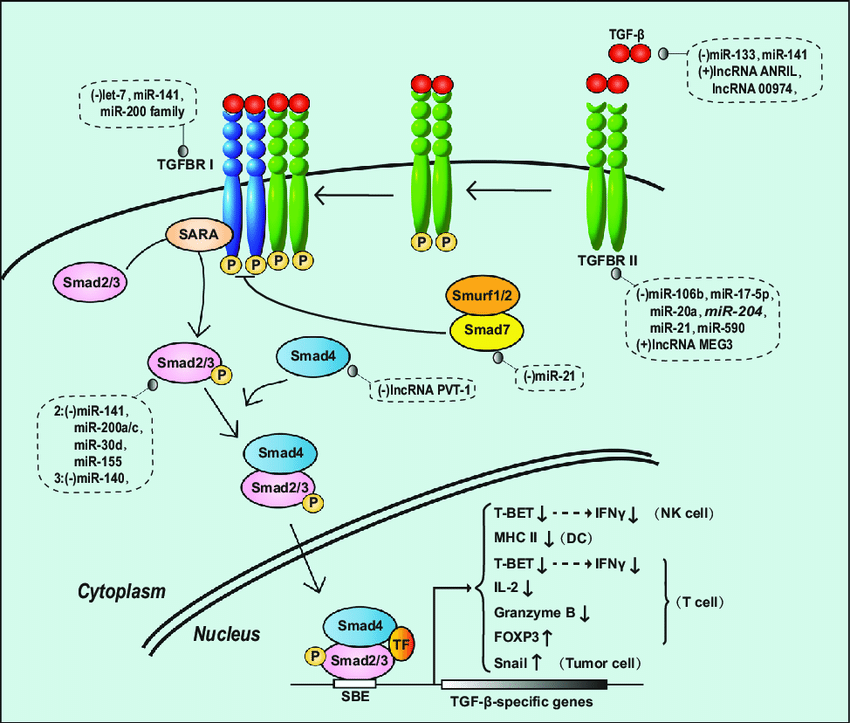
- There’s a lot more to the picture, trust me, namely RhoA, Ras, MAPK→JNK, Cdc42, PI3K activation.
-
- Type III: TGFβR3.