Rev-Erb
2022-05-19: reference:
Rev-Erb(A) (α/β) #
Rev-Erbα (NR1D) and Rev-Erbβ (NR1D2) (aka αβ). Nuclear receptor transcription factors for the circadian clock.
- Rev-Erbα is also expressed in muscle, adipose tissue, and liver. Regulates Fatty Acid Synthase.
- TLR4 antagonist.
- Detects Heme, its endogenous ligand. Whatever that’s worth.
-
Rev-erb-α modulates skeletal muscle oxidative capacity by regulating mitochondrial biogenesis and autophagy
- Activates the Stk11–AMPK–SIRT1–PGC-1α signaling pathway.
- Indeed, STK11 (aka LKB1 (liver kinase B)) activates AMPK. mRNA levels are Increased by ERα activation.
- Inhibits mitophagy. (Thereby increasing mitochondrial content and oxidative capacity of myocytes)
- A Rev-erb-α/Ppargc1-α cross-talk pathway regulates heme synthesis in hepatic cells:
- increase in glutamate-malate-stimulated and ADP-driven respiration in absence and presence of succinate of permeabilized fibers
- Represses genes involved in autophagosome formation and lysosomal degradation.
- Activates the Stk11–AMPK–SIRT1–PGC-1α signaling pathway.
- Nuclear receptor Rev-erbα: up, down, and all around (2014)
-
Nuclear receptor Rev-erbα: a heme receptor that coordinates circadian rhythm and metabolism (2010)
- Rev-Erb α dimers on RORE recruit NCoR (nuclear corepressor 1) in a Heme-dependent manner. NCoR recruits HDAC3
- Heme binding to Rev-Erbα induces feedback inhibition of its own synthesis (reducing ALAS1, via NPAS2/PGC-1α)
- In Brown Adipose (but not the liver), it promotes UCP1.
-
Rev-erbα and Rev-erbβ coordinately protect the circadian clock and normal metabolic function
- Peaks in the liver (and brown adipose tissue. Wonder about the brain?) at mouse ZT 10 (and α is a bit higher):
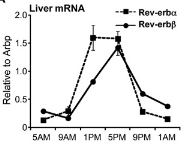 but so what, is this equivalent to 2 hours (before? After?) waking for humans? Considering that’s probably when they get up to start the
but so what, is this equivalent to 2 hours (before? After?) waking for humans? Considering that’s probably when they get up to start the daynight.
- Peaks in the liver (and brown adipose tissue. Wonder about the brain?) at mouse ZT 10 (and α is a bit higher):
-
Behavioral Changes and Dopaminergic Dysregulation in Mice Lacking the Nuclear Receptor Rev-erbα
- Deficient mice had upregulation of Tyrosine Hydroxylase, leading to increased hippocampal dopamine turnover. This lead to hyperlocomotion.
- This one is kind of surprising, maybe. Why does it repress TH?
- Decreased habituation in novel object paradigms and impaired short- and long-term memory.
- Deficient mice had upregulation of Tyrosine Hydroxylase, leading to increased hippocampal dopamine turnover. This lead to hyperlocomotion.
Rev-Erb β #
- Was originally thought to be reduntant, but it does have some distinct actions apparently.