PPAR
2022-02-01 links: reference: Travis - PPARs And Keratin
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor #
Transcription factors and nuclear receptor proteins. They all dimerize with RXR.
-
There are:
-
α, β/δ (same thing I guess), γ1, γ2, γ3 types.
-
PPAR-β/δ competes with PPAR-α and PPAR-γ. Downregulation of β/δ can increase Keratin 20 expression several fold.
-
Overexpression of PPAR-γ on the skin protects rats against Hair Loss.
-
PPAR-γ agonists administered to the brain increase insulin transport/sensitivity to the brain.
-
- [Inhibition of Peroxisome Proliferator Signaling Pathways by Thyroid Hormone Receptor: Competitive Binding to the Response Element]
- I.e. thyroid hormone (-RXR heteromers) binds to PPRE, inhibiting it.
- Both PPAR and TR bind to PPRE although only PPAR mediates transcriptional activation via PPRE. TRzRXR heterodimers are potential competitors with PPAR•RXR for binding to PPREs.
- Thyroid hormone response element and PP response element have an almost perfectly inverse relationship:
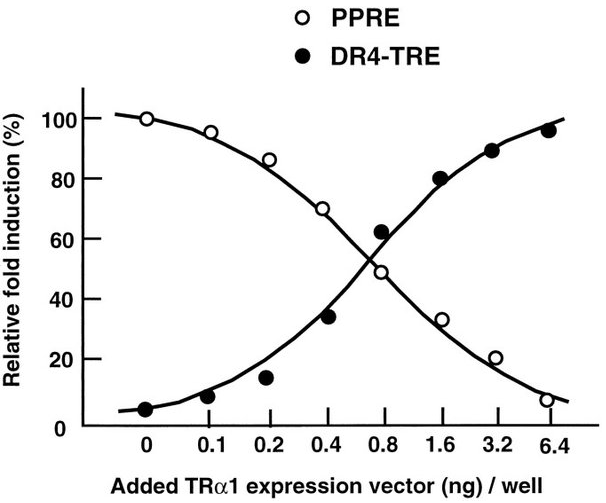
- [Inhibition of Peroxisome Proliferator Signaling Pathways by Thyroid Hormone Receptor: Competitive Binding to the Response Element]
-
Androgens increase the expression of PPAR-α1 PPAR γ coactivator
-
Causes and consequences of low grade endotoxemia and inflammatory diseases
- the expression of PPARs promotes an M2 polarization and is responsible for maintaining the basal anti-inflammatory tone of adipose tissue via promoting the co-repression of pro-inflammatory genes through co-repressors nuclear receptor corepressor 1 or 2 (NCoR). However, in our studies and in others, PPAR expression is inhibited after TLR4 stimulation by LPS, and complete knock out of this nuclear receptor promotes inflammation and IR.
-
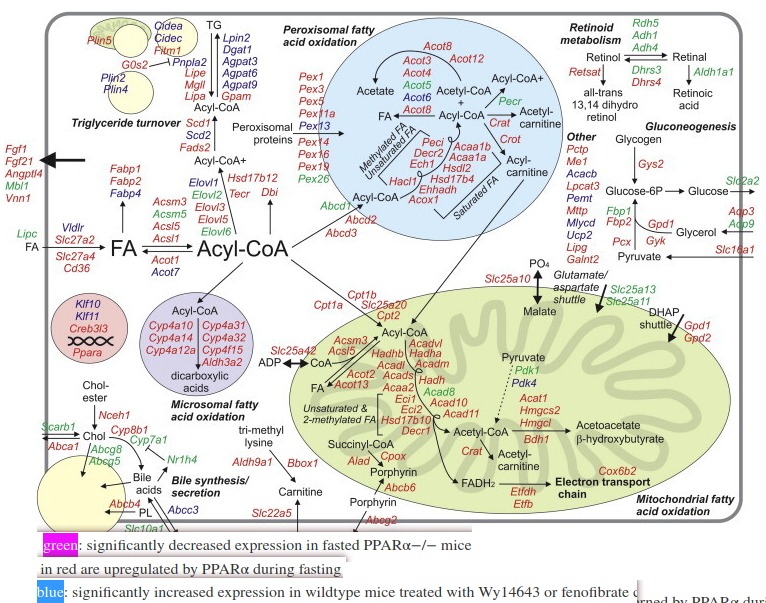
- (Wy14643 = PPARα agonist)