Bupropion
2022-08-10: Drugs reference:
Bupropion (Wellbutrin/Zyban) #
- Atypical antidepressant. NET/DAT (in high doses) inhibitor and non-competitive antagonist of α4β2, α3β4 nAChR, and α1β1γδ.
-
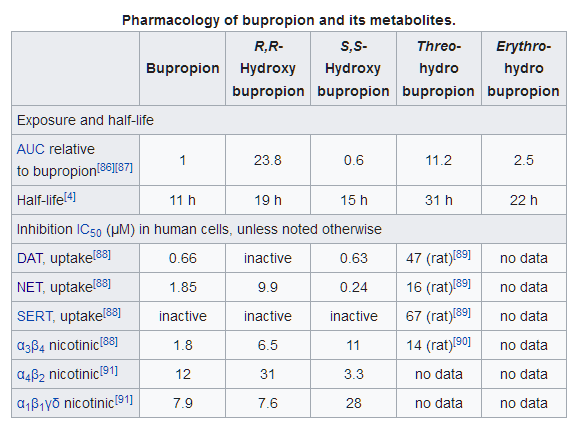
- Compare to dl-Methylphenidate’s DAT/NET IC50 of 20 and 51 respectively (.35 vs .39 ratio). The difference is in the metabolites as you can see.
-
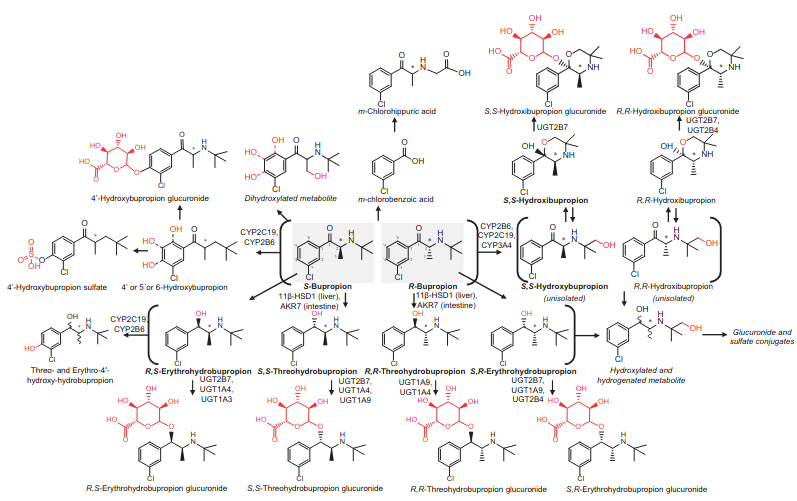
- Associated with a high risk of release of mediators from mast cells. I don’t think it activates H1 though.
-
Psychopharmacology of bupropion in normal volunteers.
- α3β4 nAChR antagonism isn’t cognitively impairing.
- [Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic of bupropion: integrative overview of relevant clinical and forensic aspects]
- Dwoskin (2006) can exacerbate depression and increase suicidal thoughts.
- Should be administered early in the morning as it exacerbates insomnia.
- Vivid dreams, hallucinations, unusual thoughts/behavior, confusion, tremors, agitation, anxiety, swollen glands, joint pain, increased blood pressure
- Non-competitive antagonist of nAChR. Never thought about this before; is that implied???
- Inhibits CYP2D6 (58 mM IC50?)
- [Seizures after overdoses of bupropion intake]
- Pronounced increase in catecholamines is the main factor, I believe. QT prolongation can be seen.
- [Alcohol significantly lowers the seizure threshold in mice when co-administered with bupropion hydrochloride]
- In mice, 116mg/kg (660 HED) without, or 89.4 for ethanol/bupropion.
-
Bupropion increases striatal vesicular monoamine transport
- Rapidly, reversibly, and dose-dependently increased vesicular DA uptake; an effect also associated with VMAT2 protein redistribution.
Antidepressive Mechanism #
-
Molecular interaction of bupropion with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
- Where in the brain it binds is important: *binds to presynaptic α4β2 nAChR on GABAergic neurons in the Ventral Tegmental Area and α3β4 nAChR in the habenulo-intrerpeduncular pathway.
- Bnding affinity for α4 is rougly equal to α1.
- Recent Developments in Novel Antidepressants Targeting α4β2-Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
-
Acute effect of the anti-addiction drug bupropion on extracellular dopamine concentrations in the human striatum: An 11C raclopride PET study
- Bupropion , 100 mg, had no effect alone but abolished the sedation and auditory vigilance impairment produced by alcohol when co-administered.
Dose #
- 150mg twice daily = ~26% DAT occupance.
- ~5% oral bioavailability; extensive first-pass metabolism (does that mean hella CYP2B6 metabolites?)