α4β2 nAChR
2022-02-18 links: reference:
α4β2 nAChR #
- Partial agonist is cnognitively enhancing, and doesn’t cause behavioral sensitization. Sirsad might get TC-1734 synthesized
- Estradiol is a PAM. Zinc potentiates α4-containing somehow.
- Selective a4b2 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Agonists Target Epigenetic Mechanisms in Cortical GABAergic Neurons
- Stimulation is associated with Growth Hormone secretion.
-
Association of a Nicotinic Receptor Mutation with Reduced Height and Blunted Physostigmine-Stimulated Growth Hormone Release
- People with the inactive CHRNA4 mutation Ser248Phe are an average of 10 cm (4 inches) shorter than average and predisposed to obesity
-
Association of a Nicotinic Receptor Mutation with Reduced Height and Blunted Physostigmine-Stimulated Growth Hormone Release
- Stimulation of dopamine release by nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligands in rat brain slices correlates with the profile of high, but not low, sensitivity α4β2 subunit combination (i.e. stimulating α4₃β2₂)
Structure #
- Can have 3 or 2 of each: $α4_2β2_3$ has high sensitivity to Nicotine, lower sensitivity to acetylcholine, and a low Ca2+ permeability relative to $α4_3β2_2$ (which has another binding site)
- So what does that even tell us about the net effect of nicotine administration? No idea really.
- Two distinct allosteric binding sites at α4β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors revealed by NS206 and NS9283 give unique insights to binding activity-associated linkage at Cys-loop receptors
Subtypes
 #
#
-
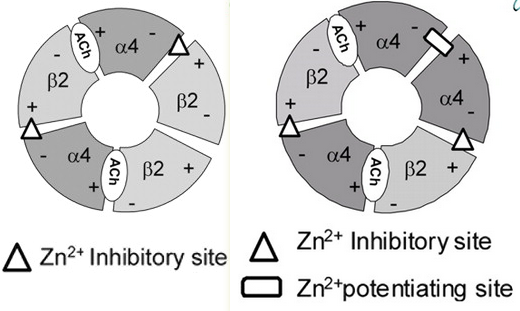
Additional Acetylcholine (ACh) Binding Site at α4/α4 Interface of (α4β2)2α4 Nicotinic Receptor Influences Agonist Sensitivity in other words, just $α4_3β2_2$.
- Notice the isoform-specific β2-β2 vs α4-α4 interfaces:
- Agonist occupation of the α4(+)-α4(-) interface leads to channel gating. α4-α4 contains a Zn2+ site that either inhibits or potentiates depending on its concentration, whereas the β2-α4 homology is only an inhibitory site.
- Previously:
Non-Agonist-Binding Subunit Interfaces Confer Distinct Functional Signatures to the Alternate Stoichiometries of the α4β2 Nicotinic Receptor: An α4–α4 Interface Is Required for Zn2+ Potentiation
- Zn2+ inhibition is voltage-dependent on (α4)2(β2)3 but not on (α4)3(β2)2.
- Previously:
Non-Agonist-Binding Subunit Interfaces Confer Distinct Functional Signatures to the Alternate Stoichiometries of the α4β2 Nicotinic Receptor: An α4–α4 Interface Is Required for Zn2+ Potentiation
- Agonist occupation of the α4(+)-α4(-) interface leads to channel gating. α4-α4 contains a Zn2+ site that either inhibits or potentiates depending on its concentration, whereas the β2-α4 homology is only an inhibitory site.
- Notice the isoform-specific β2-β2 vs α4-α4 interfaces:
Desensitization #
-
Regulation of α4β2 Nicotinic Receptor Desensitization by Calcium and Protein Kinase C
- After prolonged nicotine treatment, α4β2 nAChRs accumulate in a “deep” desensitized state, from which recovery is very slow. We suggest that PKC-dependent phosphorylation of α4 subunits changes the rates governing the transitions from “deep” to “shallow” desensitized conformations and effectively increases the overall rate of recovery from desensitization. Long-lasting dephosphorylation may underlie the “permanent” inactivation of α4β2 receptors observed after chronic Nicotine treatment
- PKC enhanced rate of recovery: α4β2 receptors containing a mutant α4 subunit that lacks a consensus PKC phosphorylation site exhibited little recovery from desensitization.
-
Recovery from desensitization of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors of rat chromaffin cells is modulated by intracellular calcium through distinct second messengers
- Desensitization of nAChRs, evoked by 2 sec focal application of nicotine, which largely raised [Ca2+]i, was not affected by intracellular application of agents that activate or depress protein kinase C (PKC) or A (PKA) or inhibit phosphatase 1, 2 A and B.
Expression #
- Located on MSNs. Not sure where else it’s mostly expressed besides the stritum. Both post- and pre-synaptic.
- Higher availability of α4β2 nicotinic receptors (nAChRs) in dorsal ACC is linked to more efficient interference control
- Finds itself on GABAergic neurons in the VTA.