Allopregnanolone
links: Steroid reference: 4-11-2021
Allopregnanolone (3α-tetrahydroprogesterone) #
Endozepine.
- Made from 5α-DHP via 3α-HSD.
- Used for treatment of postpartum depression, since it nosedives after giving birth.
-
Tolerance to allopregnanolone with focus on the GABA-A receptor
- GABA-A agonist. Chronic administration/stimulation can cause tolerance causing GABA-A endocytosis (decrease in its α4 subunit and its expression in thalamus)
- Tetrahydro-deoxyCorticosterone and AlloP during stress are correlated to cortisol and eachother, and are stimulated by Corticotrophin-releasing hormone and Adrenocortocotropic Hormone.
- Excess GABA-A stimulation increases synthesis/release of Neuropeptide FF.
- Really short half life if supplementing
-
Prefrontal allopregnanolone mediates the adverse effects of acute stress in a mouse model of tic pathophysiology
- Related:
Upregulation of neurosteroid biosynthesis as a pharmacological strategy to improve behavioral deficits in a putative mouse model of PTSD (2013)
- Upregulation of allopregnanolone biosynthesis in corticolimbic neurons may offer a novel non-traditional pharmacological target for a new generation of potent non-sedating, anxiolytic medications for the treatment of anxiety, depression, and PTSD: selective brain steroidogenic stimulants (SBSSs).
- Related:
Upregulation of neurosteroid biosynthesis as a pharmacological strategy to improve behavioral deficits in a putative mouse model of PTSD (2013)
Hepatic Encephalopathy #
-
Increased levels of pregnenolone and its neuroactive metabolite allopregnanolone in autopsied brain tissue from cirrhotic patients who died in hepatic coma
- It has been suggested that neurosteroids with agonist properties at the central GABA-A receptor are implicated in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy (HE) in chronic liver disease.
-
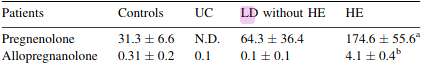 (LD=liver disease)
(LD=liver disease)
- These neurosteroid increases are consistent with PTBR activation in HE (peripheral-tupe benzodiazepine receptor)
- Brain concentrations of benzodiazepine receptor ligands estimated by radioreceptor assay were not significantly increased in cirrhotic patients with or without hepatic coma.
- ==
Altered glial–neuronal crosstalk: Cornerstone in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy==
- HE is characterized by strocyte swelling, microglial activation and Alzheimer’s Type II astrocytosis.
- early losses of expression of GFAP and EAAT2 with concomitant increases of the astrocytic/microglial mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptor (MBR).
- Nitration of tyrosine residues on key astroglial proteins such as Glutamine Synthetase and the MBR.
- Glutamine Synthetase is uniquely responsible for the removal of excess ammonia in brain. - this seems to be true if I look up how ammonia is cleared from the brainej
- Protein nitration = oxidative stress reaction; disables function. It defeated its enemy.
- Reversible inhibition of mammalian glutamine synthetase by tyrosine nitration
- Wait… why doesn’t this increase glutamatergic tone? Indeed GS activity decreases, and glutamine increases stil more, probably via inhibition of Glutaminase cellular glutamine release.
- But nonetheless, ammonia activates MBR too despite nitration.
- Increased extracellular glutamate, activation of the NMDA receptor-mediated cGMP-NO signal transduction pathway (such as what is seen in hyperAmmonia in Gonzalez-Usano et al. 2013)
- Attenuation of microglial activation by minocycline results in a delay in onset of HE and prevents brain edema in liver failure.
-
Stress steroids as accelerators of Alzheimer’s disease.: Effects of chronically elevated levels of allopregnanolone in transgenic AD models. - there is a longer full text
- Later work:
Brief but chronic increase in allopregnanolone cause accelerated AD pathology differently in two mouse models
- Teatment with allopregnanolone (ALLO) for one - or, shown previously, three months impaired learning function in the Swe/PS1 mouse model.
- Swe = swedish mutation which increases Aβ production. PS1= increases production of the more toxic Aβ42 instead of Aβ40. Arc = arctic mutation, which is primarily Aβ40 and a less hydrophilic αB more prone to form oligomers and fibrils.
- 1 month with elevated ALLO levels within physiological range impaired learning and memory function in the Swe/Arc female and male mice. Male Swe/PS1 mice also showed marginally impaired function, while the female mice did not.
- the chronic ALLO treatment caused increased levels of soluble Amyloid β in the Swe/PS1 mouse model while the levels were unchanged in the Swe/Arc model.
- Teatment with allopregnanolone (ALLO) for one - or, shown previously, three months impaired learning function in the Swe/PS1 mouse model.
- Increased during stress via the Adrenal Gland as well as indirect production in the brain.
- Decreased levels in last stage Alzheimer’s. Increased during the progesterone peak of the menstural cycle, and during gestation.
- Later work:
Brief but chronic increase in allopregnanolone cause accelerated AD pathology differently in two mouse models
-
Long-term continuous allopregnanolone elevation causes memory decline and hippocampus shrinkage, in female wild-type B6 mice - ScienceDirect
- Female mice showed increased Cerebellum weight and shrinkage of hippocampus, males did not change brain anatomy.
-
Neurosteroids in hepatic encephalopathy: Novel insights and new therapeutic opportunities
- Astrocyte swelling (cytotoxic brain edema), Alzheimer type 2 astrocytosis in cirrhosis, etc.
- Activation of TSPO sites results in increased cholesterol transport into the mitochondrion followed by stimulation of a metabolic pathway culminating in the synthesis of allopregnanolone (ALLO) and tetrahydrodeoxycorticosterone (THDOC),
- Treatment with 3α-HSD inhibitors like indomethacin improves activity in animals. They say nothing on it changing actual pathogenesis, but of course it improves learning and coordination and stuff.
- Increased brain concentrations of endogenous (non-benzodiazepine) GABA-A receptor ligands in human hepatic encephalopathy