Mildronate
links: reference: 10-29-2021
Mildronate (trade name of Meldonium) #
- Contained in Coconut apparently.
- Protects cells against stress partly by antagonizing Carnitine synthesis and transport. Carnitine transports long-chain fatty acids into the cell - therefore this inhibits Beta-oxidation.
- Specifically, I think it inhibits γ-butyrobetaine hydroxylase.
- For other FAO inhibitors, see also Trimetazidine.
- Banned by WADA for its endurance-enhancing effects.
-
Long-term mildronate treatment increased Proteobacteria level in gut microbiome, and caused behavioral deviations and transcriptome change in liver, heart and brain of healthy mice 100mg/kg for 8 weeks. (1.2g or so HED). Then, 4 weeks of continuing or having stopped.
- “Glucose oxidation is energetically less beneficial”, citing this lovely study funded by Novartis Choosing the right substrate
- Mildronate treatment also induced some behavioral changes
-
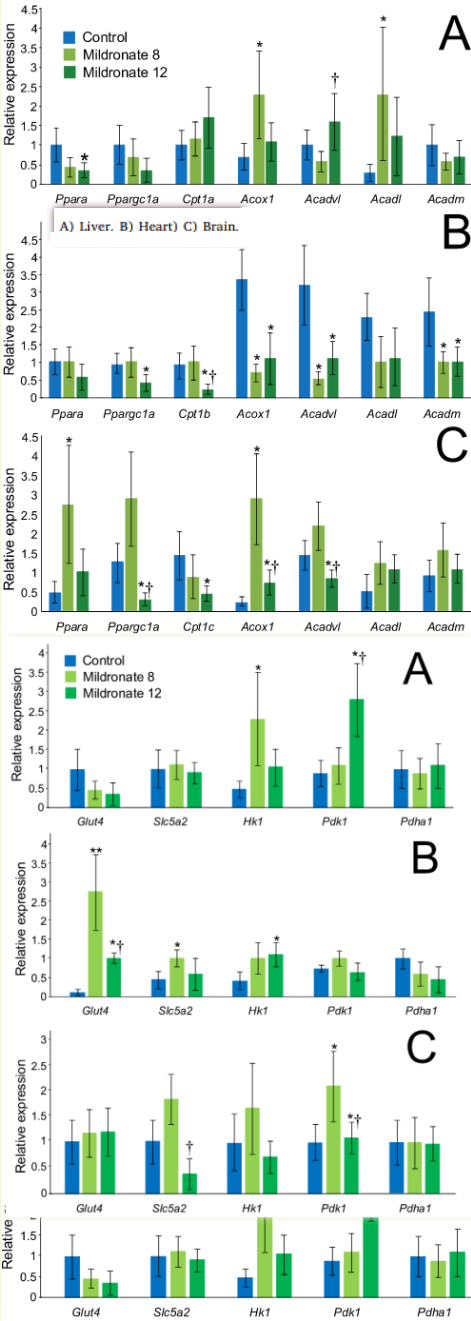 such as anxiety-related behavior and diminished explorative behavior
such as anxiety-related behavior and diminished explorative behavior
- Effect of l-carnitine and mildronate on the mitochondrial metabolism of heart and bacterial composition of the gut microbiome in ageing mice
-
RPF/Haidut: Heart Muscle Favors Ketones?
- Cardiac/skeletal muscle oxidizes fat at rest but incorporates glucose under stress or lack of oxygen.
- Peat: Heart and hormones
- Administration of L-carnitine and mildronate improves endothelial function and decreases mortality in hypertensive Dahl rats
-
Study of the effect of an inhibitor of carnitine-dependent metabolism of mildronate on the oxidation of fatty acids in the liver mitochondria of intact rats
- mildronate stimulated the carnitine-independent fatty acid oxidation which appears to occur as a compensation for inhibition of the carn itine-dependent oxidation by the drug.
- Wtf is this study?
Regulation of Lipid Flux between Liver and Adipose Tissue during Transient Hepatic Steatosis in Carnitine-depleted Rats
- up-regulation of liver activities, peripheral lipolysis, and lipoprotein lipase activity were likely essential factors for excess fat deposit and release alternately occurring in liver and adipose tissue of carnitine-depleted rats during the fed/fasted transition.