@Neurosteroids modulate compulsive and persistent behavior in rodents Implications for obsessive–compulsive disorder (Umathe et al. 2009)
2022-02-15 links:
@Neurosteroids modulate compulsive and persistent behavior in rodents Implications for obsessive–compulsive disorder (Umathe et al., 2009) #
-
This study uses marble-burying as a proxy for OCD in mice. Sure
-
Spontaneous alternation (SAB) is the tendency to alternate in their pursuit of different stimuli despite reinforcement. It’s basically a proxy of exploratory behavior. It requires optimal spatial working memory. It reduces with ageing (begins to reduce in mice 9 and 12 months) and with lesions in regions like the hippocampus.
-
Restraint stress: placing the mouse in inescapable plastic tubes or something: increases allopregnanolone. Isolation stress decreases it. Exposure to either is still in line with its negative correlation with marble-burying behavior.
- Restrain stress-induced attenuation of marble-burying behavior was blocked by Finasteride.
-
Fluoxetine (Prozac) (not Fluvoxamine) is an SSRI which increases Allopregnanolone, whose effects are basically opposite to those of [DHEA] (high in OCD): opposite effects on GABA-A allosteric modulation and on NMDARs, with DHEA increasing NMDA, and one would thus infer it lowers GABA-A
- Allopregnanolone is reported to increase firing rate of Raphe Nuclei serotoninergic [mainly 5-ht1] neurons
-
8-OH-DPAT induces disruption of SAB in rats.
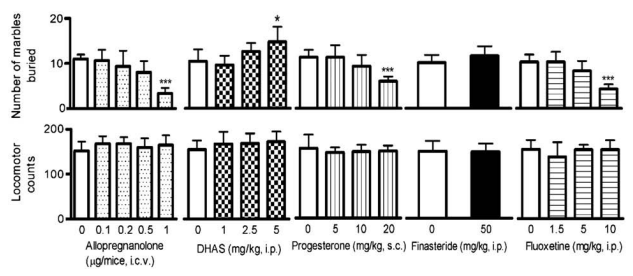
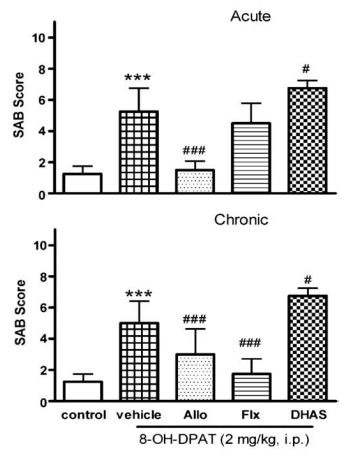
- OCD exhibit defects in the neurocircuitry of cortico-striatal-thalamic-cortical loop. (looking at the ol graph:
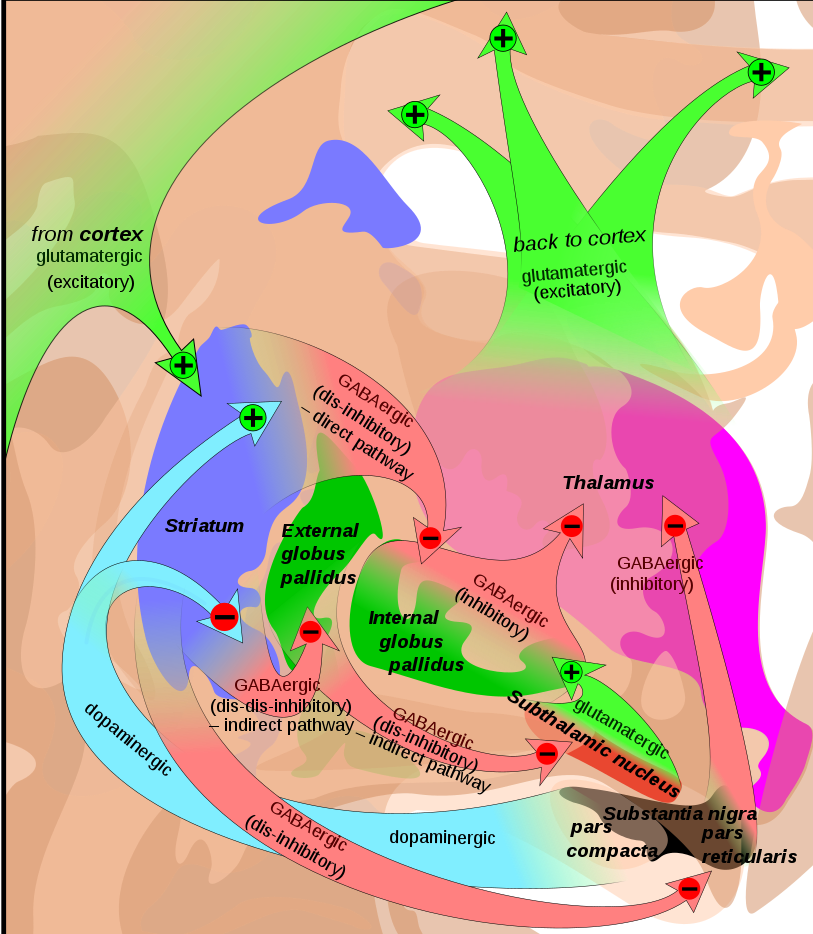 I wonder if the internal globus pallidus is a part glossed over as an intermediary thing?)
I wonder if the internal globus pallidus is a part glossed over as an intermediary thing?) - Abnormal Glutamatergic neurotransmission in Caudate. Higher CSF glutamate.
- OCD may be subsequent to serotonin dysfunction and drugs like SSRI benefit in OCD, wherein only 40–60% of patients respond satisfactorily to SSRI (Pallanti and Quercioli, 2006). Refractory patients, however respond to antidopaminergics and NMDA receptor antagonists (Denys, 2006), suggesting that multiple neurotransmitters are probably involved in the regulation of compulsive behavior.