Peptide
links: reference: /u/Polynomality https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/US/en/technical-documents/technical-article/protein-biology/protein-labeling-and-modification/peptide-stability https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0QUQI-5JJPU
- Vladimir Khavinson looks a good 20 years younger 7-1-2021
Peptide #
- Chains between two and fifty Amino Acids, linked by peptide Bonds. 1 or more of these together is a polypeptide. 1 or more (more than 1?) polypeptides is a Protein.
- Peptide bonds occur when the carboxyl reacts with another AA’s amine, displacing the hydroxyl and forming H2O:
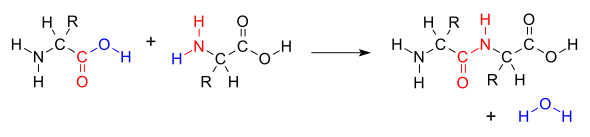
- The primary amine
- MOTS-c? Fat loss, insulin sensitivity, and ‘miracle grow for Mitochondria.’
Polymerizaton #
-
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GPCR_oligomer (oligomer: 5~100 units)
-
A polymer is a molecule consisting of multiple similar/identical repeating units which could be derived from copies of aw smaller molecule, its monomer. A dimer consists of two monomers joined by bond(s) - covalent or intermolecular; strong or weak.
- A protomer is the structural unit of an oligomeric protein (protein complex/multiprotein complex; 2+ polypeptide chains)
Action #
-
Endorphins are a class of peptide.
-
Mostly inhibitory, and second messengers. Opioids memic their effets.
-
Found throughout the entire brain and spainl cord, limbic system, hypothalamus
-
Circulate within the bloodstream without carriers.
-
Water-soluble, thus they cannot enter target cells. They bind with membrane receptors in the plasma membrane, usually a GPCR, mediating target cell response allosterically.
- The second messenger will activate transcription factors and such, beginning protein synthesis.