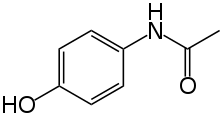
Paracetamol
2022-08-02: reference:
Paracetamol
 #
#
An NSAID. It inhibits COX-2, and to a lesser extent COX-1. In vitro screens demonstrate a rather low potency on either - influencing TRPV, Cav3.2, nitric oxide, serotonin, and endocannabinoid pathways is more apt description. Estrogenic as well.
- Paracetamol (acetaminophen) use in infants and children was never shown to be safe for neurodevelopment: a systematic review with citation tracking
- Acetaminophen (paracetamol) use, measles-mumps-rubella vaccination, and autistic disorder: the results of a parent survey
- Central dopaminergic system plays a role in the analgesic action of paracetamol: Preclinical evidence
-
The antinociceptive action of paracetamol is associated with changes in the serotonergic system in the rat brain
- Paracetamol significantly increased the Serotonin content in the pontine and cortical areas by 75% and 70% respectively.
-
Positional isomers of acetaminophen differentially induce proliferation of cultured breast cancer cells
- Increases breast cancer cell proliferation
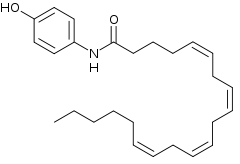
AM404 (N-arachidonoylaminophenol)
 #
#
Responsible (not solely) for its analgesic and anticonvulsant effects.
- Endocannabinoid reuptake inhibitor? Probably a FAAH inhibitor since it raises Anandamide concentrations in the synaptic cleft.
- Still a COX-1/COX-2 inhibitor. TRPV1 agonist.
- Weak CB1 and CB2 agonist.