LDL
links: Cholesterol reference: 4-12-2021
LDL (Low-density lipoprotein) #
‘Bad cholesterol’ Deboonked #
- Apparently the idea of it being causative isn’t really mainstream anymore.
-
https://jayfeldmanwellness.com/the-cholesterol-nonsense-continues/
-
Low-density lipoprotein in the setting of congestive heart failure: is lower really better?
- In a 2003 publication, this group analyzed two cohorts of Heart Failure patients (a derivation cohort in a metabolic study and a second independent group of HF patients) and also found that higher TC, LDL, and triglycerides (but not HDL) were significantly associated with improved survival
-
The relationship between cholesterol and survival in patients with chronic heart failure
- Increasing total serum cholesterol was a predictor of survival
-
The relationship between cholesterol and survival in patients with chronic heart failure
- In a 2003 publication, this group analyzed two cohorts of Heart Failure patients (a derivation cohort in a metabolic study and a second independent group of HF patients) and also found that higher TC, LDL, and triglycerides (but not HDL) were significantly associated with improved survival
- Lack of an association or an inverse association between low-density-lipoprotein cholesterol and mortality in the elderly: a systematic review
- Lack of Association Between Cholesterol and Coronary Heart Disease Mortality and Morbidity and All-Cause Mortality in Persons Older Than 70 Years
- LDL transports cholesterol from the liver to the periphery, to be used in repair or converted to steroids, among other things.
- LDL levels increase with a low metabolism/hypothyroidism as a protective measure, carried to the tissue to drive the production of protective steoids. When it’s composed of PUFA, it can become oxidized/damaged, leading to plaque formation.
-
Low-density lipoprotein in the setting of congestive heart failure: is lower really better?
- “In the roundworm C. elegans, which is now a very popular animal for testing aging theories, because its genes and cells have been thoroughly “mapped,” it was recently found that adding a gene that simply allows it to synthesize cholesterol, rather than depending on food for its sterols, increased its life span by as much as 131% (Lee, et al., 2005).”
-
http://raypeat.com/articles/articles/cholesterol-longevity.shtml
- On particle size:
- “People with larger LDL particles are remarkably resistant to heart disease… according to one study, people in the north eat 19 times more fat (mostly butter and ghee) than in the south, yet the incidence of heart disease is seven times higher in the south. A study in Sweden found that the fatty acids in milk products are associated with larger LDL particles (Sjogren, et al., 2004).”
- “In a study of the effect of dietary cholesterol on the atherogenicity of the blood lipids, 52 people were given either an egg diet (with 640 mg. of extra cholesterol per day) or a placebo diet for 30 days. Those whose LDL increased the most on the high cholesterol diet had the largest LDL particle size (Herron, et al., 2004). They concluded that “these data indicate that the consumption of a high-cholesterol diet does not negatively influence the atherogenicity of the LDL particle.” A similar study in Mexico found that “Intake of 2 eggs/d results in the maintenance of LDL:HDL and in the generation of a less atherogenic LDL in this population of Mexican children” (Ballesteros, et al., 2004).
- On particle size:
Structure #
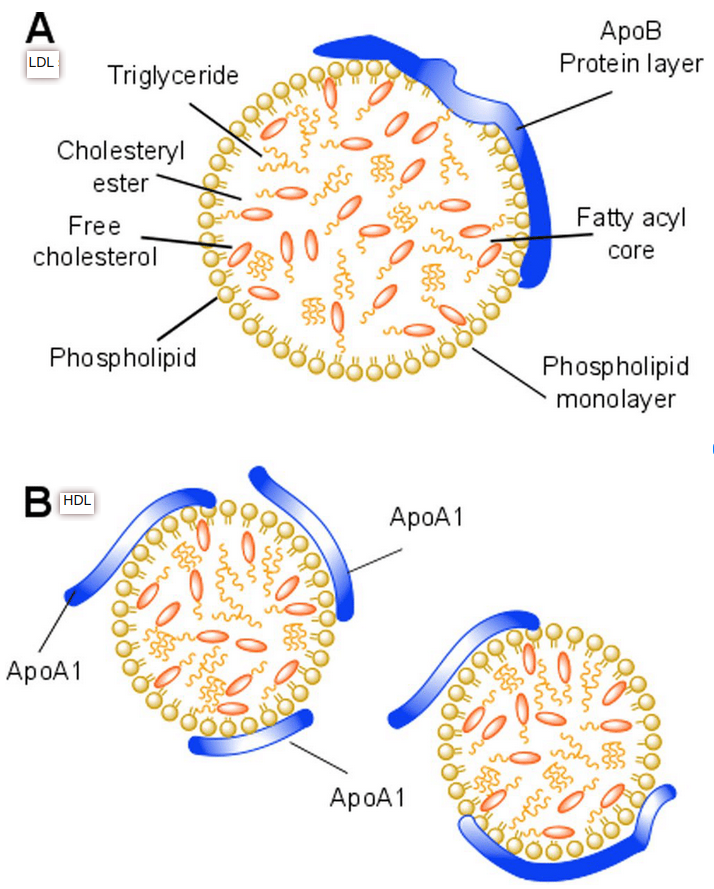
Function #
-
LDL particles with smaller surface areas are more exposed to oxidative factors in the serum.
-
“People with larger LDL particles are remarkably resistant to heart disease… according to one study, people in the north eat 19 times more fat (mostly butter and ghee) than in the south, yet the incidence of heart disease is seven times higher in the south. A study in Sweden found that the fatty acids in milk products are associated with larger LDL particles (Sjogren, et al., 2004).” Peat
-
Estrogen decreases LDL particle size - Testosterone and DHEA are protective against atherosclerosis. The LDL particle size is increased by androgens, and postprandial triglyceridemia is decreased (Hislop, et al., 2001).” Peat
-
LDL transports cholesterol from the liver to the periphery, to be used in repair or converted to steroids, among other things.
- LDL levels increase with a low metabolism/hypothyroidism as a protective measure, carried to the tissue to drive the production of protective steoids. When it’s composed of PUFA, it can become oxidized/damaged, leading to plaque formation.
-
LDL pattern A floats and doesn’t slip through arterial walls. LDL pattern B a.k.a LDL-C, the oxidized kind, can.
-
LDL-C isn’t recognized by receptors, and so they increase in quantity in the circulation.
-
Then, it enters the atheroma, right beneath the endotheleum. LDL-C is able to do this, since it increases the permeability of the endotheleum.