Genetics
links: reference:
- [Lysenko and Russian genetics: an alternative view]
- https://yewtu.be/channel/UCgppXxw5o8SpghtVSj8tX-A/videos 6-12-2021
Genetics #
Book Notes #
- Genomics is the study of complete DNA sequences of a species or an individual.
- Variable messages transcribed from the same gene are called splice variants.
- Regulatory DNA sequences (promoters and introns) that control whether and in what quantities a gene iss expressed in a given cell type.
- Chromosones (generally?) get progressively shorter from 1->22.
- Transcription: Copying a segment of DNA -> RNA -> mRNA. This takes place in the nucleus.
- RNA polymerase converts the gene into pre-mRNA (aka primary transcript mRNA), which contains introns, which are then removed during RNA splicing, leaving mature mRNA.
- Translation: In the ribosome, mature mRNA provides a template while tRNA (transfer RNA) carries and supplies the amino acids, eventualy producing a polypeptide.
- Codon: Basic unit of 3 nucleotides, which form an amino acid - or signals a stop:
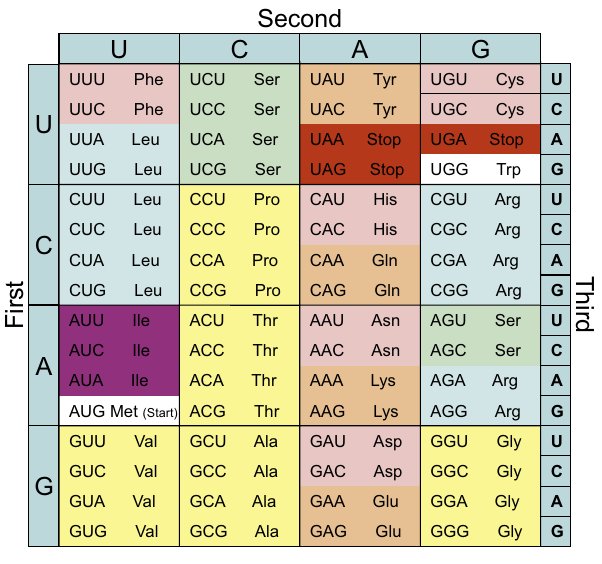
- As you can see, Methionine is always the only start codon (for archaea). And therefore, always AUG?
- “Degeneracy” refers to the fact that the amino acids besides methionine and tryptophan have >1 codon.
- Gene: a stretch of DNA that encodes for a… product. Not all transcripts are mRNA (it can also be rRNA or tRNA) so it wouldn’t be accurate to say otherwise.
- Promoters are where RNA polymerase binds.
- Enhancer somehow enhance binding of transcriptional machinery.
- Silencers (operators in prokaryotes) bind transcription factors or something.
- There’s something like 37,000 genes in the human genome.
- Intron: A region in a gene that is removed during mRNA processing beforew transcription; this is as opposed to an exon.
- Incomplete dominance is when two alleles mix. For instance: A/A = red, a/a = white, and A/a = pink. Unlike eye colors.
- Co-dominance is expressing the phenotype of both alleles simultaneously. For example, having the blood type AB = both A and B antigens.
Karyotype/Chromosome physiology #
- Centromeres are where microtubules bind on the chromosome:
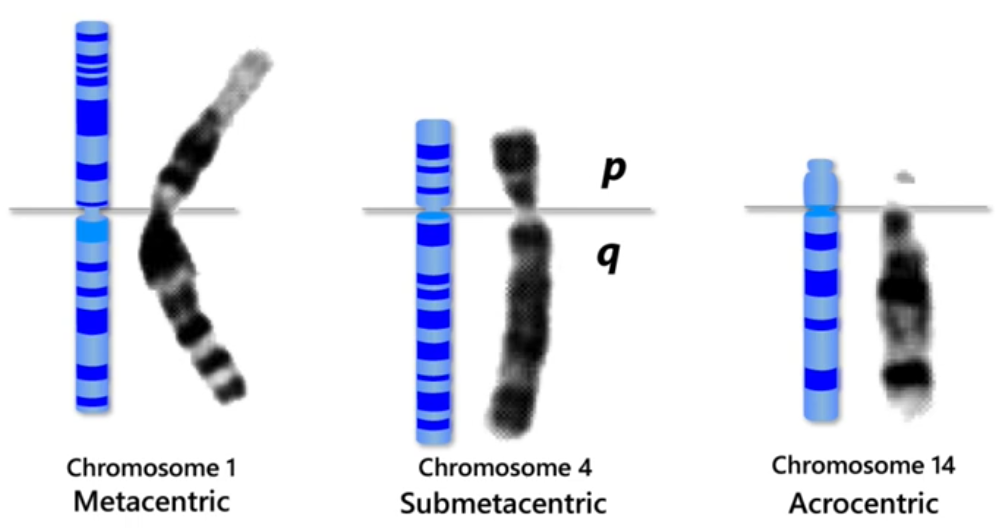 . DNA Sequencing returns blank/filler characters where the centromere is.
. DNA Sequencing returns blank/filler characters where the centromere is. - The banding is known as Giesma/G-banding. AT/GC ratio is relevant, since GC-rich domains indicates density of genes and open chromatin (euchromatin) (higher transcriptional activity), and this = light bands.
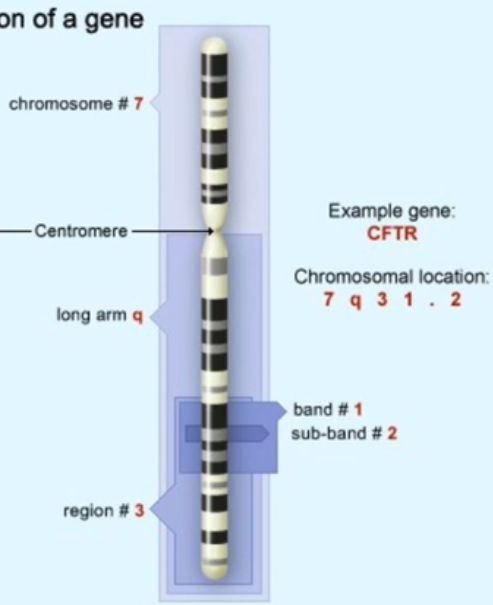
- Chromosomal locations of a gene follows this notation: